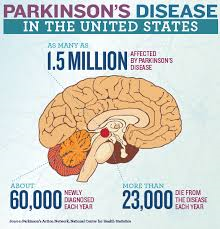
Below are 10 signs that you might have the disease. No single one of these signs means that you should worry, but if you have more than one sign you should consider making an appointment to talk to your doctor.
1-Tremor
Have you noticed a slight shaking or tremor in your finger, thumb, hand or chin? A tremor while at rest is a common early sign of Parkinson’s disease.
What is normal?
Shaking can be normal after lots of exercise, if you are stressed or if you have been injured. Shaking could also be caused by a medicine you take.
2-Small Handwriting
Has your handwriting gotten much smaller than it was in the past? You may notice the way you write words on a page has changed, such as letter sizes are smaller and the words are crowded together. A change in handwriting may be a sign of Parkinson’s disease called micrographia.
What is normal?
Sometimes writing can change as you get older, if you have stiff hands or fingers or poor vision.
3-Loss of Smell
Have you noticed you no longer smell certain foods very well? If you seem to have more trouble smelling foods like bananas, dill pickles or licorice, you should ask your doctor about Parkinson’s.
What is normal?
Your sense of smell can be changed by a cold, flu or a stuffy nose, but it should come back when you are better.
4-Trouble Sleeping
Do you thrash around in bed or act out dreams when you are deeply asleep? Sometimes, your spouse will notice or will want to move to another bed. Sudden movements during sleep may be a sign of Parkinson’s disease.
What is normal?
It is normal for everyone to have a night when they ‘toss and turn’ instead of sleeping. Similarly, quick jerks of the body when initiation sleep or when in lighter sleep are common and often normal.
5-Trouble Moving or Walking
Do you feel stiff in your body, arms or legs? Have others noticed that your arms don’t swing like they used to when you walk? Sometimes stiffness goes away as you move. If it does not, it can be a sign of Parkinson’s disease. An early sign might be stiffness or pain in your shoulder or hips. People sometimes say their feet seem “stuck to the floor.”
What is normal?
If you have injured your arm or shoulder, you may not be able to use it as well until it is healed, or another illness like arthritis might cause the same symptom.
6-Constipation
Do you have trouble moving your bowels without straining every day? Straining to move your bowels can be an early sign of Parkinson’s disease and you should talk to your doctor.
What is normal?
If you do not have enough water or fiber in your diet, it can cause problems in the bathroom. Also, some medicines, especially those used for pain, will cause constipation. If there is no other reason such as diet or medicine that would cause you to have trouble moving your bowels, you should speak with your doctor.
7-A Soft or Low Voice
Have other people told you that your voice is very soft or that you sound hoarse? If there has been a change in your voice you should see your doctor about whether it could be Parkinson’s disease. Sometimes you might think other people are losing their hearing, when really you are speaking more softly.
What is normal?
A chest cold or other virus can cause your voice to sound different, but you should go back to sounding the same when you get over your cough or cold.
8-Masked Face
Have you been told that you have a serious, depressed or mad look on your face, even when you are not in a bad mood? This is often called facial masking. If so, you should ask your doctor about Parkinson’s disease.
What is normal?
Some medicines can cause you to have the same type of serious or staring look, but you would go back to the way you were after you stopped the medication.
9-Dizziness or Fainting
Do you notice that you often feel dizzy when you stand up out of a chair? Feeling dizzy or fainting can be a sign of low blood pressure and can be linked to Parkinson’s disease (PD).
What is normal?
Everyone has had a time when they stood up and felt dizzy, but if it happens on a regular basis you should see your doctor.
10-Stooping or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease (PD).
What is normal?
If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over