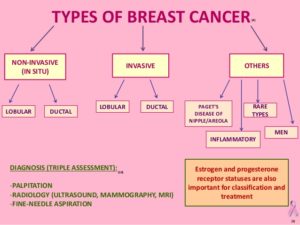
There are many types of breast cancer. The most common types are ductal carcinoma in situ, or invasive ductal carcinoma, and invasive lobular carcinoma.
When a biopsy is done to find out the specific type of breast cancer, the pathologist will also check if the cancer has spread into the surrounding tissues. The following terms are used to describe the extent of the cancer:
- In situ breast cancers have not spread.
- Invasive or infiltrating cancers have spread (invaded) into the surrounding breast tissue.
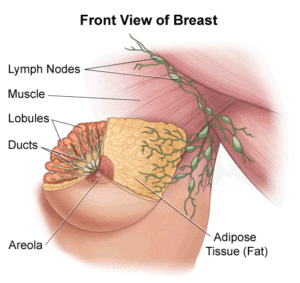
The type of breast cancer is determined by the specific cells in the breast that are affected. Most breast cancers are carcinomas. Carcinomas are tumors that start in the epithelial cells that line organs and tissues throughout the body. Sometimes, an even more specific term is used. For example, most breast cancers are a type of carcinoma called adenocarcinoma, which starts in cells that make up glands (glandular tissue). Breast adenocarcinomas start in the ducts (the milk ducts) or the lobules (milk-producing glands).
There are other, less common, types of breast cancers, too, such as sarcomas, phyllodes, Paget disease, and angiosarcomas which start in the cells of the muscle, fat, or connective tissue.
Sometimes a single breast tumor can be a combination of different types. And in some very rare types of breast cancer, the cancer cells may not form a lump or tumor at all.
Common kinds of breast cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are carcinomas, and are named based on where they form and how far they have spread.
These general kinds of breast cancer below can be further described with the terms outlined above.
In situ cancers
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS; also known as intraductal carcinoma) is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) may also be called lobular neoplasia. This breast change is not a cancer, though the name can be confusing. In LCIS, cells that look like cancer cells are growing in the lobules of the milk-producing glands of the breast, but they don’t grow through the wall of the lobules.
Invasive (infiltrating) breast cancer
Breast cancers that have spread into surrounding breast tissue are known as invasive breast cancer. There are many different kinds of invasive breast cancer, but the most common are called invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Less common types of breast cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer
This is an uncommon type of invasive breast cancer. It accounts for about 1% to 5% of all breast cancers.
Paget disease of the nipple
This starts in the breast ducts and spreads to the skin of the nipple and then to the areola(the dark circle around the nipple). It is rare, accounting for only about 1-3% of all cases of breast cancer.
Phyllodes tumor
Phyllodes tumors are rare breast tumors. They develop in the connective tissue (stroma) of the breast, in contrast to carcinomas, which develop in the ducts or lobules. Most are benign, but there are others that are malignant (cancer).
Angiosarcoma
Sarcomas of the breast are rare making up less than 1% of all breast cancers. Angiosarcoma starts in cells that line blood vessels or lymph vessels. It can involve the breast tissue or the skin of the breast. Some may be related to prior radiation therapy in that area.