Part II Top 3 Degenerative Eye Diseases – #2 Glaucoma (National Awareness Glaucoma Month)
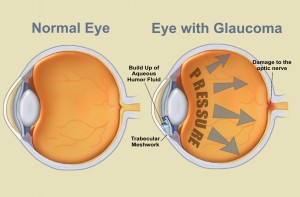
A common eye condition in which the fluid pressure inside the eye rises to a level higher than healthy for that eye. If untreated, it may damage the optic nerve, causing the loss of vision or even blindness. The elderly, African-Americans, and people with family histories of the disease are at greatest risk.
Glaucoma is a multi-factorial, complex eye disease with specific characteristics such as optic nerve damage and visual field loss. While increased pressure inside the eye (called intraocular pressure or IOP) is usually present, even patients with normal range IOP can develop glaucoma.
There is no specific level of elevated eye pressure that definitely leads to glaucoma; conversely, there is no lower level of IOP that will absolutely eliminate a person’s risk of developing glaucoma. That is why early diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma is the key to preventing vision loss.
Eye pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). Normal eye pressure ranges from 12-22 mm Hg, and eye pressure of greater than 22 mm Hg is considered higher than normal. When the IOP is higher than normal but the person does not show signs of glaucoma, this is referred to as ocular hypertension.
High eye pressure alone does not cause glaucoma. However, it is a significant risk factor. Individuals diagnosed with high eye pressure should have regular comprehensive eye examinations by an eyecare professional to check for signs of the onset of glaucoma.
A person with elevated IOP is referred to as a glaucoma suspect, because of the concern that the elevated eye pressure might lead to glaucoma. The term glaucoma suspect is also used to describe those who have other findings that could potentially, now or in the future, indicate glaucoma. For example, a suspicious optic nerve, or even a strong family history of glaucoma, could put someone in the category of a glaucoma suspect.
Vision loss from glaucoma occurs when the eye pressure is too high for the specific individual and damages the optic nerve. Any resultant damage cannot be reversed. The peripheral (side) vision is usually affected first. The changes in vision may be so gradual that they are not noticed until a lot of vision loss has already occurred.
In time, if the glaucoma is not treated, central vision will also be decreased and then lost; this is how visual impairment from glaucoma is most often noticed. The good news is that glaucoma can be managed if detected early, and with medical and/or surgical treatment, most people with glaucoma will not lose their sight.
Most common signs and symptoms of Glaucoma:
There are several forms of glaucoma; the two most common forms are primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and angle-closure glaucoma (ACG). Open-angle glaucoma is often called “the sneak thief of sight” because it has no symptoms until significant vision loss has occurred.
Symptoms of Open-Angle Glaucoma
There are typically no early warning signs or symptoms of open-angle glaucoma. It develops slowly and sometimes without noticeable sight loss for many years.
Most people who have open-angle glaucoma feel fine and do not notice a change in their vision at first because the initial loss of vision is of side or peripheral vision, and the visual acuity or sharpness of vision is maintained until late in the disease.
By the time a patient is aware of vision loss, the disease is usually quite advanced. Vision loss from glaucoma is not reversible with treatment, even with surgery.
Because open-angle glaucoma has few warning signs or symptoms before damage has occurred, it is important to see a doctor for regular eye examinations. If glaucoma is detected during an eye exam, your eye doctor can prescribe a preventative treatment to help protect your vision.
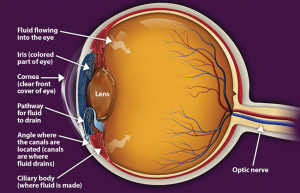
In open-angle glaucoma, the angle in your eye where the iris meets the cornea is as wide and open as it should be, but the eye’s drainage canals become clogged over time, causing an increase in internal eye pressure and subsequent damage to the optic nerve. It is the most common type of glaucoma, affecting about four million Americans, many of whom do not know they have the disease.
You are at increased risk of glaucoma if your parents or siblings have the disease, if you are African-American or Latino, and possibly if you are diabetic or have cardiovascular disease. The risk of glaucoma also increases with age.
Symptoms of Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- Hazy or blurred vision
- The appearance of rainbow-colored circles around bright lights
- Severe eye and head pain
- Nausea or vomiting (accompanying severe eye pain)
- Sudden sight loss
Angle-closure glaucoma is caused by blocked drainage canals in the eye, resulting in a sudden rise in intraocular pressure. This is a much more rare form of glaucoma, which develops very quickly and demands immediate medical attention
In contrast with open-angle glaucoma, symptoms of acute angle-closure glaucoma are very noticeable and damage occurs quickly. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate care from an ophthalmologist.
QUOTE FOR FRIDAY:
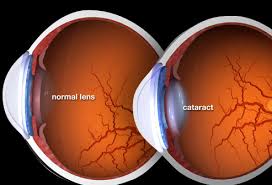
“A cataract is a medical condition affecting one or both of your eyes. It makes the normally clear lens in your eyes cloudy. This causes you to feel like you are looking through a cloudy lens or fogged-up window. Once your vision becomes cloudy, you have more difficulty doing everyday simple tasks like driving or reading.”
Part I Top 3 degenerative eye diseases – Cataracts/
The top 3 degenerative eye diseases – cataracts, glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration – can result in vision loss or complete blindness. Fortunately today, effective treatment options are available – and newer treatments are on the horizon. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent or slow vision loss associated with degenerative eye conditions; if you experience any changes to your vision or any unusual eye symptoms, schedule an appointment with an eye-doctor as soon as possible.
Part I Cataracts
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging. Cataracts are very common in older people. By age 80, more than half of all Americans either have a cataract or have had cataract surgery.
A cataract can occur in either or both eyes. It cannot spread from one eye to the other.
Yes. Although most cataracts are related to aging, there are other types of cataract:
-Secondary cataract. Cataracts can form after surgery for other eye problems, such as glaucoma. Cataracts also can develop in people who have other health problems, such as diabetes. Cataracts are sometimes linked to steroid use.
-Traumatic cataract. Cataracts can develop after an eye injury, sometimes years later.
-Congenital cataract. Some babies are born with cataracts or develop them in childhood, often in both eyes. These cataracts may be so small that they do not affect vision. If they do, the lenses may need to be removed.
-Radiation cataract. Cataracts can develop after exposure to some types of radiation
The most common symptoms of a cataract are:
- Cloudy or blurry vision.
- Colors seem faded.
- Glare. Headlights, lamps, or sunlight may appear too bright. A halo may appear around lights.
- Poor night vision.
- Double vision or multiple images in one eye. (This symptom may clear as the cataract gets larger.)
- Frequent prescription changes in your eyeglasses or contact lenses.
- These symptoms also can be a sign of other eye problems. If you have any of these symptoms, check with your eye care professional.
- TREATMENT
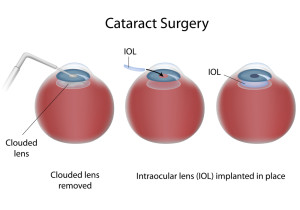
- The symptoms of early cataract may be improved with new eyeglasses, brighter lighting, anti-glare sunglasses, or magnifying lenses. If these measures do not help, surgery is the only effective treatment. Surgery involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial lens.
- A cataract needs to be removed only when vision loss interferes with your everyday activities, such as driving, reading, or watching TV. You and your eye care professional can make this decision together. Once you understand the benefits and risks of surgery, you can make an informed decision about whether cataract surgery is right for you. In most cases, delaying cataract surgery will not cause long-term damage to your eye or make the surgery more difficult. You do not have to rush into surgery.
- Sometimes a cataract should be removed even if it does not cause problems with your vision. For example, a cataract should be removed if it prevents examination or treatment of another eye problem, such as age-related macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy. If your eye care professional finds a cataract, you may not need cataract surgery for several years. In fact, you might never need cataract surgery. By having your vision tested regularly, you and your eye care professional can discuss if and when you might need treatment.
- If you choose surgery, your eye care professional may refer you to a specialist to remove the cataract.
- If you have cataracts in both eyes that require surgery, the surgery will be performed on each eye at separate times, usually four to eight weeks apart.
- Many people who need cataract surgery also have other eye conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration or glaucoma. If you have other eye conditions in addition to cataract, talk with your doctor. Learn about the risks, benefits, alternatives, and expected results of cataract surgery.
Know the risks of cataract eye surgery:
As with any surgery, cataract surgery poses risks, such as infection and bleeding. Before cataract surgery, your doctor may ask you to temporarily stop taking certain medications that increase the risk of bleeding during surgery. After surgery, you must keep your eye clean, wash your hands before touching your eye, and use the prescribed medications to help minimize the risk of infection. Serious infection can result in loss of vision.
Cataract surgery slightly increases your risk of retinal detachment. Other eye disorders, such as high myopia (nearsightedness), can further increase your risk of retinal detachment after cataract surgery. One sign of a retinal detachment is a sudden increase in flashes or floaters. Floaters are little “cobwebs” or specks that seem to float about in your field of vision. If you notice a sudden increase in floaters or flashes, see an eye care professional immediately. A retinal detachment is a medical emergency. If necessary, go to an emergency service or hospital. Your eye must be examined by an eye surgeon as soon as possible. A retinal detachment causes no pain. Early treatment for retinal detachment often can prevent permanent loss of vision. The sooner you get treatment, the more likely you will regain good vision. Even if you are treated promptly, some vision may be lost.
Talk to your eye care professional about these risks. Make sure cataract surgery is right for you.
QUOTE FOR THURSDAY:
“Simply put, enzymes are proteins that participate in cellular metabolic processes with the ability to enhance the rate of reaction between bio-molecules. Life would not exist without the presence of enzymes.”
thebalance.com.
Enzymes and how they break down proteins
Let’s not forget with enzymes they also break proteins down in our body:
The breaking down of proteins=Trypsin Proteins are large biological molecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acids. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing 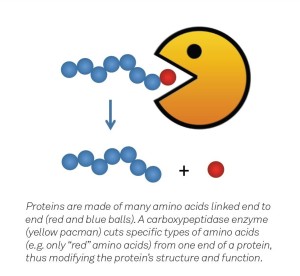 metabolic reactions, replicating DNA, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Trypsin is a enzyme catalyst, which allows the catalysis of chemical reactions. The ending product of the break down is amino acids not sugar. Know high on a protein diet continuously for years can hurt the body also.
metabolic reactions, replicating DNA, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Trypsin is a enzyme catalyst, which allows the catalysis of chemical reactions. The ending product of the break down is amino acids not sugar. Know high on a protein diet continuously for years can hurt the body also.
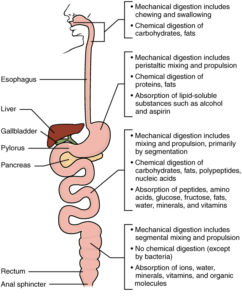
Enzymes deal with breaking down our foods because they take a major role in what we call the process digestion in the human body. but notice what the ending result is of mostly every ingredient in our 4 food groups is; SUGAR. It because of the food has some sugar in it but also the chemical reaction with the enzyme to allow the food to break down into smaller compounds to be utilized in the body with send through the entire digestion process.
There are risks with eating just high protein diets for long periods of time. You put yourself at risk for: Osteoporosis: Research shows that women who eat high protein diets based on meat have a higher rate of bone density loss than those who don’t. Women who eat meat lose an average of 35% of their bone density by age 65, while women who don’t eat meat lose an average of 18%. In the long run, bone density loss leads to osteoporosis.
Kidneys: A high protein diet puts strain on the kidneys. It is well known that patients with kidney problems suffer from eating a high protein diet which is due to the high amino acids levels. A high-protein diet may worsen kidney function in people with kidney disease because your body may have trouble eliminating all the waste products of protein metabolism.
However, the risks of using a high-protein diet with carbohydrate restriction for the long term are still being studied. Several health problems may result if a high-protein diet is followed for an extended time:
Some high-protein diets restrict carbohydrate intake so much that they can result in nutritional deficiencies or insufficient fiber, which can cause health problems such as constipation and diverticulitis.
Some high-protein diets promote foods such as red meat and full-fat dairy products, which may increase your risk of heart disease.
If you want to follow a high-protein diet, do so only as a short-term weight-loss aid. Also, choose your protein wisely. Good choices include fish, skinless chicken, lean beef, pork and low-fat dairy products. Choose carbs that are high in fiber, such as whole grains and nutrient-dense vegetables and fruit.
It’s always a good idea to talk with your doctor before starting any weight-loss diet. And that’s especially important in this case if you have kidney disease, diabetes or other chronic health condition (s).
So if you want to continue on high protein diets longer than 6 months know how to alkalize the body chemicals to decrease the proteins and there are supplements that can do that via the pharmacy or look up even online.
QUOTE FOR TUESDAY:
“What women should know about cervical cancer is Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cervical Cancer. One of the best things you can do so you don’t get cervical cancer is get regular testing for cervical cancer.”
American Cancer Society