Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a rare and serious condition that disrupts your blood flow. It is a blood clotting disorder that can turn into uncontrollable bleeding. It is sometimes called consumption coagulopathy.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a rare, life threatening condition. It’s also sometimes called consumption coagulopathy.
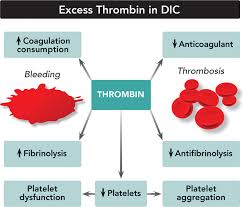
In the early stages of the condition, DIC causes your blood to clot excessively. As a result, blood clots may reduce blood flow and block blood from reaching bodily organs.
As the condition progresses, platelets and clotting factors — the substances in your blood responsible for forming clots — are used up. When this happens, you may begin to experience excessive bleeding.
DIC is a serious condition that can lead to death. If you have bleeding that won’t stop, go to an emergency room or call 911 for prompt medical treatment.
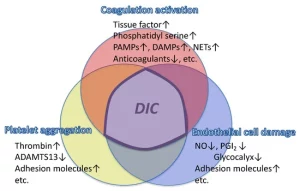
Etiology of DIC (There is more than one cause factor):
1-Acute obstetrical hemorrhage is one of the leading causes for DIC in pregnancy and is one of the most avoidable etiologies of maternal death. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a rare, life threatening condition. It’s also sometimes called consumption coagulopathy.
2-Disseminated intravascular coagulation has been linked to certain medical treatments or conditions. Medical treatments that can cause DIC include:
- Blood transfusion reactions.
- Recent surgery or anesthesia.
3-Medical conditions that can cause DIC include:
- Cancer, especially certain types of leukemia.
- Pancreatitis.
- Blood infections.
- Liver disease.
- Severe tissue injury including burns and head injuries.
- Unformed blood vessels called hemangioma.
What can you do?
Unfortunately, that means there’s very little you can do to prevent DIC. What you can do is to talk to your healthcare provider about DIC so you know what changes in your body might be a sign of it.
If you have DIC, you’re probably already coping with serious medical conditions such as sepsis and cancer, or you’re recovering from serious injuries. Fortunately, early diagnosis and supportive treatment can help to stop the blood clotting or bleeding that DIC causes so that your healthcare providers can focus on treating your underlying illnesses or injuries.
How to manage disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)?
Being diagnosed with disseminated intravascular coagulation means you have another medical concern to manage as you continue the treatment and testing for the medical condition that caused your DIC. Here are some suggestions that might help:
- Take all medicines regularly, as your healthcare provider prescribes. Do not change the amount of your medicine or skip a dose unless they tell you to.
- Ask your provider before taking any over-the-counter products such as pain relievers, vitamins, supplements or herbal remedies.
- Talk with your provider about how often you should schedule office visits and blood tests to monitor the medications you’re taking.
- If you’re taking blood thinners, make sure all your providers know so they can adjust treatment accordingly.
DIC can have serious complications. You should go to the emergency room right away if you have:
- Heavy bleeding that you can’t control.
- Heart attack symptoms-chest pain/discomfort, sudden squeezing of the heart, headache, palpitations, dizziness, SOB or dyspnea, pain down L arm, vision change-one or both eyes, loss of balance, sudden fatigue.
- Stroke symptom-difficulty speaking, change in mental status, sudden confusion, drooping of the mount on one side, one side of the body weak or paralyzed, difficulty eating, aspiration, difficulty walking or standing.