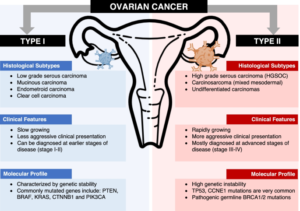
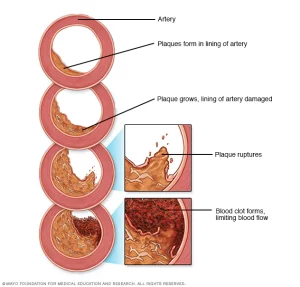
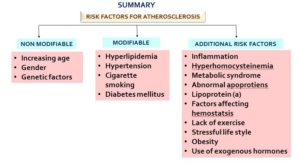
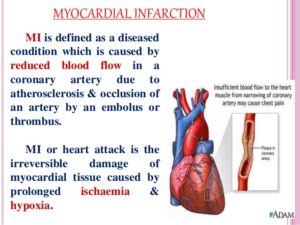
1-Local Treatments/Therapies:
Some treatments are local, meaning they treat the tumor without affecting the rest of the body.
Types of local therapy used for ovarian cancer include that include:
A-Surgery
That is the main treatment most ovarian cancers. How much surgery you have depends on how far your cancer has spread and on your general health. For women of childbearing age who have certain kinds of tumors and whose cancer is in the earliest stage, it may be possible to treat the disease without removing both ovaries and the uterus.
B-Radiation
Radiation is another form of therapy that might be used. Radiation therapy uses high energy x-rays or particles to kill cancer cells. These x-rays may be given in a procedure that is much like having a regular x-ray. Aggressive chemotherapy is usually more effective, so radiation therapy is rarely used in this country as the main treatment for ovarian cancer. However, it can be useful in treating areas where the cancer has spread, either near the main tumor or in a distant organ, like the brain or spinal cord. External beam radiation – This is the most common type of radiation therapy for women with ovarian cancer. External radiation therapy is much like getting an x-ray, but the radiation is stronger.
2-Systemic Treatment/Therapies:
This includes Chemo therapy, Hormone Therapy and Targeted Therapy.
A. Chemo Therapy:
Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of drugs to treat cancer. Most often, chemo is a systemic treatment, meaning the drugs enter the bloodstream and reach almost all areas of the body. Chemo can be useful to kill very small amounts of cancer cells that may still be around after surgery, for cancers that have metastasized (spread), or to shrink very large tumors to make surgery easier. Most of the time, chemo uses drugs that are injected into a vein (IV) or given by mouth. In some cases, chemotherapy may also be injected through a catheter (thin tube) directly into the abdominal cavity. This is called intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy.
Chemo for ovarian cancer usually involves getting two different types of drugs together. Getting a combination of drugs instead of just one drug alone seems to work better as a first treatment for ovarian cancer. Usually, the combination includes a type of chemo drug called a platinum compound (usually cisplatin or carboplatin), and another type of chemo drug called a taxane, such as paclitaxel (Taxol®) or docetaxel (Taxotere®). These drugs are usually given as an IV (put into a vein) every 3 to 4 weeks.
The typical course of chemo for epithelial ovarian cancer involves 3 to 6 cycles of treatment, depending on the stage and type of ovarian cancer. A cycle is a schedule of regular doses of a drug, followed by a rest period. Different drugs have varying cycles; your doctor will let you know what schedule is planned for your chemo.
Epithelial ovarian cancer often shrinks or even seems to go away with chemo, but the cancer cells may eventually begin to grow again. If the first chemo seemed to work well and the cancer stayed away for at least 6 to 12 months, it can be treated with the same chemotherapy used the first time. In some cases, different drugs may be used.
There are numerous other chemo drugs used that might be helpful in treating ovarian cancer.
B-Hormone Treatment/Therapies
It’s another treatment that may be used with the use of hormones or hormone-blocking drugs to fight cancer. This type of systemic therapy is rarely used to treat epithelial ovarian cancer, but is more often used to treat ovarian stromal tumors.
Meds used in Hormone therapy is:
-Luteinizing Hormone Release Hormone Agonists
LHRH agonists (sometimes called GnRH agonists) can be used in systemic treatment also that will switch off estrogen production by the ovaries. These drugs are used to lower estrogen levels in women who are premenopausal. Examples of LHRH agonists include goserelin (Zoladex®) and leuprolide (Lupron®). These drugs are injected every 1 to 3 months. Side effects can include any of the symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness. If they are taken for a long time (years), these drugs can weaken bones (sometimes leading to osteoporosis).
-Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is a drug that is often used to treat breast cancer. It can also be used to treat ovarian stromal tumors and is rarely used to treat advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Tamoxifen acts as an anti-estrogen in many tissues in the body, but as a weak estrogen in others. The goal of tamoxifen therapy is to keep any estrogens circulating in the woman’s body from stimulating cancer cell growth. The anti-estrogen activity of this drug can lead to side effects like hot flashes and vaginal dryness. Because tamoxifen acts like a weak estrogen in some areas of the body, it does not cause bone loss but can increase the risk of serious blood clots in the legs.
-Aromatase inhibitors
Aromatase inhibitors are drugs that block an enzyme (called aromatase) that turns other hormones into estrogen in post-menopausal women. They don’t stop the ovaries from making estrogen, so they are only helpful in lowering estrogen levels in women after menopause. These drugs are mainly used to treat breast cancer, but can also be used to treat some ovarian stromal tumors that have come back after treatment as well as low grade serous carcinomas. They include letrozole (Femara®), anastrozole (Arimidex®), and exemestane (Aromasin®). These drugs are taken as pills once a day.
Common side effects of aromatase inhibitors include hot flashes, joint and muscle pain, and bone thinning. The bone thinning can lead to osteoporosis and bones that break easily.
C-Targeted Drug Therapy:
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to identify and attack cancer cells while doing little damage to normal cells. These therapies attack the cancer cells’ inner workings − the programming that makes them different from normal, healthy cells. Each type of targeted therapy works differently, but they all change the way a cancer cell grows, divides, repairs itself, or interacts with other cells.
-Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab (Avastin) belongs to a class of drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors. For cancers to grow and spread, they need to make new blood vessels to nourish themselves (called angiogenesis). This drug attaches to a protein called VEGF (that signals new blood vessels to form) and slows or stops cancer growth.
Bevacizumab has been shown to shrink or slow the growth of advanced epithelial ovarian cancers. Bevacizumab appears to work even better when given along with chemotherapy having shown good results in terms of shrinking (or stopping the growth of) tumors. But it doesn’t seem to help women live longer.
Bevacizumab can also be given with olaparib (see below) as maintenance treatment in women whose cancers have the BRCA mutation or genomic instability (see below) and have shrunk quite a bit with chemotherapy containing carboplatin or cisplatin.
This drug is given as an infusion into the vein (IV) every 2 to 3 weeks.
Side effects of bevacizumab
Common side effects include high blood pressure, tiredness, bleeding, low white blood cell counts, headaches, mouth sores, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. Rare but possibly serious side effects include blood clots, severe bleeding, slow wound healing, holes forming in the colon (called perforations), and the formation of abnormal connections between the bowel and the skin or bladder (fistulas). If a perforation or fistula occurs it can lead to severe infection and may require surgery to correct.
PARP inhibitors
Olaparib (Lynparza), rucaparib (Rubraca), and niraparib (Zejula) are drugs known as a PARP (poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase) inhibitors. PARP enzymes are normally involved in one pathway to help repair damaged DNA inside cells. The BRCA genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2) are also normally involved in a different pathway of DNA repair, and mutations in those genes can block that pathway. By blocking the PARP pathway, these drugs make it very hard for tumor cells with an abnormal BRCA gene to repair damaged DNA, which often leads to the death of these cells.
If you are not known to have a BRCA mutation, your doctor might test your blood or saliva and your tumor to be sure you have one before starting treatment with one of these drugs.
All of these drugs are taken daily by mouth, as pills or capsules.
Olaparib (Lynparza) is used to treat advanced ovarian cancer, typically after chemotherapy has been tried. This drug can be used in patients with or without mutations in one of the BRCA genes.
In women with a BRCA mutation:
- Olaparib can be used as maintenance treatment for advanced ovarian cancer that has gotten smaller in response to first treatment with chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin.
- Olaparib can be used with bevacizumab (see above) as maintenance treatment in women whose cancers have shrunk quite a bit with chemotherapy containing carboplatin or cisplatin.
In women without a BRCA mutation:
- If the tumor has a high genomic instability score (a test measuring the amount of abnormal genes in cancer cells), olaparib can be used with bevacizumab as maintenance treatment in women whose cancers have shrunk quite a bit with chemotherapy containing carboplatin or cisplatin.
In women with or without a BRCA mutation:
- Olaparib can be used as maintenance treatment for advanced ovarian cancer that has come back after treatment, and then has shrunk in response to chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin.
Niraparib (Zejula) may be used in some situations to treat ovarian cancer.
In women with or without a BRCA gene mutation:
- Niraparib might be used as maintenance treatment for advanced ovarian cancer, where the cancer has shrunk with firsrt-line chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin.
- Niraparib might be used as maintenance treatment for advanced ovarian cancer that has come back after treatment, where the cancer has then shrunk with chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin.
Rucaparib (Rubraca) can be used in women with or without a BRCA mutation, as maintenance treatment for advanced ovarian cancer that has come back after treatment, and then has shrunk in response to chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin.
These drugs have been shown to help shrink or slow the growth of some advanced ovarian cancers for a time. So far, though, it’s not clear if they can help women live longer.
Side effects of PARP inhibitors
Side effects of these drugs can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, loss of appetite, taste changes, low red blood cell counts (anemia), belly pain, and muscle and joint pain. Rarely, some patients treated with these drugs have developed a blood cancer, such as myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia.
Drugs that target cells with NTRK gene changes
A very small number of ovarian cancers have changes in one of the NTRK genes. Cells with these gene changes can lead to abnormal cell growth and cancer. Larotrectinib (Vitrakvi) and entrectinib (Rozlytrek) are targeted drugs that stop the proteins made by the abnormal NTRK genes. These drugs can be used in people with advanced ovarian cancer whose tumor has an NTRK gene change and is still growing despite other treatments.
These drugs are taken as pills, once or twice a day.
Side effects of drugs that target NTRK gene changes
Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, constipation, weight gain, and diarrhea.
Less common but serious side effects can include abnormal liver tests, heart problems, and confusion.
Typically, any treatment plans for a patient with ovarian cancer are based on the type of ovarian cancer, its stage, and any special situations. Most women with ovarian cancer will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of ovarian cancer and how advanced it is, you might need other types of treatment as well, either before or after surgery, or sometimes both.
Those who to expect in treating ovarian cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include:
- A gynecologic oncologist: a gynecology doctor who is specially trained to use surgery to treat ovarian cancer; many times they are also the ones to give chemotherapy and other medicines to treat ovarian cancer
- A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer
- A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer
Many other specialists might be part of your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, sex counselors, social workers, nutritionists, genetic counselors, and other health professionals.
Your treatment plan will depend on many factors, including your overall health, personal preferences, and whether you plan to have children. Age alone isn’t a determining factor since several studies have shown that older women tolerate ovarian cancer treatments well.
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. It’s also very important to ask questions if there’s anything you’re not sure about.
If time permits, it is often a good idea to seek a second opinion. A second opinion can give you more information and help you feel more confident about the treatment plan you choose.