
What is Amyloidosis? Amyloidosis (am-uh-loi-DO-sis) is a rare disease that occurs when a substance called amyloid builds up in your organs. Amyloid is an abnormal protein that is usually produced in your bone marrow and can be deposited in any tissue or organ.
The cause of primary amyloidosis is unknown. The condition is related to abnormal and excess production of antibodies by a type of immune cell called plasma cells. Clumps of abnormal proteins build up in certain organs. This reduces their ability to work correctly.
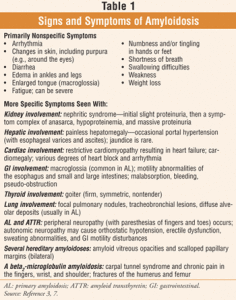
Symptoms depend on the organs affected. Amyloidosis frequently affects the heart, kidneys, liver, spleen, nervous system and digestive tract. Severe amyloidosis can lead to life-threatening organ failure. This disease can affect the tongue, intestines, skeletal and smooth muscles, nerves, skin, ligaments, heart, liver, spleen, and kidneys. Skin changes, such as thickening or easy bruising, and purplish patches around the eyes, difficulty swallowing,
Symptoms include: enlarged tongue, difficulty swallowing, feeling full quickly when eating, and significant weight loss, diarrhea possibly with blood or constipation, abnormal heart rhythm, fatigue, numbness of hands or feet, shortness of breath, hoarseness or changing voice, swelling of your ankles and legs and joint pain.
Amyloid is produced in your bone marrow and can be deposited in any tissue or organ affecting the tissue and organs like stated previously. The specific cause of this condition depends on the type of amyloidosis present.
Unfortunately, there are many different types of amyloidosis. Here are the types:
– Immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis. This is the most common type, can affect your heart, kidneys, skin, nerves and liver. It was previously known as primary amyloidosis. It occurs when your bone marrow produces abnormal antibodies that can’t be broken down. The antibodies are deposited in your tissues as amyloid, interfering with normal function. Most people diagnosed with AL amyloidosis, the most common type, are age 50 or older, although earlier onset can occur. This is hard in preventing this disease from occurring. Nearly 70 percent of people with AL amyloidosis are men.
– AA amyloidosis, mostly affects your kidneys but occasionally your digestive tract, liver or heart. It was previously known as secondary amyloidosis. It occurs along with chronic infectious or inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. One way to prevent this is through good health to prevent chronic infections, possibly rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
– Hereditary (familial) amyloidosis, is an inherited disorder that often affects the liver, nerves, heart and kidneys. One type is caused by a certain amyloid (transthyretin amyloid) that can affect the nervous system or the heart. This is hereditary and unlikely to prevent but see your MD regularly to be checked for it every 6 months or yearly. See what your MD suggests if you know this is in your family. African-Americans have a greater risk of this type than do Caucasians. It is thought to be a significant cause of heart failure in African-American men.
– Dialysis-related amyloidosis, develops when proteins in blood are deposited in joints and tendons which end up causing pain, stiffness and fluid in the joints, as well as carpal tunnel syndrome. This type generally affects people on long-term dialysis. Dialysis can’t always remove large proteins from the blood. If you’re on dialysis, abnormal proteins can build up in your blood and eventually be deposited in tissue. The good news regarding this type of amyloidosis is this condition is less common with modern dialysis techniques.
IN THE END WHAT THIS CONDITION LEAVES AS AN END RESULT TO INTEFERE WITH NORMAL FUNCTION OF TISSUES/ORGANS IN THE HUMAN BODY:
1.) Amyloid can harm the kidneys’ filtering system=our toileting system of the human body which takes toxics out of the bloodstream dumping them into the urinary bladder that our body voids out of the body through urinating. If this organ, the kidneys are affected, this ends up causing protein to leak from your blood into your urine. The kidneys’ ability to remove waste products from your body is lowered, which may eventually lead to kidney failure (if 100% failure occurs now hemodialysis starts causing the amyloidosis to be at risk for just getting worse, see above dialysis-related amyloidosis).
2.) Amyloid can harm the nervous system, which affects our electrical system of the human body. You may experience pain, numbness or tingling of the fingers or numbness, lack of feeling or a burning sensation in your toes or the soles of your feet. If amyloid affects the nerves that control your bowel function, you may experience periods of alternating constipation and diarrhea. Sometimes amyloidosis affects nerves that control blood pressure, and you may experience dizziness or near fainting when standing too quickly, as a result of a drop in your blood pressure due to orthostatic hypotension occurring secondary to the nerves affecting the B/P.
3.) Amyloid if it affects the engine of the human body it will cause reduction of that organ’s function being the heart. It causes your heart’s ability to fill with blood between heartbeats. Less blood is filled up in each chamber of the heart at the normal level an this causes the heart to pump out less cardiac output with each beat, especially the left ventricle of the heart that pumps out oxygenated blood throughout the body. This causes less oxygenated blood to our tissues and like plumbing when the pipes (in this case the arteries with veins) cause back up in the running of blood which go back to the lungs first (does not take long) all the way down to the feet (this takes time). This in the end can make you experience shortness of breath due to fluid build up in the lungs. If amyloidosis affects your heart’s electrical system, your heart rhythm may be disturbed. This can put you into arrhythmias the longer you don’t take care of the situation the worse the rhythm will get.
You may go to your general practitioner first depending on your insurance coverage but if it is questionable or your GP thinks it amyloidosis you should be referred to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist). Be prepared with questions already written out at home when you see your doctor so you don’t walk out of the office knocking your head saying “I forgot to ask him…”. That could be from signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, tests, treatments/medications, etc…
There’s no cure unfortunately for amyloidosis. But treatments can help you manage your symptoms and limit the production of amyloid protein.
Diagnosis and Tests for Amyloidosis:
*1. First your doctor would do a thorough medical exam with blood/urine tests searching for clues of high protein where it shouldn’t belong or certain liver or thyroid abnormal findings. The MD will follow with further diagnostic tooling especially if these findings show up in blood/urine tests. Common blood exams used are BNP (basic natriuretic peptide). BNP is a substance secreted from the ventricles or lower chambers of the heart in response to stress and changes in pressure that occur when to heart failure develops and worsens. The level of BNP in the blood increases when heart failure symptoms worsen, and decreases when heart failure condition is stable. It is not so much elevated over the norm but more with this disease patients the MD will see where the BNP level was at last visit & compare.
Another blood test is troponin and this gets released into the bloodstream when your heart is affected by amyloids.
*2. Second your MD may want to further diagnose for this disease through getting a tissue biopsy where the MD’s intent is to check for signs indicating this is highly possible for amyloidosis. The biopsy could be taken from your abdominal fat, bone marrow, or an organ such as your liver or kidney. Tissue analysis can help determine the type of amyloid deposit.
*3. Imaging Tests. Images taken of the organs that are affected by amloidosis can help the MD establish the intensity or stage your disease is at. There are 2 most commonly imaging tests used and can diagnose the disease early. There is the echocardiogram test, sound wave imaging of the heart, that will be used to assess the size and functioning capability level of the heart. Another test is a MRI of the heart (magnetic residence imaging). Other imaging tests can evaluate the extent of amyloidosis in the liver or spleen.
When the heart chambers become filled with amyloids it thickens the walls of those chambers especially the lower chambers which can be picked up by the echocardiogram through the different angles of sound waves that go via the heart during this exam. Another thing that can be measured through the echocardiogram is your diagnostic function; that represents a measure of how stiff your heart is and how well is your heart actually functioning.
Another technique that can be used is strain imaging. This is also done through echocardiogram. This tells the doctor in more detail how much the muscle fibers in the heart are actually shortening and contracting. It measures certain parts of the heart in actually contracting and function. This is actually better in help diagnosing compared to just looking at ejection fraction, which is the amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle chamber upon contraction of the heart (When he hear lub dub of the heart with a stethoscope that is the heart actually contracting. First the upper chamber on lub is contracting and on dub is the lower chambers contracting). This test is a specializing test and is not widely used but it is available in certain hospitals.
Ending line amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which one or more organ systems in the body accumulate abnormal proteins known as amyloid. The name amyloidosis was first used more than 150 years ago, but cases were described over 300 years ago. However, only in the past ¼ of a century have MD’s understood the specific make up and structure of amyloid proteins. Although amyloidosis is not a cancer but it is a serious condition. It is disabilitating and gets to life threatening. However, growing awareness of the condition seems to be leading to substantial new research and Rx alternatives.
Through “The Amyloidosis Foundation” they provide over the world medical facilities/hospitals that major in this disease.
Hope I have helped you in someway for yourself or family or friend in better understanding about the disease, knowing tests for it, and places majored with this unfortunate disease an expert can treat in a medical facility.