Tests and procedures used to diagnose glioblastoma include:
- Neurological exam. During a neurological exam, your doctor will ask you about your signs and symptoms. He or she may check your vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength and reflexes. Problems in one or more of these areas may provide clues about the part of your brain that could be affected by a brain tumor.
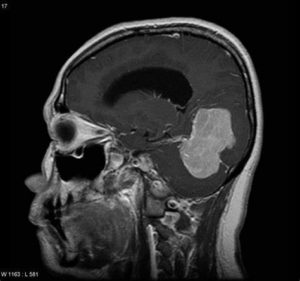
- Imaging tests. Imaging tests can help your doctor determine the location and size of your brain tumor. MRI is often used to diagnose brain tumors, and it may be used along with specialized MRI imaging, such as functional MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Imaging tests can help your doctor determine the location and size of your brain tumor. Other imaging tests may include CT and positron emission tomography (PET).
- Removing a sample of tissue for testing (biopsy). A biopsy can be done with a needle before surgery or during surgery to remove your glioblastoma, depending on your particular situation and the location of your tumor. The sample of suspicious tissue is analyzed in a laboratory to determine the types of cells and their level of aggressiveness.Depending on the location of the glioma, a biopsy may be performed with a needle before treatment or as part of an operation to remove the brain tumor. Specialized tests of the tumor cells can tell your doctor the types of mutations the cells have acquired. This gives your doctor clues about your prognosis and may guide your treatment options.A biopsy is the only way to definitively diagnose a brain tumor and give a prognosis to guide treatment decisions. Based on this information, a doctor who specializes in diagnosing cancer and other tissue abnormalities (pathologist) can determine the grade or stage of a brain tumor.The pathologist will also examine the physical appearance and growth rate of your biopsy sample (molecular diagnosis). Your doctor will explain the pathologist’s findings to you. This information helps guide decision-making about your treatment plan.
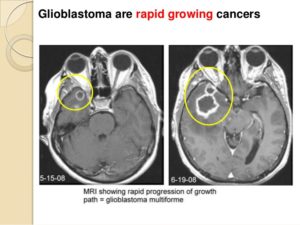
Treatments:
Treatment for glioma depends on the type, size, grade and location of the tumor, as well as your age, overall health and preferences.
In addition to actions to remove the tumor itself, treatment for glioma may also require using drugs to reduce the signs and symptoms of your tumor.
Your doctor may prescribe steroids to reduce swelling and relieve pressure on affected areas of the brain. Anti-epileptic drugs may be used to control seizures.
1-Surgery
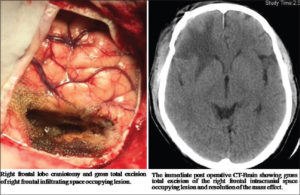
Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible is usually the first step in treating most types of gliomas.
In some cases, gliomas are small and easy to separate from surrounding healthy brain tissue, which makes complete surgical removal possible. In other cases, tumors can’t be separated from surrounding tissue, or they’re located near sensitive areas in your brain and make surgery risky. In these situations your doctor removes as much of the tumor as is safe.
Even removing a portion of the tumor may help reduce your signs and symptoms.
In some cases, neuropathologists may analyze tissue samples removed by a surgeon and report the results while surgery is underway. This information helps the surgeon decide how much tissue to remove.
A variety of surgical technologies and techniques may be used to assist the neurosurgeon in protecting as much healthy brain tissue as possible while removing the tumor, including computer-assisted brain surgery, intraoperative MRI, awake brain surgery and lasers. For example, during awake brain surgery, you may be asked to perform a task with the goal of ensuring the area of the brain controlling that function is not damaged.
Surgery to remove a glioma carries risks, such as infection and bleeding. Other risks may depend on the part of your brain in which your tumor is located. For instance, surgery on a tumor near nerves that connect to your eyes may carry a risk of vision loss.

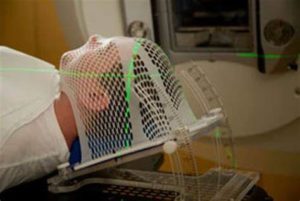
2-Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy usually follows surgery in treatment of glioma, especially high-grade gliomas. Radiation uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill tumor cells. Radiation therapy for glioma comes from a machine outside your body (external beam radiation).
There are several types of external beam radiation currently used and under study for the treatment of glioma. The type of glioma you have, its grade and other prognostic factors are considered in determining the timing and type of radiation therapy you may receive. A doctor who specializes in radiation therapy for cancer (radiation oncologist) will work closely with your other doctors to plan and coordinate the most appropriate radiation treatment for you.
Radiation therapy options include:
- Using computers to pinpoint delivery of radiation treatment to the exact location of the brain tumor. Techniques include intensity-modulated radiation therapy and 3D conformal radiation therapy.
- Using protons — the positive parts of atoms — rather than X-rays as the source of radiation. This technique, called conformal proton beam therapy, delivers radiation only once proton beams reach the tumor, causing less damage than X-rays to surrounding tissue.
- Using multiple beams of radiation to give a highly focused form of radiation treatment. While this technique is called stereotactic radiation therapy (radiosurgery), it doesn’t actually involve surgery in the traditional sense. Each beam of radiation isn’t particularly powerful, but the point where all the beams meet — at the brain tumor — receives a very large dose of radiation to kill the tumor cells in a very small area.
There are different types of technology used in radiosurgery to deliver radiation to treat brain tumors, such as a Gamma Knife or linear accelerator (LINAC).
Side effects of radiation therapy depend on the type and dose of radiation you receive. Common side effects during or immediately following radiation include fatigue, headaches and scalp irritation.
3-Chemotherapy Treatment:
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill tumor cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be taken in pill form (orally) or injected into a vein (intravenously).
Chemotherapy is usually used in combination with radiation therapy to treat gliomas.
The chemotherapy drug used most often to treat gliomas is temozolomide (Temodar), which is taken as a pill.
Side effects of chemotherapy depend on the type and dose of drugs you receive. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting, headache, hair loss, fever, and weakness. Some side effects may be managed with medication.
4-Targeted drug therapy:
Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die.
One targeted drug therapy used to treat a type of brain cancer called glioblastoma is bevacizumab (Avastin). This drug, given through a vein (intravenously), stops the formation of new blood vessels, cutting off blood supply to a tumor and killing the tumor cells.
5-Treatment innovations:
Brain cancer research is a very active field of study. Researchers are investigating new ways to deliver drugs to brain tumors, including pumps that release a continuous, slow flow of chemotherapy or targeted drug therapies to a tumor. This type of treatment is called convection-enhanced delivery (CED).
Another type of therapy uses technology called tumor treating fields (Optune) to deliver electric fields to the brain, which can help stop the proliferation of cancer cells. Optune is a wearable, portable device and is used in combination with temozolomide to treat newly diagnosed glioblastoma in adults.
Implanted, biodegradable wafer therapy (Gliadel) relies on an implanted disc to release chemotherapy to tumor tissue that remains after surgery. And in nanoparticle therapy, particles with an unusually high surface area carry chemotherapy across the blood-brain barrier directly to a tumor.
6-Rehabilitation after treatment:
Because brain tumors can develop in parts of the brain that control motor skills, speech, vision and thinking, rehabilitation may be a necessary part of recovery. Your doctor may refer you to services that can help, such as:
- Physical therapy can help you regain lost motor skills or muscle strength
- Occupational therapy, which can help you get back to your normal daily activities, including work, after a brain tumor or other illness
- Speech therapy with specialists in speech difficulties (speech pathologists), which can help if you have difficulty speaking
- Tutoring for school-age children, which can help kids cope with changes in memory and thinking after a brain tumor