The heart is like the engine to a car but for us it’s the “pump” for the human body; without the engine the car won’t run and without the pump we won’t live. The normal size of the heart is about the size of your fist, maybe a little bigger. It pumps blood continuously through your entire circulatory system. The heart consists of four chambers, 2 on the right and 2 on the left. The right side only pumps high carbon dioxide levels of blood, after all the oxygen was used by the tissues and returns to the heart in the right upper chamber and leaves to the lung from the right lower chamber. From the lungs it than goes to the left side of the heart now, which is a very short distance as opposed to where the left side pumps the blood. The L side of the heart pumps blood to the feet, brain and all tissues in between with high oxygen levels of blood. This is why the L side of the heart does more work than the R side since the blood leaving the L side has a longer distance in distributing oxygen. The heart pumps the blood with high oxygen blood levels to reach all your tissues and cells, going to the feet, brain, and to all other tissues in between returning home again to the right side of the heart (upper chamber) to get sent to the lungs again for more oxygen. This is why the muscle on the L side of the heart is larger than the right, it works harder. Every time your heart beats (the sound we call lub dub) the organ is sending out a cardiac output of blood either to the lungs for more oxygen or to the body tissues through the aorta to give oxygenated blood to your tissues and cells. This is the mechanics of how the heart works in our body.
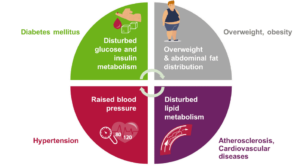
Let’s see what can occur if the heart doesn’t function properly. If your heart is not pumping out a sufficient amount in your cardiac output to either the lungs (from rt. Side) or to the tissues (from the lt. side) than it tries to work harder where it does ok at first but over time weakens. As this weak heart struggles to pump blood the muscle fibers of the heart stretch. Over time, this stretching leaves the heart with larger, weaker chambers. The heart enlarges (cardiomegaly). If this continues to go on this could go into R or L sided heart failure. When this happens, blood that should be pumped out of the heart backs up in the lungs (L sided failure) or in the tissues (R sided failure). The side the failure is on doesn’t allow proper filling of the chambers on that side and back up happens; so if on the L the fluids back up in the lungs or the R the fluids first back up in the veins which can expand to hold extra blood but at some point dump the extra fluids in your tissues (This is edema in feet first due to gravity). This is all due to overloading of the blood not filling up in the chambers of the heart to make a good cardiac output of blood and in time the fluid backs up (bad pumping=backup of blood=fluid overload in the lungs (pulmonary congestion) to fluid staying in the skin (first the lower extremities due to gravity=feet which we call edema working its way up the legs.). This condition in time with no treatment will go into congestive heart failure (CHF) to the other side of the heart if not controlled. CHF can range from mild to severe. There is 670,000 cases are diagnosed with this every year and is the leading cause of hospitalization in people over 65 y/o. Causes of CHF are: heart attack, CAD (coronary artery disease), cardiomyopathy, conditions that overwork the heart like high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity (These diseases can be completely preventable or at least well controlled).
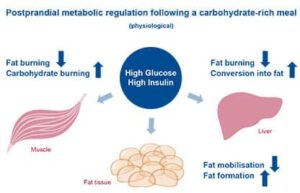
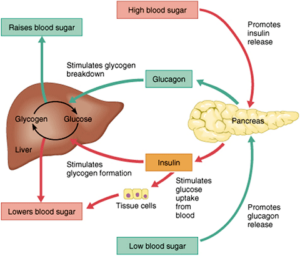
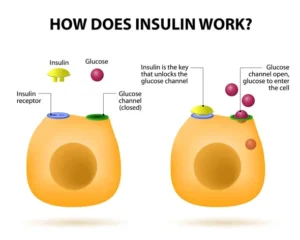
There is many of us in this world with knowing how our activity/exercise, eating, and habits could be better for health but do little action if any on our own to change it, which is a large part for certain diseases being so high in America (diabetes, stroke, cardiac diseases=high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis to CHF and more). If people were more healthier and more active regarding these diseases alone it would decrease in population creating a positive impact on how our health system with insurance presently (a disaster) with our economy for many could get better. A healthy heart can pump to all parts of the body in a few seconds which is good cardiac output from the organ but when it gets hard for the heart to keep up with its regular routine it first compensates to eventually it decompensates causing ischemia (lack of oxygen to the heart tissue). It’s like any tissue in the body, lack of oxygen=lack of nutrients to the body tissue=STARVATION and with lack of oxygen will come PAIN eventually to death if not treated. Take the heart, if it isn’t getting enough oxygen it can go into angina. That is reversible since it is heart pain due to not enough oxygen to the heart tissue=no damage but if left untreated what will occur is a heart attack=myocardial infarction (MI) and is permanent damage because scarring to the heart tissue takes place that is permanent damage to that area of the heart for life.
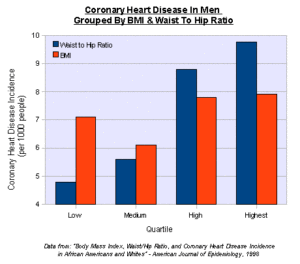
Let’s understand what happens to the heart when the organ can become diseased due to bad health habits. If you are eating too much for too long that consist of foods high in sodium your vessels will narrow in size. By allowing this you increase the pressure in the vessels that increases your blood pressure called hypertension. If you are also inactive you are at risk of obesity which puts stress on the heart and in time causing high B/P. Constantly be in a high B/P and this could cause the vessel to rupture (at the heart=possible heart attack, at the brain=possible stroke, also called CVA with both on high occurrences in our population of the US.). With bad habits (especially poor diet, inactive, and smoking) you can cause over time atherosclerosis=a blockage in the artery with the resolution surgery (from a cardiac catheterization up your groin or having difficulty in the arm to the heart where an angiogram to an angioplasty with possibly a stent is performed or if the blockage to blockages is so bad a CABG=coronary artery bypass=a 6hr plus operation where diversion of a vein from your leg (donor graft site) around the blockage is done. Smoking can lead to this but it also can cause your vessels to become brittle=arteriosclerosis. Healthy Habits would impact a positive result for all people who have had this diagnosis before but most important be a great PREVENTATIVE measure for people not diagnosed with cardiac disease. There are 4 things you have no control over heredity, age, sex, and race but healthy habits are sure to benefit you by keeping the odds down of you inheriting, help your age factor, and race a lot can be associated with eating cultural habits.
If you make the decision to live a life that’s healthy for your heart through proper eating, doing healthy habits and doing some exercise or activity with balancing rest in your busy schedule and would like direction or want to expand your diet/exercise/healthy habits then your taking the right step.
Wouldn’t you want less chance of heart disease or obesity or diabetes for yourself and for others throughout the nation including the future generations? Let’s build a stronger foundation regarding HEALTH in America.