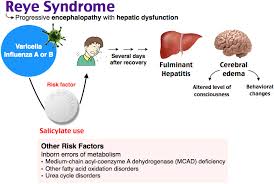

What Causes It?
Doctors don’t fully understand what causes Reye’s syndrome. They do know that some people are prone to get it when they take aspirin for a virus.
Others have a greater chance of getting it if they:
- Have a disorder that affects how their bodies break down fatty acids
- Have been exposed to certain toxins, including paint thinners and products to kill insects and weeds
When Reye’s syndrome strikes, cells throughout your body become swollen and build up fats. In turn, your blood sugar levels drop. Ammonia and acid levels in the blood rise. These changes can hit many organs, such as the brain and liver, where severe swelling can occur.
Symptoms
The signs of Reye’s typically appear 3 to 5 days after the start of a viral infection.
- Personality changes (more irritable or aggressive)
- Confusion or hallucinations
- Weakness or inability to move arms or legs
- Seizure or convulsions
- Extreme tiredness
- Loss of consciousness
Reye’s can be life-threatening. You should call 911 if you see these severe symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment is crucial.
The syndrome can be mistaken for other conditions, including meningitis (a swelling of membranes covering the brain and spinal cord), a diabetes reaction, or poisoning.
Diagnosis
Doctors don’t have a specific test for Reye’s. They usually do urine and blood tests. They also screen for disorders involving fatty acids.
Other tests may include:
- Spinal taps (a needle is inserted into a space below the end of the spinal cord to collect fluid)
- Liver biopsies (a needle is pushed through the abdomen into the liver to get a sample of tissue)
- Skin biopsies (a doctor scrapes a small skin sample to test)
- CT or MRI scans (which can also rule out other problems)
Is There a Treatment?
There’s no single treatment that will stop Reye’s syndrome, but doctors can do some things to make sure it is managed. They can also try to prevent more severe symptoms and see that brain swelling is held down. These steps include:
- Intravenous (IV) fluids that includes glucose and an electrolyte solution may be given through an intravenous (IV) line.
- Diuretics to help your body get rid of salt and water (and stop swelling)
- Medications to prevent bleeding
- Vitamin K, plasma, and platelets (tiny blood cells that help form clots) in instances of liver bleeding
- Cooling blankets. This intervention helps maintain internal body temperature at a safe level.