Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis may include:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- A dry cough
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Aching muscles and joints
- Widening and rounding of the tips of the fingers or toes (clubbing)
The course of pulmonary fibrosis — and the severity of symptoms — can vary considerably from person to person. Some people become ill very quickly with severe disease. Others have moderate symptoms that worsen more slowly, over months or years.
Some people may experience a rapid worsening of their symptoms (acute exacerbation), such as severe shortness of breath, that may last for several days to weeks. People who have acute exacerbations may be placed on a mechanical ventilator. Doctors may also prescribe antibiotics, corticosteroid medications or other medications to treat an acute exacerbation.
Complications
Complications of pulmonary fibrosis may include:
- High blood pressure in your lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Unlike systemic high blood pressure, this condition affects only the arteries in your lungs. It begins when the smallest arteries and capillaries are compressed by scar tissue, causing increased resistance to blood flow in your lungs.This in turn raises pressure within the pulmonary arteries and the lower right heart chamber (right ventricle). Some forms of pulmonary hypertension are serious illnesses that become progressively worse and are sometimes fatal.
- Right-sided heart failure (cor pulmonale). This serious condition occurs when your heart’s lower right chamber (ventricle) has to pump harder than usual to move blood through partially blocked pulmonary arteries.
- Respiratory failure. This is often the last stage of chronic lung disease. It occurs when blood oxygen levels fall dangerously low.
- Lung cancer. Long-standing pulmonary fibrosis also increases your risk of developing lung cancer.
- Lung complications. As pulmonary fibrosis progresses, it may lead to complications such as blood clots in the lungs, a collapsed lung or lung infections.
Diagnosis
To diagnose your condition, your doctor may review your medical and family history, discuss your signs and symptoms, review any exposure you’ve had to dusts, gases and chemicals, and conduct a physical exam. During the physical exam, your doctor will use a stethoscope to listen carefully to your lungs while you breathe. He or she may also suggest one or more of the following tests.
Imaging tests
- Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray shows images of your chest. This may show the scar tissue typical of pulmonary fibrosis, and it may be useful for monitoring the course of the illness and treatment. However, sometimes the chest X-ray may be normal, and further tests may be required to explain your shortness of breath.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan. CT scanners use a computer to combine X-ray images taken from many different angles to produce cross-sectional images of internal structures in the body. A high-resolution CT scan can be particularly helpful in determining the extent of lung damage caused by pulmonary fibrosis. Also, some kinds of fibrosis have characteristic patterns.
- Echocardiogram. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to visualize the heart. It can produce still images of your heart’s structures, as well as videos that show how your heart is functioning. This test can evaluate the amount of pressure occurring in the right side of your heart.
Lung function tests
- Pulmonary function testing. Several types of pulmonary function tests may be conducted. In a test called spirometry, you exhale quickly and forcefully through a tube connected to a machine. The machine measures how much air your lungs can hold and how quickly you can move air in and out of your lungs. Other tests may be conducted to measure your lung volumes and diffusing capacity.
- Pulse oximetry. This simple test uses a small device placed on one of your fingers to measure the oxygen saturation in your blood. Oximetry can serve as a way to monitor the course of the disease.
- Exercise stress test. An exercise test on a treadmill or stationary bike may be used to monitor your lung function when you’re active.
- Arterial blood gas test. In this test, your doctor tests a sample of your blood, usually taken from an artery in your wrist. The oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the sample are then measured.
Tissue sample (biopsy)
If other tests haven’t diagnosed the condition, doctors may need to remove a small amount of lung tissue (biopsy). The biopsy is then examined in a laboratory to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis or rule out other conditions. The tissue sample may be obtained in one of these ways:
- Bronchoscopy. In this procedure, your doctor removes very small tissue samples — generally no larger than the head of a pin — using a small, flexible tube (bronchoscope) that’s passed through your mouth or nose into your lungs. The tissue samples are sometimes too small for an accurate diagnosis. The biopsy may also be used to rule out other conditions.The risks of bronchoscopy are generally minor and might include a temporary sore throat or discomfort in your nose from the passage of the bronchoscope. However, serious complications can include bleeding or a deflated lung.During bronchoscopy, your doctor may conduct an additional procedure called bronchoalveolar lavage. In this procedure, your doctor injects salt water through a bronchoscope into a section of your lung, and then immediately suctions it out. The solution that’s withdrawn contains cells from your air sacs.Although bronchoalveolar lavage samples a larger area of the lung than other procedures do, it may not provide enough information to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis. It might also be used to rule out other conditions.
- Surgical biopsy. Although a surgical biopsy is more invasive and has potential complications, it may be the only way to obtain a large enough tissue sample to make an accurate diagnosis. This procedure may be done as a minimally invasive surgery, called video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), or as an open surgery (thoracotomy).During VATS, your surgeon inserts surgical instruments and a small camera through two or three small incisions between your ribs. The camera allows your surgeon to view your lungs on a video monitor while removing tissue samples from your lungs. This procedure is performed after you’ve been given a general anesthetic, so you’ll be asleep during the procedure.During open surgery (thoracotomy), a surgeon removes a lung sample through an incision in the chest between your ribs. The procedure takes place after you’ve been given a general anesthetic.
Blood tests
Doctors may also order blood tests to evaluate your liver and kidney function, and to test for and rule out other conditions.
Treatments
The lung scarring that occurs in pulmonary fibrosis can’t be reversed, and no current treatment has proved effective in stopping progression of the disease. Some treatments may improve symptoms temporarily or slow the disease’s progression. Others may help improve quality of life. Doctors will evaluate the severity of your condition to determine the most appropriate treatment for your condition.
Medications
Your doctor may recommend newer medications, including pirfenidone (Esbriet) and nintedanib (Ofev). These medications may help slow the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Both medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Additional medications and new formulations of these medications are being developed but have not yet been FDA approved.
Nintedanib can cause side effects such as diarrhea and nausea. Side effects of pirfenidone include rash, nausea and diarrhea.
Researchers continue to study medications to treat pulmonary fibrosis.
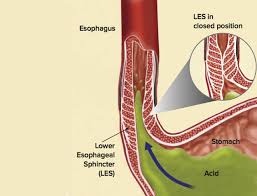
Doctors may recommend anti-acid medications to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a digestive condition that commonly occurs in people with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Oxygen therapy
Using oxygen can’t stop lung damage, but it can:
- Make breathing and exercise easier
- Prevent or lessen complications from low blood oxygen levels
- Reduce blood pressure in the right side of your heart
- Improve your sleep and sense of well-being
You may receive oxygen when you sleep or exercise, although some people may use it all the time. Some people carry a canister of oxygen, making them more mobile.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation can help you manage your symptoms and improve your daily functioning. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs focus on:
- Physical exercise to improve your endurance
- Breathing techniques that may improve lung efficiency
- Nutritional counseling
- Counseling and support
- Education about your condition
Lung transplant
Lung transplantation may be an option for people with pulmonary fibrosis. Having a lung transplant can improve your quality of life and allow you to live a longer life. However, a lung transplant can involve complications such as rejection and infection. Your doctor may discuss with you if a lung transplant may be appropriate for your condition.