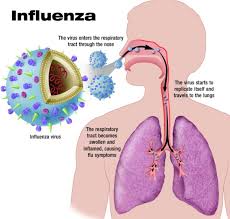
Influenza (flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild to severe illness. Serious outcomes of flu infection can result in hospitalization or death. Some people, such as older people, young children, and people with certain health conditions, are at high risk of serious flu complications. There are two main types of influenza (flu) virus: Types A and B. The influenza A and B viruses that routinely spread in people (human influenza viruses) are responsible for seasonal flu epidemics each year.
Influenza virus infection is so common that the number of people infected each season can only be estimated. These statistical estimations are based on CDC-measured flu hospitalization rates that are adjusted to produce an estimate of the total number of influenza infections in the United States for a given flu season.
The estimates for the number of infections are then divided by the census population to estimate the seasonal incidence (or attack rate) of influenza.
Does seasonal incidence of influenza change based on the severity of flu season?
Yes. The proportion of people who get sick from flu varies.
You may be able to spread flu to someone else before you know you are sick, as well as while you are sick. It spreads in the following time:
- People with flu are most contagious in the first 3-4 days after their illness begins.
- Some otherwise healthy adults may be able to infect others beginning 1 day before symptoms develop and up to 5 to 7 days after becoming sick.
- Some people, especially young children and people with weakened immune systems, might be able to infect others for an even longer time.
Signs and Symptoms:
Flu is different from a cold. Flu usually comes on suddenly. People who have flu often feel some or all of these symptoms:
- fever* or feeling feverish/chills
- cough
- sore throat
- runny or stuffy nose
- muscle or body aches
- headaches
- fatigue (tiredness)
- some people may have vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in children than adults.
*It’s important to note that not everyone with flu will have a fever.
How the flu is treated:
One is through PREVENTION=Get Vaccinated, you can’t get it after you have it.
Usually, you’ll need nothing more than bed rest and plenty of fluids to treat the flu. But if you have severe infection or are at higher risk for complications, your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medication, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu), zanamivir (Relenza), peramivir (Rapivab) or baloxavir (Xofluza). These drugs may shorten your illness by a day or so and help prevent serious complications.
Oseltamivir is an oral medication. Zanamivir is inhaled through a device similar to an asthma inhaler and shouldn’t be used by anyone with certain chronic respiratory problems, such as asthma and lung disease.
Antiviral medication side effects may include nausea and vomiting. These side effects may be lessened if the drug is taken with food.
Most circulating strains of influenza have become resistant to amantadine and rimantadine (Flumadine), which are older antiviral drugs that are no longer recommended.