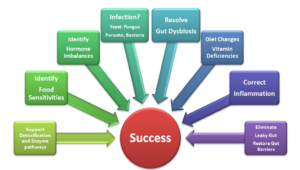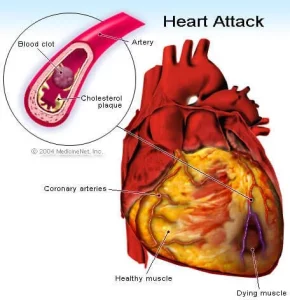

People who are at risk for the development of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction include those who fall into any of the categories listed below:
-People with a history of heart disease.
-Males.
-Smokers.
-People with high cholesterol.
-People with high blood pressure.
-Obese people.
-People with diabetes.
-People who suffer stress.
-People who live a sedentary life style.
-Heredity is a powerful factor that contributes to early heart disease. Being male is a risk factor, but the incidence of heart disease in women increases dramatically after menopause.
-The risk factors to concentrate upon are those that can be modified. These include cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, cholesterol, obesity, sedentary life style and stress. Cigarette smoking causes many deaths from myocardial infarction and other heart diseases. Smoking contributes to almost half of the heart attacks of women under age 55.
-Stopping smoking can greatly reduce your chances of having a heart attack. Controlling blood pressure can reduce your risk of heart attack. Lowering cholesterol to safe levels through diet and medications can reduce your risk and may even lead to some regression of the plaques already present. Lean body weight and a regular exercise program are helpful.
-If you are diabetic, precise control of your diabetes will help reduce your risk of blood vessel damage due to diabetes. Stress is a risk factor that is common, difficult to quantify and difficult to control effectively over time. Methods of stress reduction include meditation, regular exercise, time management, and a supportive environment.
How is a heart attack diagnosed?
Chest pain is the most common symptom of a heart attack. The chest pain is usually a burning or pressure sensation beneath the mid or upper breast bone. The pain may radiate into the upper mid back, neck, jaw or arms. The pain may be severe but often is only moderate in severity.
There may be associated shortness of breath or sweating. If patients have had angina previously, the heart attack pain will feel the same as their usual angina only stronger and more prolonged. If you have a pain like this that lasts longer than 15 minutes, it is best to be evaluated immediately.
Calling your medic unit is the fastest and safest way to ask for help. If you have symptoms like this that wax and wane, this is often a warning sign that a heart attack is about to occur and prompt medical attention is needed.
Once you are in an emergency room or a doctor’s office an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) will be obtained. This is often helpful in diagnosing a heart attack. Sometimes, however, the test is normal even when the heart injury is present but usually a great diagnostic tool.
When heart cells die, certain enzymes present in heart cells are released into the bloodstream that serve as a marker of heart injury (troponin I and CPK or CK-MB). These enzymes can be measured by blood tests. The amount of enzyme released into the blood stream also helps assess how much heart damage has occurred.
TREATMENT:
The best way to limit the size of a heart attack is to restore the flow of blood to the heat muscle as fast as possible. There are two basic methods to do this.
Because most heart attacks are caused by clots forming within the coronary artery, dissolving the clot quickly will restore blood flow. Drugs called thrombolytics are quite effective OR having a angiogram to angioplasty to remove the blockage.
The sooner these drugs are given, the quicker the blood flow will be restored. An alternative method involves the use of balloon angioplasty.
Angiogram to angioplasty involves taking the heart attack victim promptly to the cardiac cath lab in the hospital.
An angiogram is performed to show the blocked blood vessel leading to the heart attack. Then a balloon catheter is placed across the blockage and flow is restored.
Sometimes a stent (a device that assists in holding the blood vessel open) is placed to create a large channel.
Smaller heart attacks, often those not producing significant abnormalities on the ECG are often treated with bedrest and blood thinners such as heparin as well as drugs to reduce the work the heart does.
These heart attacks are called non-transmural myocardial infarctions. Before discharge, x-ray studies of the heart arteries are often carried out to see if angioplasty or surgery will be necessary.
Following thrombolytic (clot reducing) therapy, angiogram are often performed to outline the coronary anatomy to help determine if additional therapy such as angioplasty or bypass surgery is indicated. This may be done during the initial hospitalization or later as an outpatient procedure.