Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia is named for the Swedish physician Jan Gosta Waldenström (1906-1996), who in 1944 identified a rare condition in which two patients experienced a thickening of their blood serum, bleeding of the mouth, nose, and blood vessels of the retina, low red blood cell and platelet counts, high erythrocyte sedimentation rates, and lymph node involvement. Bone marrow biopsies showed an excess of lymphoid cells and bone X-rays were normal, excluding a diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Both patients also had a large amount of a single unknown blood protein with an extremely high molecular weight, a “macro” globulin. We now know this globulin as IgM.
The over-production of IgM may also cause many of the symptoms associated with the disease. IgM is a large antibody and tends to make the blood thicker than normal, a condition called hyperviscosity. Unlike normal antibodies that fight infection, the IgM produced by WM cells has no useful function. Sometimes the IgM may incorrectly recognize the body’s tissues as “foreign” and attach to them, causing inflammation and injury.
What are the symptoms of this condition?
People with Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia may experience the following symptoms or signs. Sometimes, people with Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia do not have any of these changes. Or, the cause of a symptom may be a different medical condition that is not cancer.
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Enlarged lymph nodes or spleen
- Numbness, weakness or other nervous system problems, pain in the hands or feet, sometimes called peripheral neuropathy
- Abdominal swelling and diarrhea
- Weakness and shortness of breath
- Infections
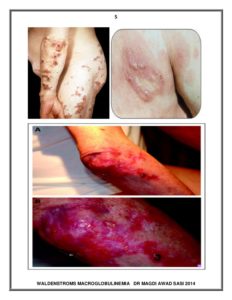
- Raised pink or flesh-colored lesions on the skin
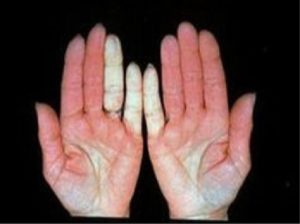
- Changes in the color of the fingertips when exposed to cold
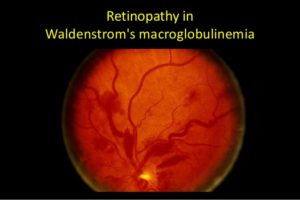
- Changes in vision, which may include blurry vision or “double” vision
May signal a more aggressive cancer:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Unexplained fever
- Heavy sweating, especially at night, which may drench one’s nightclothes or sheets on the bed.
- Severe and/or extensive skin itchiness
How is it diagnosed?
For starters LAB TESTS:
WM might be suspected if your doctor finds you have low blood cell counts or unusual protein levels on blood tests. If so, your doctor may order a blood test called serum protein electrophoresis to find out what the abnormal proteins are. It is usually only after these tests are done that a biopsy of either the bone marrow or a lymph node is considered.
Simply a CBC Complete blood count, that measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. If lymphoma cells occupy too much of the bone marrow, these levels will be low.
Quantitative Immunoglobulins – This test measures the levels of the different antibodies (immunoglobulins) in the blood – IgA, IgE, IgG, and IgM – to see if any are abnormally high or low. In WM the level of IgM is high but the IgG level is often low.
Electrophoresis
The abnormal immunoglobulin made in WM is an IgM antibody. This antibody is monoclonal, meaning that it is many copies of the exact same antibody. Serum protein electrophoresi s (SPEP) is a test that measures the total amount of immunoglobulins in the blood and finds any monoclonal immunoglobulin. Another test, such as immunofixation or immunoelectrophoresis, is then used to determine the type of antibody that is abnormal (IgM or some other type).
Finding a monoclonal IgM antibody in the blood is needed to diagnose WM. This abnormal protein in WM is known by many different names, including monoclonal immunoglobulin M, IgM protein, IgM spike, IgM paraprotein, M protein, and M-spike. High levels of other types of monoclonal immunoglobulins, like IgA or IgG, are seen in different disorders (like multiple myeloma and some other lymphomas).
Sometimes pieces of the IgM protein are excreted by the kidneys into the urine. These proteins can be detected with a test called urine protein electrophoresis (or UPEP).
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of how thick the blood is. If the IgM level is too high, the blood will become thick (viscous) and can’t flow freely (think about pouring honey compared to pouring water).
Cryocrit
This test measures the blood levels of cryoglobulins (proteins that clump together in cool temperatures and can block blood vessels).
Cold agglutinins
Cold agglutinins are antibodies that attack and kill red blood cells, especially at cooler temperatures. These dead cells can then build up and block blood vessels. A blood test can be used to detect these antibodies.
Beta-2 microglobulin (β2M)
This test measures another protein made by the cancer cells in WM. This protein itself doesn’t cause any problems, but it’s a useful indicator of a patient’s prognosis (outlook). High levels of β2M are linked with a worse outlook.
Biopsies
The symptoms of WM and NHL are not distinctive enough for a doctor to know for certain if person has one of them, based on symptoms alone. Most symptoms can also be caused by non-cancerous problems like infections or by other kinds of cancers. Blood tests can help point to the correct diagnosis, but a biopsy (removing samples of affected tissue to look at under a microscope) is the only way to be sure. Several types of biopsies might be used.
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
This is the most important type of biopsy for WM, and is needed to confirm the diagnosis. It can be done at the doctor’s office or at the hospital.
The bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are usually done at the same time. The samples are taken from the back of the pelvic (hip) bone, although in some cases they may be taken from the sternum (breast bone) or other bones.
In bone marrow aspiration, you lie on a table (either on your side or on your belly). The doctor cleans the skin over the hip and then numbs the area and the surface of the bone by injecting a local anesthetic. This may briefly sting or burn. A thin, hollow needle is then inserted into the bone, and a syringe is used to suck out a small amount of liquid bone marrow. Even with the anesthetic, most patients still have some brief pain when the marrow is removed.
A bone marrow biopsy is usually done just after the aspiration. A small piece of bone and marrow is removed with a slightly larger needle that is pushed down into the bone. This may also cause some brief pain.
Once the biopsy is done, pressure is applied to the site to help stop any bleeding. There will be some soreness in the biopsy area when the numbing medicine wears off. Most patients can go home right after the procedure.
The bone marrow samples are then sent to a lab, where they are tested to see if they have lymphoma cells (see below). For a diagnosis of WM, at least 10% of the cells in the bone marrow must be lymphoplasmacytoid lymphoma cells.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy
In an FNA biopsy, the doctor uses a very thin, hollow needle with a syringe to withdraw a small amount of tissue from a tumor or lymph node. This type of biopsy is useful for sampling lymph nodes to see if they are enlarged because of cancer or another cause such as infection. FNA can help diagnose some lymphomas, but WM is usually diagnosed with a bone marrow biopsy instead.
For an FNA on an enlarged node near the surface of the body, the doctor can aim the needle while feeling the node. If the enlarged node (or tumor) is deep inside the body, the needle can be guided while it is seen on a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound (see the descriptions of imaging tests later in this section).
The main advantage of FNA is that it does not require surgery and can often be done in a doctor’s office. The main drawback is that in some cases it might not get enough tissue to make a definite diagnosis of lymphoma. However, advances in lab tests (discussed later in this section) and the growing experience of many doctors with FNA have improved the accuracy of this procedure.
Excisional or incisional biopsy
For these types of biopsies, a surgeon cuts through the skin to remove an entire lymph node or tumor (excisional biopsy) or a just a small part of a large tumor or lymph node (incisional biopsy). These biopsies are rarely needed in people with WM because the diagnosis is usually made with a bone marrow biopsy. They are used more often for other types of lymphoma.
If the area to be biopsied is near the skin surface, this can be done using local anesthesia (numbing medicine). If the area is inside the chest or abdomen, general anesthesia or deep sedation is used (where the patient is asleep). These types of biopsies almost always provide enough tissue to diagnose the exact type of lymphoma.
Fat pad fine needle aspiration
This type of biopsy may be used in some people with WM to check for amyloid. In this procedure, a thin, hollow needle with a syringe attached is inserted into an area of fat (usually under the skin of the abdomen/belly). A small amount of fat is removed and sent to the lab for testing.
Lab tests on biopsy specimens
All biopsy specimens are looked at under a microscope by a pathologist – a doctor with special training in using lab tests to diagnose diseases. In some cases, a hematopathologist, a doctor with further training in diagnosing blood and lymph node diseases, might also look at the biopsy. The doctors look at the size and shape of the cells and how the cells are arranged. Sometimes just looking at the cells doesn’t provide a clear answer, so other lab tests are needed.
Immunohistochemistry
In this test, a part of the biopsy sample is treated with special man-made antibodies that attach to cells only if they contain specific molecules. These antibodies cause color changes, which can be seen under a microscope. This test may help tell different types of lymphoma from one another and from other diseases.
Flow cytometry
In this test, cells are treated with special man-made antibodies. Each antibody sticks only to certain types of cells. The cells are then passed in front of a laser beam. If the cells now have antibodies attached to them, the laser will make them give off light, which is measured and analyzed by a computer.
This is the most common test for immunophenotyping – classifying lymphoma cells according to the substances (antigens) on their surfaces. Different types of lymphocytes have different antigens on their surface. These antigens also change as each cell matures.
This test can help show whether a lymph node is swollen because of lymphoma, some other cancer, or a non-cancerous disease. It has become very important in helping doctors determine the exact type of lymphoma so they can select the best treatment.
Cytogenetics
Doctors use this technique to look at the chromosomes (long strands of DNA) inside lymphoma cells. Cells (usually from the bone marrow) are first grown in the lab. Then the chromosomes are stained and looked at under a microscope. Because it takes time for the cells to start dividing, this test can take weeks.
In some lymphomas, the cells may have too many chromosomes, too few chromosomes, missing parts of chromosomes (called deletions), or other abnormalities. These changes can help identify the type of lymphoma. In WM, deletions are the most common type of chromosome change.
Molecular genetic tests
Molecular tests such as fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are not usually needed to diagnose WM, but they are sometimes used to diagnose other types of NHL. These tests look at the cells’ DNA without having to grow the cells in the lab first. The tests can give results in less time than cytogenetics and can be done on cells from different sources (like lymph nodes, blood, and bone marrow). They are generally used to look for specific chromosome or gene changes, not just any change.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests use x-rays, magnetic fields, sound waves, or radioactive particles to produce pictures of the inside of the body. These tests are not needed to diagnose WM, but one or more of them might be done to help show the extent of the disease in the body.
Chest x-ray
An x-ray might be done to look at the chest for enlarged lymph nodes.
Computed tomography (CT) scan
The CT scan uses x-rays to make detailed cross-sectional images of your body. Unlike a regular x-ray, CT scans can show the detail in soft tissues (such as internal organs). This scan can help show if any lymph nodes or organs in your body are enlarged. CT scans are useful for looking for signs of lymphoma in the chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
Before the test, you may be asked to drink a contrast solution and/or get an intravenous (IV) injection of a contrast dye to better outline abnormal areas in the body. You might need an IV line through which the contrast dye is injected. The injection can cause some flushing (a feeling of warmth, especially in the face). Some people are allergic to the dye and get hives or a flushed feeling or, rarely, have more serious reactions like trouble breathing and low blood pressure. Be sure to tell the doctor if you have any allergies (especially iodine or shellfish) or have ever had a reaction to any contrast material used for x-rays. Medication can be given to help prevent and treat allergic reactions.
A CT scanner has been described as a large donut, with a narrow table that slides in and out of the middle opening. You need to lie still on the table while the scan is being done. CT scans take longer than regular x-rays, and some people might feel a bit confined by the ring while the pictures are being taken.
CT-guided needle biopsy: CT scans can also be used to guide a biopsy needle into a suspicious area. For this procedure, the patient lies on the CT scanning table while the doctor moves a biopsy needle through the skin and toward the area. CT scans are repeated until the needle is in the right place. A biopsy sample is then removed and sent to the lab to be looked at under a microscope.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
Like CT scans, MRI scans make detailed images of soft tissues in the body. But MRI scans use radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays. This test is rarely used in WM, but if your doctor is concerned about the brain or spinal cord, MRI is very useful for looking at these areas.
Sometimes a contrast material is injected into a vein to make some structures clearer. This contrast is not the same as the contrast used for CT scans, but allergic reactions can still occur. Again, medicine can be given to prevent and treat allergic reactions.
MRI scans take longer than CT scans – often up to an hour. You may have to lie inside a narrow tube, which is confining and can upset some people. Newer, more open MRI machines might be another option. The machine makes loud buzzing and clicking noises that some people find disturbing. Some places provide headphones or earplugs to help block this noise out.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves and their echoes to make pictures of internal organs or masses.
Ultrasound can be used to look at lymph nodes near the surface of the body or to look inside your abdomen for enlarged lymph nodes or organs such as the liver, spleen, and kidneys. (It can’t be used to look at organs or lymph nodes in the chest because the ribs block the sound waves.) It is sometimes used to help guide a biopsy needle into an enlarged lymph node.
For this test, a small, microphone-like instrument called a transducer is placed on the skin (which is first lubricated with a gel). It gives off sound waves and picks up the echoes as they bounce off the organs. A computer then converts the echoes into a black and white image on a screen.
This is an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation. For most ultrasounds, you simply lie on a table, and a technician moves the transducer over the part of your body being looked at.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
For a PET scan, a radioactive sugar (known as FDG) is injected into the blood. (The amount of radioactivity used is very low and will pass out of the body in a day or so.) Because cancer cells in the body grow quickly, they absorb large amounts of the sugar. You then lie on a table in the PET scanner for about 30 minutes while a special camera creates a picture of areas of radioactivity. The picture is not detailed like a CT or MRI scan, but it can provide helpful informa- tion about your whole body.
PET scans can help tell if an enlarged lymph node contains lymphoma or not. It can also help spot small areas that might be lymphoma, even if the area looks normal on a CT scan. These tests can be used to tell if a lymphoma is responding to treatment. They can also be used after treatment to help decide whether an enlarged lymph node still contains lymphoma or is merely scar tissue.
Many medical centers now use a machine that combines the PET scan with a CT scan (PET/CT scan). This lets the doctor compare areas of higher radioactivity on the PET scan with the more detailed appearance of that area on the CT scan.
Questions you might be thinking and would like answered.
Should I get a second opinion? If so when?
What treatments are approved for WM?