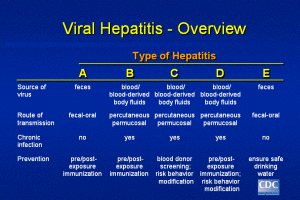
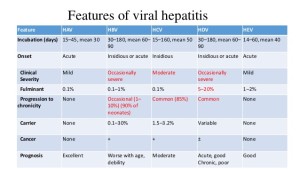
Viral hepatitis, including hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, are distinct diseases that affect the liver and have different hepatitis symptoms and treatments. Other causes of hepatitis include recreational drugs and prescription medications. Hepatitis type is determined by laboratory tests.
HEPATITIS A:
If you have this infection, you have inflammation in your liver that’s caused by a virus. You don’t always get symptoms, but when you do, you might have: Jaundice (yellowing of the skin), Pain in your belly, Loss of appetite, Nausea, Fever, Diarrhea, Fatigue, Loss of weight, fever, sore muscles, **Pain on the right side of the belly, under the rib cage-where your liver is located** (if not a combination of these symptoms).
Children often have the disease with few symptoms.
You can spread the Hepatitis A virus about 2 weeks before your symptoms appear and during the first week they show up, or even if you don’t have any.
How it’s transmitted:
You can catch the disease if you drink water or food that’s been contaminated with the stool of someone with the virus. You can also get infected if you:
-Eat fruits, vegetables, or other foods that were contaminated during handling.
-Eat raw shellfish harvested from water that’s got the virus in it.
-Swallow contaminated food.
Examples: Sometimes a group of people who eat at the same restaurant can get hepatitis A. This can happen when an employee with hepatitis A doesn’t wash his or her hands well after using the bathroom and then prepares food. It can also happen when a food item is contaminated by raw sewage or by an infected garden worker.
-The disease can also spread in day care centers. Children, especially those in diapers, may get stool on their hands and then touch objects that other children put into their mouths. And workers can spread the virus if they don’t wash their hands well after changing a diaper.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Blood tests allow doctors to diagnose it. **It is important to identify the type of hepatitis virus causing the infection to prevent it from spreading and to start the proper treatment. Since this Hepatitis A virus infection is spread through food or water that has been contaminated by the feces (stool) of an infected person.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects?
Usually the virus doesn’t cause any long-term problems or complications. But according to the CDC, 10% to 15% of people with hepatitis A will have symptoms that last a long time or come back over a 6- to 9-month period. In rare situations, some people may have liver failure or need a transplant.
What’s the Treatment?
No treatments can cure the disease. Your doctor may take tests that check your liver function to be sure your body is healing.
Who is at highest risk for this?
-Live with or have sex with someone who’s infected.*
-Travel to countries where hepatitis A is common.*
Remember the people who are also at risk:
-Men who have sex with men*
-People who inject illegal drugs*
-Kids in child care and their teachers*
HEPATITIS B
Hepatitis is a serious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Infection with this virus can cause scarring of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death. What happens to most cases of Hepatitis patients is the adult cases (up to 95%), hepatitis B causes limited infection. Usually people manage to fight off the infection successfully within a few months, developing an immunity that lasts a lifetime. (This means you won’t get the infection again). Blood tests show evidence of this immunity, but no signs of active infection. Unfortunately, this is not true in infants and young children in which 90% of infants and 30% to 50% of children will develop a chronic infection.
Symptoms of acute infection (when a person is first infected with hepatitis) include:
-Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes and/or a brownish or orange tint to the urine)/Unusually light colored stool/Unexplained fatigue that persists for weeks or months/Flu-like symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting/Abdominal Pain
Often, symptoms occur one to six months after exposure, with an average of three month. An estimated 30% of those infected do not have any symptoms at all.
How it’s transmitted:
Hepatitis B is spread in infected blood and other bodily fluids such as semen and vaginal secretions. It is spread in the same way that the virus that causes AIDS (HIV) is spread but hepatitis B is 50 to 100 times more infectious. Most people who are infected with hepatitis B in the U.S. do not know they have it. If you’re pregnant and you’ve got hepatitis B, you could give the disease to your unborn child. If you deliver a baby who’s got it, he needs to get treatment in the first 12 hours after birth.
How it’s diagnosed:
If your doctor suspects that you may have hepatitis B, he or she will perform a complete physical exam and order blood tests to look at the function of your liver. Hepatitis B is confirmed with blood tests that detect the virus.
If your disease becomes chronic, liver biopsies (tissue samples) may be obtained to detect the severity of the disease.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects?
Liver damage if the virus is not taken care will happen with multiple organ crash from putting affect on other organs from doing their jobs.
WHAT’S THE TREATMENT:
Treatment depends on whether you:
-Have been recently infected with the virus (treating acute hepatitis B).*
-Have the symptoms of an acute infection. *
-Have chronic infection (Have had the hepatitis B for a chronic period of time).
-Acute vs Chronic=different RX.*
Acute Hep B. you should get a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and the first of three shots of the hepatitis B Vaccine (What is a PDF document?). It is important to receive this treatment within 7 days after a needle stick and within 2 weeks after sexual contact that may have exposed you to the virus. The sooner you receive treatment after exposure, the better the treatment works.
Regarding Chronic Hep B treatment depends on how active the virus is in your body and your chance of liver damage. The goal of treatment is to stop liver damage by keeping the virus from multiplying.
Antiviral medicine is used if the virus is active and you are at risk for liver damage. Medicine slows the ability of the virus to multiply.
Antiviral treatment isn’t given to everyone who has chronic hepatitis B.
Follow-up visits
Whether or not you take medicine, you will need to visit your doctor regularly. He or she will do blood tests to check your liver and the activity of the hepatitis B virus in your body.
Some of the tests can find out whether the virus is multiplying in your liver, which would increase your risk of liver damage.
Liver transplant
If you develop advanced liver damage and your condition becomes life-threatening, you may need a liver transplant. But not everyone is a good candidate for a liver transplant.
If you have not gotten a hepatitis B vaccine and think you may have been exposed to the virus, you should get a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and the first of three shots of the hepatitis B vaccine. It is important to receive this treatment within 7 days after a needle stick and within 2 weeks after sexual contact that may have exposed you to the virus. The sooner you receive treatment after exposure, the better the treatment works.
THOSE AT HIGHEST RISK FOR HEPATITIS B:
-Being born in, or spending more than 6 months in, parts of the world where hepatitis B is common or where a large number of people have been infected for a long time. Such areas include Southeast and Central Asia, the islands of the South Pacific, the Amazon River basin, the Middle East, Africa, Eastern Europe, and China.
-Being a man who has sex with men.
-Being sexually active. This includes having unprotected sex with someone who is infected with the virus or whose sexual history is unknown to you.
-Having more than one yex partner. (Your risk is higher if you have another sexually transmitted infection such as chlamydia.)
-Living with someone who has a chronic hepatitis B infection.
-Getting or body piercing and tattoos from someone who doesn’t sterilize his or her equipment.
-Sharing needles or other equipment (such as cotton, spoons, and water) to inject illegal drugs.