
In most instances, painful sensations arise from tissue injury in the body. Sensitive nerve endings pick up pain signals and carry these messages along nerves to the spinal cord and then onto the brain. All along these complex pathways, there are biological “gates” that can be either opened or closed. When these gates are closed, pain is reduced or eliminated. When open, pain messages continue through the circuit. It is when these gates are jammed open that chronic pain cycles begin.
As you recall, acute pain is short lived and serves as a warning signal. When you fix whatever is wrong, the pain usually goes away. In the case of chronic pain, pain does not necessarily signal that the body is undergoing more damage. Most chronic pain is caused by a malfunction of the nervous system, either in nerves or the brain. The malfunction or opening of the pain gates causes and endless barrage of pain signals to cycle. Chronic pain then becomes a disease itself, taking on a life of its own.
How can we close the gates of pain?
The gates are affected by several factors, most importantly by the pattern of nerve impulses which reach the spinal cord from the rest of the body, and nerve impulses coming from the brain. Sometimes the nerve impulses traveling through the spinal gates can be affected by other forms of physical stimulation. Giving your nervous system a competing source of input can fool the nervous system and alter your perception of pain.
There are many ways to accomplish this. You may have noticed that rubbing or massaging a painful area may have relieved your pain in the past. Applying electrical stimulation (e.g. TENS), applying heat or cold, acupuncture, or nerve blocks may also provide a competing source of input. It is also important to realize that certain mental activities or thoughts taking place in the brain can help to close the spinal gates.
Another way we can work to close the gates of pain is to affect the release of several chemicals that help pain signals travel to the brain. Neurotransmitters are biochemical messengers that carry pain signals from one nerve cell to the next. The three main neurotransmitters that send pain signals to the brain are substance P, NMDA (n-methyl-d-aspartate), and glutamate. Excess amounts of these chemicals, especially substance P, make it easier for pain signals to reach the brain.
Therefore, another way of stopping pain involves manipulating pain provoking neurotransmitters. This can be accomplished by prescription or over the counter medications, acupuncture, injections, hypnosis, or biofeedback.:
The role of the Endorphins:
The endorphins are another class of chemicals which are produced in the brain and serve an important role in the pain experience. These chemical are naturally occurring pain relieving substances, similar to morphine or other opiates, produced in the body. Endorphins work on special receptor sites in the brain. They act as keys which unlock receptors thus generating nerve impulses to shut down pain. Morphine and other opiates have similar chemical structures which turn off pain.
Several situations or conditions raise endorphin levels in the brain thus reducing pain. They include thinking with a positive attitude, happiness, and regular exercise.
The Role of Stress:
It is natural to connect a physical stress to the body, such a broken arm, to the perception of pain. The role of psychological stress may not seem as obvious. The brain structures involved in stress can affect the production of key hormones in the body, suppress the body’s immune system, and activate the autonomic nervous. These are the same biological changes that may occur from physical stresses on the body-the body may not differentiate between physical and psychological stress. The net effects of these changes on the body are to lower our internal resistance to pain, thus further encouraging the chronic pain cycle.
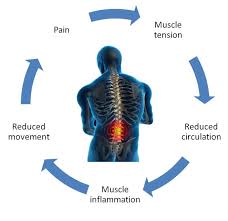
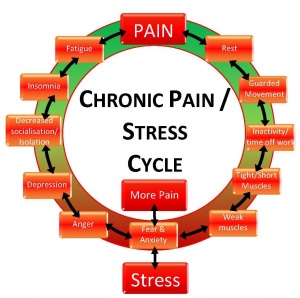
Many sources of stress feed into the chronic pain cycle. First off, as you would expect, pain itself is stressful. Pain sensations are perceived as undesirable and are at very least annoying. Pain creates tension, both physical and emotional. Physical tension may show itself as muscle tension or affect the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, or immune systems. Emotional tension may reveal itself as anger, frustration, worry, depression, or frustration. Both physical and emotional tension, initially set in motion by pain, worsen pain. Thus the vicious cycle of pain is begins-pain leads to tension and tension leads to more pain.
A second source of stress comes from all the negative consequences that occur as a result of a chronic pain condition. Chronic pain may create difficulties with family relationships, social or recreation activities, self-esteem, and employment.
Yet another source of stress arises from the hardships that can be encountered from the stresses of everyday living. Everything from difficulties putting on your shoes in the morning to difficulties standing long enough to go grocery shopping are added on top of pain-related stressors. In the end, an individual not only suffers from chronic pain, but from chronic stress.
The consequences of chronic stress:
Whatever the type of stress, either physical or psychological, the outcome on pain is to worsen it. Chronic stress also may result in other physical ailments such as tension headaches, muscle spasms, gastrointestinal problems, and elevated blood pressure. It can also lead to fatigue, depression, and a sense of hopelessness.
The key is how to prevent chronic pain:
Chronic pain can’t always be prevented But rememeber if you have pain go to a MD to help you get to your optimal level of function and hopes you get to PAIN FREE.
1- ONE is staying in good physical and mental health may be the best way to prevent it or help you cope with it.
2- Treat your health problems early.
3- Get enough sleep every night. Learn to alternate activity with rest throughout each day.
4- Exercise.
5- Eat a balanced diet.
Try to reduce stress in your life.