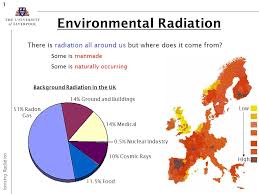
Radon is a naturally occurring gas that seeps out of rocks and soil. Radon comes from uranium that has been in the ground since the time the earth was formed, and the rate of radon seepage is very variable, partly because the amounts of uranium in the soil vary considerably. Radon flows from the soil into outdoor air and also into the air in homes from the movement of gases in the soil beneath homes. Outside air typically contains very low levels of radon, but it builds up to higher concentrations indoors when it is unable to disperse. Some underground mines, especially uranium mines, contain much higher levels of radon.
Radon is present outdoors and indoors. It is normally found at very low levels in outdoor air and in drinking water from rivers and lakes. It can be found at higher levels in the air in houses and other buildings, as well as in water from underground sources, such as well water.
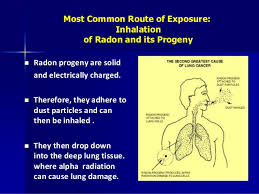
Radon breaks down into solid radioactive elements called radon progeny (such as polonium-218, polonium-214, and lead-214). Radon progeny can attach to dust and other particles and can be breathed into the lungs. As radon and radon progeny in the air break down, they give off radiation that can damage the DNA inside the body’s cells.
How are people exposed to radon?
1-At home and in other buildings.
For both adults and children, most exposure to radon comes from being indoors in homes, offices, schools, and other buildings. The levels of radon in homes and other buildings depend on the characteristics of the rock and soil in the area. As a result, radon levels vary greatly in different parts of the United States, sometimes even within neighborhoods. Elevated radon levels have been found in every state.
Radon gas given off by soil or rock can enter buildings through cracks in floors or walls; construction joints; or gaps in foundations around pipes, wires, or pumps. Radon levels are usually highest in the basement or crawl space. This level is closest to the soil or rock that is the source of the radon. Therefore, people who spend much of their time in basement rooms at home or at work have a greater risk for being exposed.
Small amounts of radon can also be released from the water supply into the air. As the radon moves from the water to air, it can be inhaled. Water that comes from deep, underground wells in rock may have higher levels of radon, whereas surface water (from lakes or rivers) usually has very low radon levels. For the most part, water does not contribute much to overall exposure to radon.
Radon exposure can also occur from some building materials if they are made from radon-containing substances. Almost any building material made from natural substances, including concrete and wallboard, may give off some level of radon. In most cases these levels are very low, but in a few instances these materials may contribute significantly to radon exposure.
Some granite countertops may expose people to different levels of radon. Most health and radiation experts agree that while a small portion of granite countertops might give off increased levels of radon, most countertops give off extremely low levels.
According to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), it’s very unlikely that a granite countertop in a home would increase the radiation level above the normal, natural background level that comes from nearby soil and rocks. Still, people concerned about radon from countertops and from other household sources can test these levels using home detection kits or can hire a professional to do the testing (see the section “How can I avoid exposure to radon?”).
According to the EPA, the average indoor radon level is about 1.3 picocuries per liter (pCi/L). People should take action to lower radon levels in the home if the level is 4.0 pCi/L or higher. The EPA estimates that nearly 1 out of every 15 homes in the United States has elevated radon levels.
Outdoors, radon generally disperses and does not reach high levels. Average levels of radon outdoors, according to the EPA, are about 0.4 pCi/L.
2-At certain jobs
In the workplace, people working underground, such as some types of miners, are among the most likely to be exposed to high levels of radon. High death rates from lung problems among miners in some parts of the world were first noted hundreds of years ago, long before people knew what radon was. Studies of radon-exposed miners during the 1950s and 1960s confirmed the link between radon exposure and lung cancer.
Higher levels of radon exposure are also more likely for people who work in uranium processing factories or who come in contact with phosphate fertilizers, which may have high levels of radium (an element that can break down into radon).
Does radon cause cancer?
Being exposed to radon for a long period of time can lead to lung cancer. Radon gas in the air breaks down into tiny radioactive elements (radon progeny) that can lodge in the lining of the lungs, where they can give off radiation. This radiation can damage lung cells and eventually lead to lung cancer.
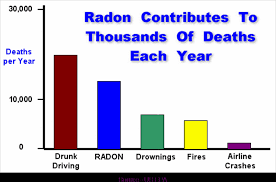
Cigarette smoking is by far the most common cause of lung cancer in the United States, but radon is the second leading cause. Scientists estimate that about 20,000 lung cancer deaths per year are related to radon.
Exposure to the combination of radon gas and cigarette smoke creates a greater risk for lung cancer than either factor alone. Most radon-related lung cancers develop in smokers. However, radon is also thought to cause a significant number of lung cancer deaths among non-smokers in the United States each year.
Although radon is chemically inert and electrically uncharged, it is radioactive, which means that radon atoms in the air can spontaneously decay, or change to other atoms. When the resulting atoms, called radon progeny, are formed, they are electrically charged and can attach themselves to tiny dust particles in indoor air. These dust particles can easily be inhaled into the lung and can adhere to the lining of the lung. The deposited atoms decay, or change, by emitting a type of radiation called alpha radiation, which has the potential to damage cells in the lung. Alpha radiations can disrupt DNA of these lung cells. This DNA damage has the potential to be one step in a chain of events that can lead to cancer. Alpha radiations travel only extremely short distances in the body. Thus, alpha radiations from decay of radon progeny in the lungs cannot reach cells in any other organs, so it is likely that lung cancer is the only potentially important cancer hazard posed by radon.
For centuries, it has been known that some underground miners suffered from higher rates of lung cancer than the general population. In recent decades, a growing body of evidence has causally linked their lung cancers to exposure to high levels of radon and also to cigarette smoking. The connection between radon and lung cancer in miners has raised concern that radon in homes might be causing lung cancer in the general population, although the radon levels in most homes are much lower than in most mines. The National Research Council study, which has been carried out by the sixth Committee on Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) VI, has used the most recent information available to estimate the risks posed by exposure to radon in homes.
You can’t see, smell or taste radon, but it could be present at a dangerous level in your home. Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer deaths among nonsmokers in America and claims the lives of about 21,000 Americans each year. In fact, the EPA and the U.S. Surgeon General urge all Americans to protect their health by testing their homes, schools and other buildings for radon.
Exposure to radon is a preventable health risk and testing radon levels in your home can help prevent unnecessary exposure. If a high radon level is detected in your home, you can take steps to fix the problem to protect yourself and your family.
Radon, being naturally occurring, cannot be entirely eliminated from our homes. Of the deaths that attributes to radon (both independently and through joint action with smoking), perhaps one-third could be avoided by reducing radon in homes where it is above the “action guideline level” of 148 Bqm-3 (4 pCiL-1) to below the action levels recommended by the Environmental Protection Agency.4
The risk of lung cancer caused by smoking is much higher than the risk of lung cancer caused by indoor radon. Most of the radon-related deaths among smokers would not have occurred if the victims had not smoked. Furthermore, there is evidence for a synergistic interaction between smoking and radon.