It’s Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia Care Education Month.
At one time Alzheimer’s disease was a disease considered with unknown etiology (or cause). Today it is considered different in the eyes of many in the medical profession. By a Dr. Mercola a physician who founded Mercola.com (Mercola.com is now the world’s top natural health resource site, with over 1.5 million subscribers.) feels this about Alzheimer’s disease: “The cause of the debilitating, and fatal, brain disease Alzheimer’s is conventionally said to be a mystery.”
While we know that certain diseases, like type 2 diabetes, are definitively connected to the foods you eat, Alzheimer’s is generally thought to strike without warning or reason.
That is, until recently.
Now, a growing body of research suggests there may be a powerful connection between the foods you eat and your risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia, via similar pathways that cause type 2 diabetes. Some have even re-named Alzheimer’s as “type 3 diabetes.””
Can You Eat Your Way to Alzheimer’s?
In a recent animal study, researchers from Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island were able to induce many of the characteristic brain changes seen with Alzheimer’s disease (disorientation, confusion, inability to learn and remember) by interfering with insulin signaling in their brains.
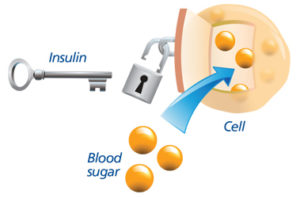
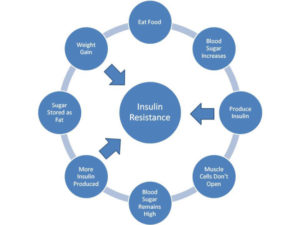
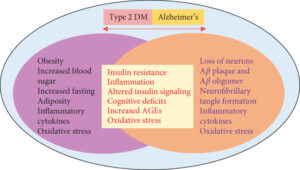
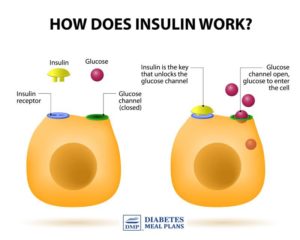
Know that faulty insulin (and leptin, another hormone) signaling is an underlying cause for insulin resistance, which, of course, typically leads to type 2 diabetes. However, while insulin is usually associated with its role in keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range, it also plays a role in brain signaling. When researchers disrupted the proper signaling of insulin in the brain, it resulted in dementia.
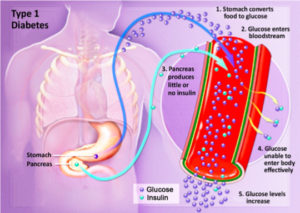
What does this have to do with your diet? Let us go back to one of my articles on diabetes this week and how it impacts your diet. It states “The foods we eat that contain starches, carbohydrates, calories are made up of sugar. When food reaches our stomach in time digestion starts to take place where these foods are broken down in the stomach into individual or complex sugar molecules ( glucose being one of the most common and important ones). The glucose then passes from our stomach into our bloodstream when it reaches the liver 60 to 80 % of the glucose gets stored in that organ turning glucose into inactive glucose that’s converted to glycogen. The purpose for glycogen is when our glucose is low and our body needing energy we have this extra stored sugar, glycogen, to rely on. This is done by the liver which allows the sugar to be stored and released back into the bloodstream if we need it=energy, since nothing is in our stomach at that time, in that case scenario). When glucose=an active sugar, it is our energy for our cells and tissues and is a sugar ready to be utilized by the body where it is needed, by many organs. Think of a car for one moment, and what makes it run? That would be gas/fuel for it to function. The same principle with glucose in your bloodstream=fuel for the human body so we can function, for without it we wouldn’t survive. That is the problem with a person that has diabetes. They eat, they break the food down, the glucose gets in the blood but the glucose fuel can’t be used due to lack of or NO insulin at all. Insulin allows glucose to pass into our cells and tissues to be used as energy/fuel for the body parts to work. Glucose is used as the principle source of energy (It is used by the brain for energy, the muscles for both energy and some storage, liver for more glucose storage=that is where glucose is converted to glycogen, and even stored in fat tissue using it for triglyceride production). Glucose does get sent to other organs for more storage, as well. Insulin plays that vital role in allowing glucose to be distributed throughout the body. Without insulin the glucose has nowhere to go.”
So how does this impact your brain thinking?
“This new focus on the Alzheimer’s/Diabetes/Insulin connection follows a growing recognition of insulin’s role in the brain. Until recently, the hormone was typecast as a regulator of blood sugar, giving the cue for muscles, liver and fat cells to extract sugar from the blood and either use it for energy or store it as fat. We now know that it is also a master multitasker: it helps neurons, particularly in the hippocampus and frontal lobe, take up glucose for energy, and it also regulates neurotransmitters, like acetylcholine, which are crucial for memory and learning.” What is effected with Alzheimer’s disease? Your memory and learning, So your diet plays a big role in Alzheimer’s disease.”
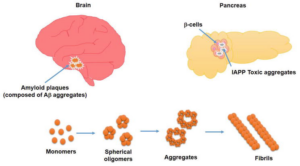
Over-consumption of sugars and grains is what ultimately causes your body to be incapable of “hearing” the proper signals from insulin and leptin, leaving you insulin resistant in both body and brain. Alzheimer’s disease was tentatively dubbed “type 3 diabetes” in early 2005 when researchers learned that the pancreas is not the only organ that produces insulin. Your brain also produces insulin, and this brain insulin is necessary for the survival of your brain cells.
If You Have Diabetes, Your Risk of Alzheimer’s Increases Dramatically
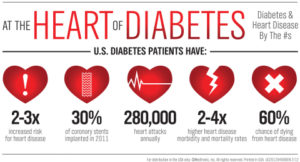
Diabetes is linked to a 65 percent increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s, which may be due, in part, because insulin resistance and/or diabetes appear to accelerate the development of plaque in your brain, which is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s. Separate research has found that impaired insulin response was associated with a 30 percent higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease, and overall dementia and cognitive risks were associated with high fasting serum insulin, insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion and glucose intolerance.
A drop in insulin production in your brain may contribute to the degeneration of your brain cells, mainly by depriving them of glucose, and studies have found that people with lower levels of insulin and insulin receptors in their brain often have Alzheimer’s disease (people with type 2 diabetes often wind up with low levels of insulin in their brains as well). As explained in New Scientist, which highlighted this latest research:
What’s more, it encourages the process through which neurons change shape, make new connections and strengthen others. And it is important for the function and growth of blood vessels, which supply the brain with oxygen and glucose.
As a result, reducing the level of insulin in the brain can immediately impair cognition. Spatial memory, in particular, seems to suffer when you block insulin uptake in the hippocampus… Conversely, a boost of insulin seems to improve its functioning.
When people frequently gorge on fatty, sugary food, their insulin spikes repeatedly until it sticks at a high level. Muscle, liver and fat cells then stop responding to the hormone, meaning they don’t mop up glucose and fat in the blood. As a result, the pancreas desperately works overtime to make more insulin to control the glucose – and levels of the two molecules skyrocket.
The pancreas can’t keep up with the demand indefinitely, however, and as time passes people with type 2 diabetes often end up with abnormally low levels of insulin.”
 =
=