
Here is a fast review of Part I and Part II:
Diabetes occurs when the pancreas, a gland behind the stomach, does not produce enough of the hormone insulin, or the body cannot use insulin properly. Insulin helps carry sugar from the bloodstream into the cells. Once inside the cells, sugar is converted into energy for immediate use or stored for the future. That energy fuels many of our bodily functions.
The body produces glucose from the foods you eat. The liver also releases sugar when you are not eating. The pancreas produces the hormone insulin, which allows glucose from the bloodstream to enter the body’s cells where it is used for energy. In type 2 diabetes, too little insulin is produced, or the body cannot use insulin properly, or both. This results in a build-up of glucose in the blood.
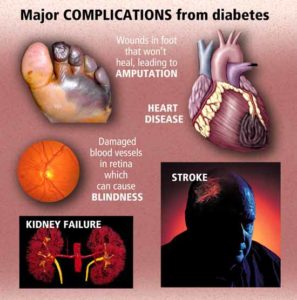
People with diabetes are at risk of developing signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia to serious health problems (complications).
HOW we can decrease the risk of complications and decrease the chance of diabetes worsening = KEEP IT UNDER CONTROL = PRACTICING VERY GOOD MANAGEMENT IN CARING FOR YOUR DIABETES.
This is how you can reach this goal:
-Controlling your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol can make a huge difference in staying healthy. Talk with your doctor about what your goals should be and how to reach them but make sure you are given information on paper or write down what it is you have discussed in the doctor’s office based on your care for diabetes and what to do. Usually diabetic information on paper is available and given to you.
To reach controlling your glucose and treatment for Diabetes:
-Your healthy eating plan that you and your doctor with a dietician have discussed.
-Overweight? Than diet down to your therapeutic weight range for your height after discussed with by you with your doctor.
-Be physically active for 30 to 60 minutes most days but if this is new get your doctor to clear this activity for you with what kind of activity you are allowed and not allowed.
-Take your medicines as directed and keep taking them even after you’ve reached your goals; or you will be at high risk of ending up the way you were earlier=Diabetes badly controlled with running into the problems you had earlier.It’s very important to take your diabetes medications as recommended by your doctor. Left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious, even life-threatening complications.
-If you smoke=QUIT.
-Check your skin daily in particular the FEET and LOWER LEGS to check for redness, swelling to blisters, sores and sore toenails
-Ask your doctor if you should be taking aspirin to prevent a heart attack or stroke by making the blood less thick to thinner making it easier for the heart to pump and less stress to the organ.
The key is to controlling your DIABETES is to be living a healthy life! This consists of diet, exercise or activity and healthy habits learned and practiced routinely in your life that will help prevent or assist in treating diabetic disease. The better we treat ourselves regarding health the higher the odds we will live a longer and healthier life. There is not just one food to eat or one type of exercise to do or one healthy habit to practice in order to keep you healthy, there’s choices. To be a part learn what healthier habits or changes you want for a healthier way of living; learn how to eat out of the 4 food groups to prevent Diabetes or eating out of the 4 food groups that are following your diabetic diet as ordered by your MD. It allows you to make all the decisions in what you want to do regarding what to eat (diet). Now with diet you must include exercise/activity, and what healthy habits you want to add in your life that are not so healthy; you know what that is and if not read a book on how to get heathier-including how to prevent diabetes where the library and book stores have many options for you. Provide yourself with the information and healthy foods in your diet, if you decide you want it. You make all the choices.
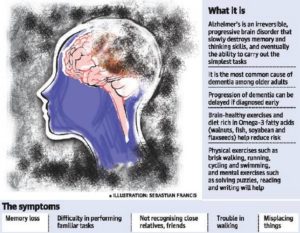
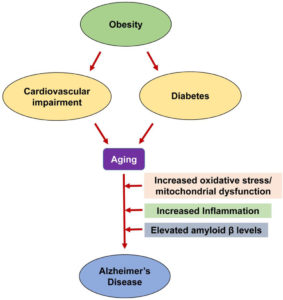
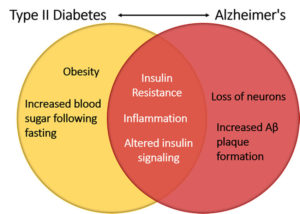
The ending line of all problems resulting from Diabetes is due to the thick high glucose blood in the blood stream filtering throughout the different organs in our body causing from peripheral neuropathy to necrotic skin to amputations for LE’s usually or same effect elsewhere causing macular degeneration to blindness or increase of cancers, heart disease, Diabetes Alzheimer’s and we could go on about the effects of diabetes. Get it now its control your blood glucose keeping it in therapeutic range decreasing the odds of developing these conditions or the severity of these conditions.
If you don’t have diabetes than take the steps to prevent being diagnosed with it later in life. WHAT are those steps? Eat Right (Healthy), Keep your weight in therapeutic range, Exercise the body balancing it with rest, decrease stress, and take care of yourself. BUT if there is heredity in the family, especially your nuclear family, when you see your primary care doctor every 6 months or yearly have your glucose checked to see if it is high or not. Simply get a BMP or CMP blood test that looks at blood electrolyte levels that includes glucose. If its high the next step is getting the doctor to check your hemoglobin A1C another blood test done with no eating for 12 hrs prior to see what your real glucose level is prior to your first meal in the morning (done on a empty stomach). For if you eat prior to the test it won’t accurate on your true glucose level. 2 Easy blood tests.
It is all up to you!
Wouldn’t you want less disease/illness for yourself, for your family, others significant to you and even throughout the nation including our future generations. Wouldn’t it be great to see Diabetes decrease in America for future years and giving us an ending result of higher probability that we would overall a healthier country with less diseases. If that included Diabetes decreased significantly what an impact it would play in decreasing other diseases, that occurred due to the diabetes alone (That would decrease cardiac disease, renal disease, blurred vision, neuropathy, I could go on). Besides how much it would decrease in this country to take care of patients with diabetes.
I’m not a diabetic but eating overall healthy and in my diet range (barely) but there and trying to increase my activity. Do yourself and maybe others a favor by making yourself and America a healthier country for less Diabetes and the diseases it can cause from cardiac to vision to renal to brain, etc…

Again its all up to you!
–REFERENCES for Part I, Part II & III this week on diabetes:
1.) Center for Disease (CDC) – “National Diabetes Fact Sheet”
2.) NYS Dept. of Health –Diabetes
3.) Diabetic Neuropathy.org “All about diabetic neuropathy and nerve damage caused by Diabetes.”
4.) NIDDK “National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
5.) National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse (NIDC) – U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. “Preventing Diabetes Problems: What you need to know”