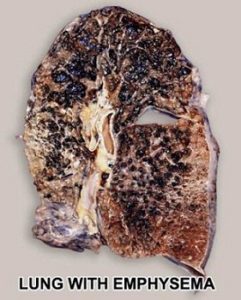
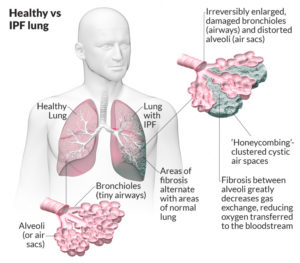
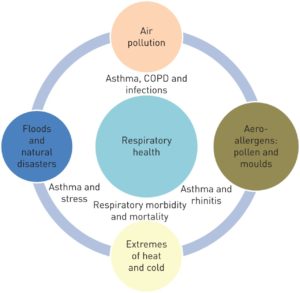
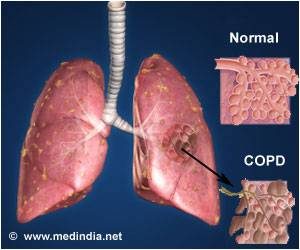
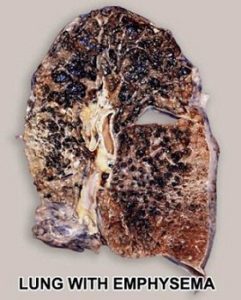
The normal lung is capable of receiving and distributing a large flow of air and blood to its alveoli. In emphysema, the elastic recoil of the lung decreases with loss of alveolar septa, presumably because the reduced alveolar surface area exerts a lower surface tension. Inspiration lowers alveolar pressure, allowing air to flow into the lungs; the bronchiole dilates when the pressure in the surrounding alveoli is less than that within the lumen of the bronchiole. Conversely, in expiration, the airways are compressed because the alveolar pressure surrounding the bronchiole exceeds that within the bronchiolar lumen. There is a greater tendency for airflow obstruction during expiration. In emphysema, bronchiolar obstruction due to loss of alveolar structure is irreversible.
The bronchial glands and goblet cells may be hypertrophied, producing excessive amounts of mucus, which frequently obstructs bronchiolar lumina. One aspect of therapy focuses on increasing the fluidity and mobility of mucus. Submucosal edema and cellular infiltration cause a thickening of the bronchiolar wall and narrowing of the lumen. Because vasodilatation often leads to edema, another aspect of treatment is to cause vasoconstriction by means of alpha-adrenergics. The smooth muscle may be hypertrophied in bronchitis or asthma, narrowing the lumen. Adrenergic drugs are used to smooth the muscle. COPD is usually insidious, existing in an asymptomatic unrecognized form for years prior to the appearance of noticeable dyspnea on exertion. With mild to moderate COPD, bronchiolar obstruction is found in a patchy distribution throughout the lungs. This results in uneven ventilation/perfusion ratios, which will be discussed at the end of this section. The less involved, better-ventilated lung units become insufficient to compensate for the more involved, poorly ventilated units in cases of advanced COPD or superimposed viral or bacterial infections.
Severe arterial hypoxemia is likely to increase production of erythropoietin, which stimulates the bone marrow causing erythrocytosis. This erythrocytosis may be either useful or harmful. The higher hemoglobin associated with increased O2 capacity is good; but the increased blood volume in the presence of a failing heart is not. Increased blood viscosity causes a harmful resistance to blood flow through the lungs and coronary vessels. Early medicine utilized phlebotomies to treat hypoxia instead of O2. This resulted in a stimulus for increased erythropoiesis causing a snowball effect.
Patients with severe bronchitis have mismatched ventilation/perfusion. This leads to arterial hypoxemia, secondary erythrocytosis, and cor pulmonale with congestive heart failure. They are called blue bloaters due to their cyanosis and edema, or anasarca. A patient with severe emphysema may have decreased cardiac output and a relatively small heart, but as long as he/she can effectively hyperventilate and match ventilation/perfusion, he/she will not develop hypoxemia. They are called pink puffers because they maintain a near normal PaO2 and are hyperpneic.
Auscultation
Auscultation of the lungs provides information about the airflow through the tracheobronchial tree and the presence of fluid, mucus or obstruction of the airway. Vesicular breath sounds are normally heard over the chest. They are soft and low in pitch. Bronchovesicular breath sounds are medium in intensity and pitch and heard over the large, main stem bronchi. Bronchial breath sounds are loud and high in pitch and normally heard over the trachea. One type of bronchial breath sound rarely heard is the amphoric breath sound heard over a thick walled cavity that communicates freely with a large sized bronchus. The sound resembles blowing over the top of a wine bottle. Vesicular breath sounds last longest on inspiration and when airflow to an area is diminished, they may be decreased or absent. Bronchial breath sounds are longest on expiration. Consolidation of lung tissue, as occurs in pneumonia, blocks the passage of air through the affected area and prevents the exchange of sound quality.
Remember that a patient with particularly severe asthma may have a rather quiet chest on auscultation. This is probably because airflow is so slow that it can no longer generate much sound. Breath sounds will also be absent or decreased in COPD. This is caused by lung distention and poor transmission of sound to the chest wall.
Abnormal breath sounds (adventitious or “added”) include rales, rhonchi, wheezes and pleural friction rubs. Rales are noisy murmurs caused by passage of air through liquid. Moisture causes a sound like soda fizzing, cellophane crinkling, or the sound you hear when you roll your hair between your fingers near your ears. Rales are usually heard on inspiration. Coarse rales may clear after a cough but fine rales near the bases of long fields rarely do. Rales are sometimes called “crackles.” The crackles of interstitial lung disease, such as fibrosing alveolitis, are typically heard on late inspiration as opposed to crackles from secretions.
Rhonchi are rumbling, snoring or rattling sounds caused by obstruction of a large bronchus or the collection of secretions in a large bronchus. They are most prominent on expiration. Another name for rhonchus is a “wheeze.” Snoring sounds are called sonorous rhonchi, and high-pitched musical sounds are called sibilant rhonchi. Wheezes may be audible without a stethoscope.
Pleural friction rubs occur when the pleural fluid that normally lubricates the pleura is decreased or absent. The membranes rub together causing a loud creak or a soft click that resembles a grating sound. They are heard on inspiration and expiration and are associated with pain and splinting.
Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) Ratio
Effective gas exchange depends on uniform distribution of function throughout the lung. Ventilation must be distributed to 300 million alveoli through 23 generations of branching airways along with blood distribution through a myriad of capillaries. Even in normal lung function, distribution is not uniform. There is a gravity-dependent gradient of pleural pressure in the upright lung of about 0.3 cm H2O pressure/cm vertical distance. The pleural pressure over a normal adult lung 30 cm in height is about 9 cm H2O more negative at the apex than at the base. Lung units near the lung apex are distended by a greater transpulmonary pressure and are more fully inflated than those at the base.
Blood flow, like ventilation, is least at the apex and increases down the lung. However, alveolar ventilation and perfusion are not evenly matched, so the gradient of perfusion is steeper than that of ventilation. The average V/Q (Ventilation-Perfusion Ratio) is 0.8.
In regions of the lung where the V/Q ratio is increased above normal, wasted ventilation occurs. This has the effect of adding a space that is ventilated but does not participate adequately in gas exchange. An extreme example can occur when perfusion is virtually eliminated, by a blood clot or following ligation of a pulmonary artery.
Ventilation of regions of the lung with high V/Q ratios is partly wasted and contributes to alveolar dead space ventilation. In decreased states, this is not uncommon. It results in hyperventilation and increased work of breathing.
When ventilation is impaired without decreased blood flow or when perfusion continues to non-ventilated regions of the lung, as in atelectasis, there is a decreased V/Q. Gas exchange is extremely impaired or absent and perfusing blood is poorly oxygenated. Hyperventilation can help hypercapnia, but not hypoxemia. The addition of poorly oxygenated blood from areas of low V/Q to normally oxygenated blood acts like a shunt. This “physiologic shunting” must be differentiated from true venous admixture produced by an “anatomic” shunt.
A shunt study can be performed by having the patient breathe 100% O2 for 20 minutes and then obtaining arterial blood gases. True venous admixture will not be changed by breathing 100% O2. Use extreme caution in some patients, however, making sure hypoxic drive is what is keeping them ventilated.
Clinical Features of COPD:
History & Physical Findings
Patients with COPD have at least one symptom in common: undue breathlessness on exertion. Chronic bronchitis is unusual in nonsmokers and is more common in men than in women. Cough is often worse on arising due to accumulation of secretions while sleeping. Wheezing and exercise intolerance are often present and tend to worsen during acute infections of the lower respiratory tract. The sputum may become mucopurulent or purulent. Unless the patient has a hobby or job that requires strenuous exertion, the disease may go unnoticed until quite extensive.
In general, the COPDer appears anxious and malnourished, and complains of lost appetite, use of accessory muscles, muscle atrophy, jugular engorgement, cyanosis, and digital clubbing.
The COPDer’s chest will have increased AP diameter, barrel chest, or hyper-resonant chest, with decreased breath sounds and adventitious breath sounds. Their ventilatory pattern may include paradoxical movement of the abdomen, prolonged expiratory time, active exhalation and pursed lip breathing. In advanced disease, peripheral edema may be present.
Asthmatics who show some degree of persistent airway obstruction and exertional dyspnea are classified as COPD. The accompanying cough is often paroxysmal, and wheezing is severe. Asthma can be brought on by intrinsic or extrinsic factors. An example of an intrinsic factor would be an emotional upset that brings on an attack; extrinsic factors would include specific allergens, etc. Usually by the time an emphysema patient reaches the fifth decade, dyspnea is the primary complaint. Hyperventilation may be present if the patient becomes anxious, but true orthopnea is uncommon unless heart failure is present.
The history may be helpful to distinguish other conditions like chronic pulmonary fibrosis, recurrent pulmonary thromboembolism, polycythemia vera, the diseases of hypoventilation, and myxedema. Aerophagia with gastric distension causes early satiety. Patients often complain of upper abdominal soreness, distention, and fullness, or even epigastric pain. It is important to note that 20 to 25% of emphysema patients develop ulcers at some stage of their disease.
With deteriorating blood gases, there will be gradual impairment of mental acuity, memory, and judgment, along with headache and insomnia. Patients with cor pulmonale complain of easy fatigability, and may have anterior chest pain and palpitation on exertion. With right heart failure, ankle edema appears and liver enlargement with or without ascites develops.
Clinical features of bronchiectasis principally include a chronic, loose cough with mucopurulent, foul-smelling sputum. In advanced cases, the mucus settles out into three layers: cloudy on top, clear saliva in the middle, and cloudy, purulent material on the bottom. It is frequently associated with chronic paranasal sinusitis. Hemoptysis, occasionally severe, occurs in at least a half of all cases. Advanced cases result in chronic malnutrition, sinusitis, clubbing, cor pulmonale and right heart failure. Physical signs are variable; rales may be present at times. A plain chest film may not be helpful if dilatations of air fluid levels are not present.
Often the diagnosis of the disease can be made from history alone. It is confirmed by bronchography after vigorous treatment for at least one week. A lung resection may be indicated. Iodized oil and iodine in water have been the standard contrast media for many years. Powdered tantalum appears to offer a reliable substitute without the risk of iodine sensitivity. (We will be learning more about roentgenologic features in the next section.) Bronchoscopy in bronchiectasis often reveals a deep velvety red mucosa with pus swelling up from areas of involvement. Gram stains may show fusospirochetal organisms and cultures will reveal common mouth flora and anaerobic streptococci or others. Microscopic exam of sputum may show necrotic tissue, muscle fibers and epithelial debris.
Roentgenologic Features
Correlation among symptoms, physical findings, and the appearance of chest x-rays is often poor in COPD. Films of moderately advanced disease can be read “essentially normal,” but at least they can be used to rule out other complications. In acute asthma, hyperlucency may mask emphysema, but will clear after attack. Emphysema patients will show attenuation of the peripheral pulmonary vasculature. Those with alpha-1-antitrypsin will have scarcity of vascular markings in bases, and hilar shadows present.
“By far the best ways to treat COPD are to catch it early and to stop smoking.”
Increased prominence of the basal vascular markings is often seen in patients with severe chronic bronchitis or bronchiectasis, with or without emphysema. In patients with pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular enlargement, classically there is prominence of the main pulmonary artery segment, bulging of the anterior cardiac contour into the retrosternal space, and enlargement of the right and left pulmonary artery shadows. In combined right and left ventricular failure, the transverse diameter of the heart is widened, and the basal vascular markings show increased prominence. Comparison with x-rays previously taken may show progressive flattening of the diaphragm, increased radiolucency of the lung fields, increased size of bullous areas, and increased heart size.
The best radiologic criteria for the presence of emphysema is a flattened diaphragm, as seen in lateral view, and an increased depth of the retrosternal space of more than 3 cm between the anterior wall of the origin of the ascending aorta and the sternum. Fluoroscopy in COPD may be helpful because radiolucency of the lung bases tend to persist during forced expiration, in contrast to the increased density seen in normal subjects. Expiratory films should be obtained four or five seconds after the command to exhale is given, to allow time for the full effects of airway obstruction to be registered. CT Scans and modern MRI’s have replaced most need for older lung laminagrams to demonstrate size and location of bullae. Lung photoscans following intravenous injection of macroaggregated particles of serum albumin tagged with iodine are helpful in demonstrating areas of non-perfused or under-perfused areas. Occasionally, Xenon scans are used for this purpose. Pulmonary arteriograms may be indicated to rule out embolism.
EKG Aspects
The electrocardiogram is often normal in early or moderate emphysema. One of the most frequent changes in COPD is a shift of the P wave axis toward the right, often greater than +80 degrees in the frontal plane. Observing the P wave in a VL easily assesses this; it is isoelectric at the +60 degree axis and becomes increasingly negative as its axis moves further to the right, greater than +60 degrees. The P waves frequently are symmetrically peaked in leads II, III, and a VF; and when their height is 2.5 mm or more they are classified as “P pulmonale.”
The QRS complexes often show low voltage in both the limb leads and the precordial leads, especially leads V5- 6. The mean QRS axis is displaced posteriorly and superiorly and shifted toward the left (clockwise rotation). The frontal electrical axis is often vertical, frequently more than +70 degrees. Superior rotation of the electrical vector manifested by a late R wave in a VR ABG gives rise to a SI, SII, SIII pattern with an indeterminate mean axis. With more severe rotation, axes greater than -30 degrees (left axis deviation) may be seen.
When right ventricular hypertrophy develops as a result of increased pulmonary vascular resistance and pulmonary hypertension, the QRS vector shift anteriorly and to the right. R waves then appear in the right precordial leads. Complete right bundle branch block is occasionally observed.
The QRS abnormalities may sometimes simulate those of myocardial infarction, particularly of the inferior portion of the heart. The presence of abnormal pulmonale-type P Ò26 waves suggests that emphysema is the sole cause of the EKG abnormality.








 =
=