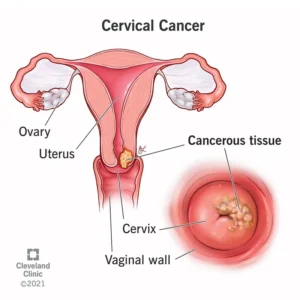
Cervical cancer risk factors
GENERAL
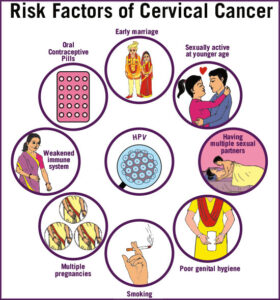
- Pregnancy: Women who have had three or more full-term pregnancies, or who had their first full-term pregnancy before age 17, are twice as likely to get cervical cancer.
GENETICS
- Family history: Women with a sister or mother who had cervical cancer are two to three times more likely to develop cervical cancer.
LIFESTYLE
- Sexual history: Certain types of sexual behavior are considered risk factors for cervical cancer and HPV infection. These include: sex before age 18, sex with multiple partners and sex with someone who has had multiple partners. Studies also show a link between chlamydia infection and cervical cancer.
- Smoking: A woman who smokes doubles her risk of cervical cancer.
- Oral contraceptive use: Women who take oral contraceptives for more than five years have an increased risk of cervical cancer, but this risk returns to normal within a few years after the pills are stopped.
OTHER CONDITIONS
- Weakened immune system: In most people with healthy immune systems, the HPV virus clears itself from the body within 12-18 months. However, people with HIV or other health conditions or who take medications that limit the body’s ability to fight off infection have a higher risk of developing cervical cancer.
- Diethylstilbestrol (DES): Women whose mothers took DES, a drug given to some women to prevent miscarriage between 1940 and 1971, have a higher risk of developing cervical cancer.
- HPV: Though HPV causes cancer, having HPV does not mean you will get cancer. The majority of women who contract HPV clear the virus or have treatment so the abnormal cells are removed. HPV is a skin infection, spread through skin-to-skin contact with a person who has the virus.
Additional facts about HPV:
- There are more than 100 types of HPV, 30-40 of which are sexually transmitted.
- Of these, at least 15 are high-risk HPV strains that can cause cervical cancer. The others cause no symptoms or genital warts.
- Up to 80 percent of women will contract HPV in their lifetime. Men get HPV, too, but there is no test for them.
- A healthy immune system will usually clear the HPV virus before there is a symptom, including the high-risk types of HPV.
- Only a small percentage of women with high-risk HPV develop cervical cancer.
Understanding risk factors:
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer. Not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. If you think you may be at risk, you should discuss it with your doctor.
Regarding symptoms of cervical cancer:
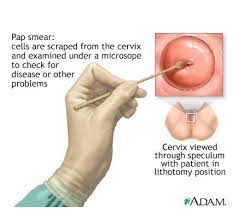
In most cases, cervical cancer does not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages of the disease. Routine Pap screening is important to check for abnormal cells in the cervix, so they can be monitored and treated as early as possible. Most women are advised to get a Pap test starting at age 21.
The Pap test is one of the most reliable and effective cancer screening methods available, and women should have yearly exams by an OB-GYN. However, the Pap test may not detect some cases of abnormal cells in the cervix. The HPV test screens women for the high-risk HPV strains that may lead to cervical cancer. It is approved for women over age 30.
Although screening methods are not 100 percent accurate, these tests are often an effective method for detecting cervical cancer in the early stages when it is still highly treatable. Talk with your doctor about which type of cervical cancer screening is right for you.
When present, common symptoms of cervical cancer may include:
- Vaginal bleeding: This includes bleeding between periods, after sexual intercourse or post-menopausal bleeding.
- Unusual vaginal discharge: A watery, pink or foul-smelling discharge is common.
- Pelvic pain: Pain during intercourse or at other times may be a sign of abnormal changes to the cervix, or less serious conditions.
All of these cervical cancer symptoms should be discussed with your doctor.
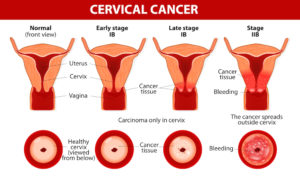
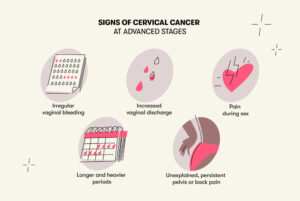
Signs of advanced stages of cervical cancer:
Cervical cancer may spread (metastasize) within the pelvis, to the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. Signs of advanced cervical cancer include:
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Leg pain or swelling
- Leakage of urine or feces from the vagina
- Bone fractures