Diabetes is becoming more common in the United States. From 1980 through 2011, the number of Americans with diagnosed diabetes has more than tripled as of 2011 (from 5.6 million to 20.9 million). Do you know how much it is costing in our country? Its a combination of factors that has caused such and increase in the disease of Diabetes in the U.S. Factors:
-Look how much our population has increased with fast food companies pushing the unhealthy foods the sell in restaurants or food stores.
-Also people from other countries who permanently came into America becoming a citizen from 1980 to now and came in to the U.S. already eating poor OR picked up the bad habits of eating poor foods that the U.S. media pushes that is acceptable to enough by U.S. society (that is continues) and is adding to the diabetic population whether they came in the U.S. with it or got it when coming to live in America.
-Than people born in U.S. with family having a history of diabetes or worse parents who did not watch good eating habits when raising their children who got obese putting them at high risk for diabetes.
-Ending line, these factors massively increased making the number of Diabetic Americans 3x higher since 1980.
-Than another factor is the illegals with diabetes also adds to the number of diabetic people in America; for they are not left out and are treated in hospitals with citizens. If the come to an ER in the U.S. we treat them.
These factors all IMPACT an increase in the number of Diabetics in America!
Wake up America! We need to get this disease under better control! See how Diabetes keeps increasing in the U.S.?
That’s right. The metabolic condition is about as American as you can get, according to a national report card on diabetes by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2011.
The report shows that nearly half of Americans have diabetes or prediabetes, which puts them at high risk for the condition. A good number of these folks haven’t been diagnosed and don’t even realize their predicament.
People with diabetes have too much sugar in their blood. If the disease isn’t controlled, they can wind up with heart disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, eye damage and other serious health problems.
The new report combines data from the CDC, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Indian Health Service and the Census Bureau. Here’s a numerical look at what they reveal about diabetes in America.
30.3 million – The number of people in the U.S. who had diabetes in 2015.
That’s right. The metabolic condition is about as American as you can get, according to a new national report card on diabetes released Tuesday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There are 2 types of Diabetes:
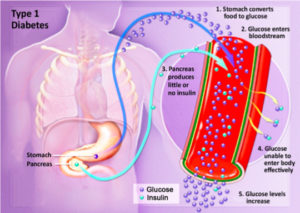
Type 1 diabetes was previously called insulin-dependent mellitus (IDDM) or juvenile-onset diabetes. This type of diabetes happens when the immune system ends up destroying beta cells in the body that come from our pancreas and they are the only cells in the human body that make the hormone INSULIN the regulates your glucose. Insulin allows glucose to transfer into the cells and tissues of our body to give them their energy to do their job in the body and nutrition to work properly=sugar-glucose. To live with this diabetes the person must have their insulin delivered by injection or a pump. This form of diabetes usually occurs in children or young adults but can occur at any age.
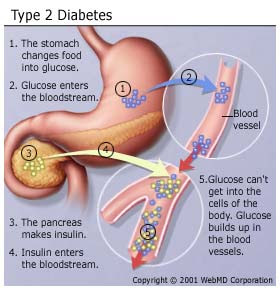
Type 2 diabetes was called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult-onset diabetes. In adults, type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90-95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes. It usually begins as insulin resistance, a disease in which the cells do not use insulin properly due to the pancreas not making enough or the pancreas not secreting the correct form o of insulin to do its function. Ending line the insulin isn’t working properly. As the need for insulin rises, the pancreas gradually loses its ability to produce it.
Type 2 diabetes is associated with older age, OBESITY, family history of diabetes, history of gestational diabetes, impaired glucose metabolism, physical inactivity and race/ethnicity.
Gestational diabetes is a form of glucose intolerance diagnosed during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes occurs more frequently among African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, and American Indians. It is also more common among obese women and women with a family history of diabetes. During pregnancy, gestational diabetes requires treatment to optimize maternal blood glucose levels to lessen the risk of complications in the infant.
Other types of diabetes result from; specific genetic conditions (such as maturity-onset diabetes of youth), surgery, medications, infections, pancreatic disease, and other illnesses. Such types of diabetes account for 1% to 5% of all diagnosed cases.
Treatment for Diabetes:
Diet, insulin, and oral medication to lower blood glucose levels are the foundation of diabetes treatment and management. Patient education and self-care practices are also important aspects of disease management that help people with diabetes lead normal lives.
To survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by injection or a pump.
Many people with type 2 diabetes can control their blood glucose by following a healthy meal plan and exercise program, losing excess weight, and taking oral medication. Medications for each individual with diabetes will often change during the course of the disease. Some people with type 2 diabetes may also need insulin to control their blood glucose.
Self-management education or training is a key step in improving health outcomes and quality of life. It focuses on self-care behaviors, such as healthy eating, being active, and monitoring blood sugar.
Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes:
A fasting blood sugar level ≥126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after an overnight fast, which is just taking the finger stick right when you wake up before breakfast OR
A 2-hour blood sugar level ≥200 mg/dL after a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), OR
An A1c level ≥6.5%. (The A1C test is a simple lab test that measures average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months. A small blood sample to check your A1C can be taken at any time of the day=simply a blood test)
Pretty simple isn’t it but you have to the move! Take action and make changes if you need to!
Diabetes is not only common and serious; it is also VERY COSTLY! Let us take a look:
The cost of treating diabetes is staggering. According to the American Diabetes Association, the annual cost of diabetes in medical expenses and lost productivity rose for $98 billion in 1997 to $132 billion in $2002 to $174 billion in 2007.
One out of every 5 U.S. federal health care dollars is spent treating people with diabetes. The average yearly health care costs for a person without diabetes is 2,560 dollars; for a person with diabetes that figure soars to $11,744. Much of the human and financial costs can be avoided with proven diabetes prevention and management steps.