The liver is like our transmission to the human body—it cleans out end products of what enters our body keeping the essentials we need inside. This is what this organ does for us:
Your liver is your very own chemical processing plant. It receives 30% of the blood circulating in your system every minute – performing chemical reactions to remove harmful toxins and distribute and store essential nutrients. This vital process is called ‘metabolism’ and cells in the liver, known as hepatocytes, are put to work to keep your body working at its best. Essentially, your liver loves and cares for you.
Once carbs have been broken down into glucose in your gastrointestinal tract, the glucose enters the blood stream and is taken straight to your liver to regulate and maintain healthy levels. Your liver also stores excess glucose in the form of glycogen (inactive glucose) and the liver will fill up with this glycogenl (like a gas tank). When the tank of the liver gets full the excess of the sugar floating in your bloodstream is used by our tissues that need it right than. The sugar that couldn’t go in the liver is extra glucose that now needs a place to store (if the liver is full) than it gets dumped in our fat tissue next. This is how we get obese. This is the logic of eating small meals not 3 large meals a day. The small meals are utilized mostly where there is no extra floating glucose that needs to be stored anywhere like in our case the fatty tissue. The average American doesn’t realize this with knowing that glycogen (inactive glucose) when needed by our body is ready for converting back into glucose when levels drop between meals which usually occurs during exercise or when you’re fasting; which most of us in America don’t do by overall population. For our liver to do these processes of breakdown of our foods (including medications), to convert active glucose to inactive glucose (glycogen), store glycogen in the liver and to do much more the liver has to be working meaning healthy.
And here’s the really clever thing. Your liver can also convert non-sugars, such as amino acids, into glucose to keep levels healthy. It does some pretty impressive things with fats too.
Every time you eat either through food or protein fluid drinks in place of your food, your liver feeds you. Once food is digested, nutrients enters the blood from the stomach after digestion in that organ takes place including the small intestines, which are taken straight to your liver for processing. Depending on how low or plentiful these nutrients are in your body, the liver cells will either release the goodness of these processed broken down nutrient end products to where it’s needed (regarding our tissues of the body) or store they will be stored away for when your body tissues needs a boost later.
And here’s the really clever thing. Your liver can also convert non-sugars, such as amino acids, into glucose to keep levels healthy. It does some pretty impressive things with fats too.
Your liver is your fat processing factory – it breaks down fat and compounds such as lipoproteins, cholesterol and phospholipids. If fat is in excess, the liver combines fatty acids and glycerol to form a storage molecule and transports it to your body’s storage depots, such as the subcutaneous tissue (tissue just under the skin). Then, at times when energy levels are low, between meals and during exercise, this stored fat is converted back into glycerol and the liver turns the remaining fatty acids into an alternative energy supply. To aid absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins and flush out unwanted substances from your body, your liver produces bile. It stores the bile in your gall bladder, where it can be emptied into your intestines when needed.
Proteins are also vital for a healthy body, and your liver takes charge of these too. Once proteins are broken down into amino acids in your intestines, they enter the blood stream and flow direct to the liver. Here, the liver cells (hepatocytes) go to work on removing nitrogen from the proteins which rapidly changes into ammonia – a highly toxic substance. Your liver then acts fast to convert this into urea to be excreted into the urine and eliminated from your body. With excess amino acids, your liver converts them into fat for storage or, if your body needs an energy boost, it will use them to create glucose.
Ending line the liver breaks down our Calories & CHOs, Fats, and Proteins that enter our body.
Our liver watches out for us. When harmful toxins and substances enter your blood stream, your liver acts fast to detoxify and destroy them. Some may simply be a by-product of a normal metabolism, others may be ingested or inhaled substances such as drugs and alcohol. Filtering the blood, your liver removes dead cells and invading bacteria, processes nitrogen and cholesterol and neutralises harmful hormones.
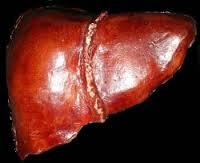
The problem comes when the body liver can’t do this function anymore, meaning it can’t break down or do the processing of out nutrients we eat causing toxins to build up in our body. Soon this break down of the liver with no reversal or without treatment will go into liver failure. Liver failure can put a big hold up in your life but if you can reverse it your smart since you addressed the problem in getting cared for by a doctor. You can even be better than this in being healthy to your body which is you taking PREVENTION in allowing yourself never to deal with this headache.
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognized, acute and chronic.
Acute liver failure defined as “the rapid development of hepatocellular dysfunction, specifically coagulopathy and mental status changes (encephalopathy) in a patient without known prior liver disease.”.
Chronic liver failure usually occurs in the context of cirrhosis, itself potentially the result of many possible causes, such as excessive alcohol intake, hepatitis B or C, autoimmune, hereditary and metabolic causes (such as iron or copper overload, Steatohepatitis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease).
CHRONIC can be prevented. How important is your health?





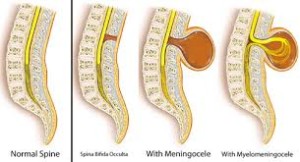
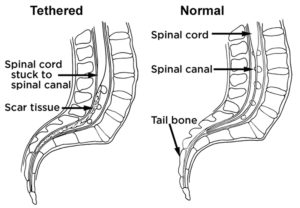
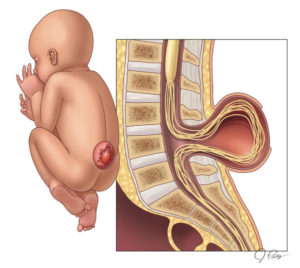 SPINA BIFIDA
SPINA BIFIDA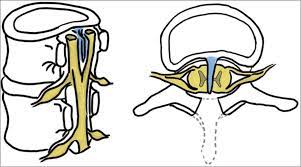
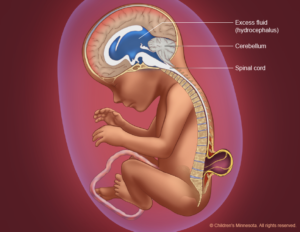
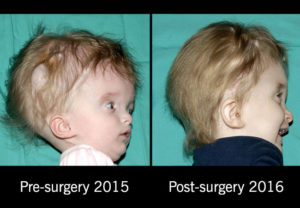 HYDROCEPHALUS
HYDROCEPHALUS