Unmodified Risk factors for Breast Cancer and those are factors we can’t change putting us at risk for breast cancer, which are:
DES Exposure
In the 1950s and 1960s, many pregnant women took a synthetic form of estrogen called diethylstilbestrol (DES) to prevent miscarriage. Many of these women’s daughters eventually developed vaginal and cervical cancer at a rate that seemed higher than normal, and studies found that DES exposure was indeed associated with an increased risk of these types of cancer.
Because of the exposure to additional estrogen, women who were exposed to DES in utero also may be at higher risk for breast cancer. A study published in October 2002 found that in women who were 40 years and older, breast cancer risk was in fact increased if a woman had been exposed to DES.
Because DES is a banned substance, people are no longer at risk for new exposures; however, if you know or suspect that your mother or grandmother took DES while pregnant, you should notify your doctor.
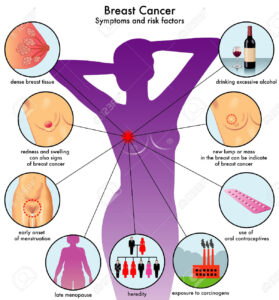
Age at Menstruation
A woman’s amount of exposure to estrogen and progesterone during her lifetime is believed to be a risk factor. The longer a woman is exposed, the more likely she is to develop breast cancer. Therefore, if a woman begins menstruation before age 12, she is believed to be at slightly higher risk.
Age at First Birth
It has been observed that women who have their first child after age 29, or who do not have any children, are at slightly higher risk for breast cancer than women who have their first child before age 29. It has been proposed that breast changes during pregnancy may have protective effects against cancer development because risk of breast cancer appears to decrease with each additional childbirth.
It is important to note that evidence suggests the opposite is true for women who have a family history of breast cancer. In other words, women who have a family history of breast cancer are at lower risk if they have no children or have their children at a later age.
Age at Menopause
Women who go through menopause after the age of 54 have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer than women who go through menopause at age 54 or younger. Their higher risk may be related to their higher lifetime exposure to estrogen and progesterone.
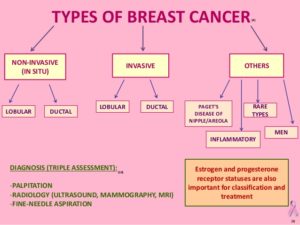
Atypical Hyperplasia or Atypia
Either atypical hyperplasia or atypia indicates the growth of abnormal cells in the breast. The diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia can be made from a core biopsy or excisional biopsy, and has been correlated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
The diagnosis of atypia can be made from nipple aspiration, ductal lavage, or fine needle aspiration (FNA), and also indicates an increased breast cancer risk. Although these cells are not yet cancerous, they do raise a woman’s risk of eventually developing breast cancer. While biopsies and FNAs are usually reserved for when there is a current indication that a woman might have breast cancer, nipple aspiration and ductal lavage are methods that may help assess a woman’s future risk of breast cancer.
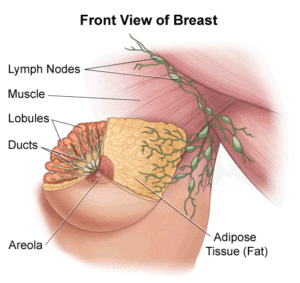
Breast Density
Studies have consistently shown that higher breast density is linked with increased risk of breast cancer. Research is examining whether breast density may be modifiable by changing women’s hormones or diet. One medication that has been demonstrated to reduce breast density is tamoxifen.
Serum Estradiol Level
Estradiol is the predominant form of estrogen circulating in the body. ‘Serum estradiol’ refers to the amount of estradiol in the blood, so a woman’s level of serum estradiol may be measured with a simple blood test.
In postmenopausal women, higher hormone levels in the blood have been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.