Dandelion
Dandelion
Some people may ask if a vegetable or fruit is it considered a plant. Through a very resourceful site “MAYO Clinic” the state the following:
“According to botanists (those who study plants) a fruit is the part of the plant that develops from a flower. It’s also the section of the plant that contains the seeds. The other parts of plants are considered vegetables. These include the stems, leaves and roots — and even the flower bud.
The following are technically fruits: avocado, beans, peapods, corn kernels, cucumbers, grains, nuts, olives peppers, pumpkin, squash, sunflower seeds and tomatoes. Vegetables include celery (stem), lettuce (leaves), cauliflower and broccoli (buds), and beets, carrots and potatoes (roots).
From a culinary standpoint, vegetables are less sweet — or more savory — and served as part of the main dish. Fruits are more sweet and tart and are most often served as a dessert or snack. Both fruits and vegetables can be made into juice for a refreshing beverage. Some fruits are “grains” or “nuts” or “seeds” — and are served accordingly.
Nutritionally speaking, fruits and vegetables are similar. Compared with animal products, they’re generally lower in calories and fat, but higher in fiber. Fruits and vegetables also contain health-enhancing plant compounds such as antioxidants. And they’re loaded with vitamins and minerals.”
So yes part of a plant can be a fruit or vegetable.
How we get benefits from plants medically:
Ginger:
Ginger is one spice that I recommend keeping on hand in your kitchen at all times. Not only is it a wonderful addition to your cooking (especially paired with garlic) but it also has enough medical properties to fill several books.
Ginger is best known for its anti-nausea effects but also has broad-spectrum antibacterial, antiviral, antioxidant, and anti-parasitic properties, to name just several of its more than 40 scientifically confirmed pharmacological actions. It is anti-inflammatory, making it valuable for pain relief for joint pain, menstrual pain, headaches, and more.
The pain-relieving potential of ginger appears to be far-reaching. Along with help for muscle and joint pain, ginger has been found to reduce the severity of migraine headaches as well as the migraine medication Sumatriptan – with fewer side effects.4
Ginger also shows promise for fighting cancer, diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, asthma, bacterial and fungal infections, and it is one of the best natural remedies available for motion sickness or nausea (from pregnancy or chemotherapy, for example).
Taking one gram of ginger daily may help reduce nausea and vomiting in pregnant women, or those with migraines and ginger has been shown to work better than a placebo in relieving morning sickness.5
Ginger is also a must-have if you struggle with indigestion, and it does more than simply relieve pain. Ginger contains powerful protein-digesting enzymes and helps to stimulate the emptying of your stomach without any negative effect, and it’s an antispasmodic agent, which may explain its beneficial effects on your intestinal tract.
Many people enjoy ginger tea on a regular basis, and this is one of the simplest ways to use it. Simply chop off a couple of inches of ginger root and let it steep in hot water for fresh ginger tea. I would advise against using it daily as it can lead to an allergy and is what happened to me about twenty years ago.
You can also peel the root using a paring knife and then slice it thinly (or grate it or mince it) to add to tea or cooked dishes. You can’t go wrong by adding ginger to stir fries or even your favorite homemade chicken soup. For serious issues, a natural health care provider can help you get the maximum therapeutic benefits of ginger.
Garlic:
Eating a clove or two of fresh garlic a day may indeed keep the doctor away, in part because it has immune-boosting, antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-fungal effects. Many of garlic’s therapeutic effects are derived from its sulfur-containing compounds, such as allicin, which are also what give it its characteristic smell. In general, garlic’s benefits fall into four main categories:
-Reducing inflammation (reduces the risk of osteoarthritis and other disease associated with inflammation).
-Boosting immune function (antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and antiparasitic properties).
-Improving cardiovascular health and circulation (protects against clotting, retards plaque, improves lipids, and reduces blood pressure).
-Toxic to at least 14 kinds of cancer cells (including brain, lung, breast, gastric, and pancreatic).
In addition, garlic may be effective against drug-resistant bacteria, and research has revealed that as allicin digests in your body, it produces sulfenic acid, a compound that reacts with dangerous free radicals faster than any other known compound. This is one of the reasons in my article garlic what listed as one of the top seven anti-aging foods you can consume.
In order to get the health benefits, the fresh clove must be crushed or chopped in order to stimulate the release of an enzyme called alliinase, which in turn catalyzes the formation of allicin.
Allicin, in turn, rapidly breaks down to form a number of different organosulfur compounds. So to “activate” garlic’s medicinal properties, compress a fresh clove with a spoon prior to swallowing it, or put it through your juicer to add to your vegetable juice.
A single medium-size clove or two is usually sufficient and is well-tolerated by most people. The active ingredient, allicin, is destroyed within one hour of smashing the garlic, so garlic pills are virtually worthless. Black garlic, which is basically fermented garlic, and sprouted garlic may contain even more antioxidants than regular garlic.
Peppermint:
Peppermint offers benefits to the respiratory system, including for coughs, colds, asthma, allergies, and tuberculosis. In terms of digestive health, peppermint oil capsules have been described as “the drug of first choice” in IBS patients,7 and peppermint oil is an effective alternative to drugs like Buscopan for reducing colonic spasms.8
It may also relax the muscles of your intestines, allowing gas to pass and easing abdominal pain. Try peppermint oil or leaves added to tea for gas relief. Inhaling the peppermint aroma may offer memory enhancement and stress relief, and peppermint oil acts as an expectorant and decongestant, and may help clear your respiratory tract.
Use peppermint essential oil as a cold rub on your chest or inhale it through a vaporizer to help clear nasal congestion and relieve cough and cold symptoms. Peppermint oil may also help relieve tension headache pain. For headache pain, try dabbing a few drops on your wrist or sprinkling a few drops on a cloth, then inhaling the aroma. You can also massage the oil directly onto your temples and forehead. Peppermint essential oil is ideal for muscle and chest rubs, headache pain, dental care, and aromatherapy. You can even add it to your homemade cleaning supplies for extra antimicrobial power and natural fragrance.
When selecting peppermint for your own use, the fresh leaves will impart a superior flavor to dried leaves (such as for use in tea). Look for fresh leaves that are green in color without any dark spots or yellowing. In addition to using fresh mint leaves in tea, you can add them to soups, fruit salad, or gazpacho. Additionally, it is really easy to grow peppermint yourself and the plant works as a highly effective deterrent to many insects that might invade your garden or your home.
Lavender:
Lavender oil is known for its calming and relaxing properties, and has been used aromatherapeutically for alleviating insomnia, anxiety, depression, restlessness, dental anxiety, and stress. It has also been proven effective for nearly all kinds of ailments, from pain to infections.
It is particularly fascinated by its oil potential in fighting antifungal-resistant skin and nail infections. Scientists from the University of Coimbra found that lavender oil is lethal to skin-pathogenic strains known as dermatophytes, as well as various Candida species. Lavender oil can also be used to:
Relieve pain. It can ease sore or tense muscles, joint pain and rheumatism, sprains, backache, and lumbago. Simply massage a small amount of lavender oil onto the affected area. Lavender oil may also help lessen pain following needle insertion.
Treat various skin disorders like acne, psoriasis, eczema, and wrinkles. It also helps form scar tissues, which may be essential in healing wounds, cuts, and burns. Lavender can also help soothe insect bites and itchy skin (lavender oil can help ward off mosquitoes and moths. It is actually used as an ingredient in some mosquito repellents).
Keep your hair healthy. It helps kill lice, lice eggs, and nits. The Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database (NMCB) says that lavender is possibly effective for treating alopecia areata (hair loss), boosting hair growth by up to 44 percent after just seven months of treatment.11
Improve your digestion. This oil helps stimulate the mobility of your intestine and stimulates the production of bile and gastric juices, which may help treat stomach pain, indigestion, flatulence, colic, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Relieve respiratory disorders. Lavender oil can help alleviate respiratory problems like colds and flu, throat infections, cough, asthma, whooping cough, sinus congestion, bronchitis, tonsillitis, and laryngitis. It can be applied on your neck, chest, or back, or inhaled via steam inhalation or through a vaporizer.
Stimulate urine production, which helps restore hormonal balance, prevent cystitis (inflammation of the urinary bladder), and relieve cramps and other urinary disorders.
Improve your blood circulation. It helps lower elevated blood pressure levels and can be used for hypertension.
Thyme:
Thyme is a fragrant herb that makes a wonderful addition to your cooking, in part because it is rich in antioxidants. Thyme contains health-boosting flavonoids including apigenin, naringenin, luteolin, and thymonin, and has been shown to protect and increase the percentage of healthy fats found in cell membranes. As reported by the George Mateljan Foundation:12 “In particular, the amount of DHA (docosahexaenoic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid) in brain, kidney, and heart cell membranes was increased after dietary supplementation with thyme.”
Thyme is also nutrient dense, containing vitamin C, vitamin A, iron, manganese, copper, and dietary fiber. When used in cooked dishes, thyme may also help inhibit glycation and the formation of dangerous advanced glycation (meaning glucose broken down) end products (AGEs) in your food, making thyme a potential preventer of heart disease and premature aging. Due to thyme oil’s antibacterial, antispasmodic, anti-rheumatic, expectorant, hypertensive, and calming properties, it also has a long list of topical uses, including:
Home remedy – Thyme oil is used to relieve and treat problems like gout, arthritis, wounds, bites, and sores, water retention, menstrual and menopausal problems, nausea and fatigue, respiratory problems (like colds), skin conditions (oily skin and scars), athlete’s foot, hangovers, and even depression.
Aromatherapy oil – The oil can be used to stimulate the mind, strengthen memory and concentration, and calm the nerves.
Hair product – It is said that thyme oil can prevent hair loss. It is used as a treatment for the scalp and is added to shampoos and other hair products.
Skin product – Thyme oil can help tone aged skin and prevent acne outbreaks.
Mouthwashes and herbal rinses – Like peppermint, wintergreen, and eucalyptus oils, thyme oil is used to improve oral health.
Insecticide/insect repellent – Thyme oil can keep insects and parasites like mosquitoes, fleas, lice, and moths away.
Chamomile:
Chamomile is most popular in tea form for use to calm upset stomach and help support restful sleep. Germany’s Commission E (a government organization) has even approved the use of chamomile for reducing swelling on your skin and fighting bacteria. Chamomile is a powerful anti-inflammatory that also has antibacterial, anti-spasmodic, anti-allergenic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. It is used to treat psoriasis, eczema, chickenpox, diaper rash, slow-healing wounds, abscesses, and gum inflammation, and according to Herb Wisdom may also be useful for the following conditions:
The oil serves many medicinal purposes, but one of the best-documented uses is for relaxation. The oil has a calming effect on people, and can be used to help induce sleep, ease frayed nerves, and promote a general sense of calmness and well being. It is great for those with nervousness or anxiety problems.
Aside from having mental calming properties, chamomile is also good at relaxing sore muscles and tight joints.
It can ease menstrual cramps and back aches, as well as relax the digestive system to ease upset stomach or indigestion issues.
When applied topically to the skin, it soothes redness and irritation. For this reason, it is a common ingredient in skincare. It also eliminates itchiness and is good for those with allergic reactions. Sometimes chamomile is used on rashes. Because of its anti-inflammatory properties, it can work to take down swelling caused by rashes or skin irritants.
Dandelion:
Dandelion, a plant, has traditionally been used as a liver tonic, useful for detoxification and improving liver function. Dandelion is known as a stimulant that is typically used for kidney and liver disorders. It is also traditionally used to reduce the side effects of prescription drugs, as well as to treat infections, gallbladder problems, water retention and swelling.15 Dandelion greens, which you can prepare simply by blanching them in boiling water for 20 seconds to help remove their bitter flavor (they can also be added to vegetable juice), contain many nutrients, including vitamin C, vitamin B6, thiamin, riboflavin, calcium, iron, potassium, and manganese. They are a particularly good source of vitamin A and may also have cancer fighting properties.
So believe it or not plants enhance our lives and with technology it will further expand in helping human lives.


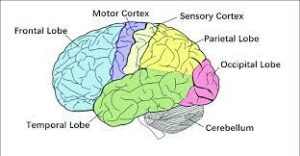
 The Motor Cortex
The Motor Cortex