The answer is even with a name; it is called Post-polio syndrome.
Around 40% of people who survive paralytic polio may develop additional symptoms 15–40 years after the original illness. These symptoms – called post-polio syndrome – include new progressive muscle weakness, severe fatigue and pain in the muscles and joints.
This is how it works:
What is post-polio syndrome?
Post-polio syndrome is an illness of the nervous system that can appear 15 to 50 years after you had polio. It affects your muscles and nerves, and it causes you to have weakness, fatigue, and muscle or joint pain.
Although post-polio syndrome can make some day-to-day activities more difficult, treatment can help control symptoms and help you stay active. Your symptoms may not get worse for many years. Post-polio syndrome usually progresses very slowly.
Only people who have had polio can get post-polio syndrome. But having post-polio syndrome doesn’t mean that you have polio again. Unlike polio, post-polio syndrome doesn’t spread from person to person.
What causes post-polio syndrome?
Post-polio syndrome most likely arises from the damage left over from having the polio viruse in the body still.
The polio virus harms the nerves that control muscles, and it makes the muscles weak. If you had polio, you may have gained back the use of your muscles. But the nerves that connect to the muscles could be damaged without your knowing it. The nerves may break down over time and cause you to have weak muscles again.
Researchers are studying other possible causes of post-polio syndrome. One theory is that the immune system plays a role.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of post-polio syndrome tend to show up very slowly. The main symptoms are:
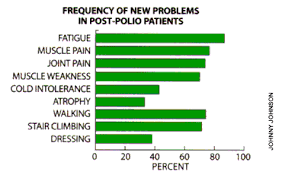
- New muscle weakness. This is most common in the muscles that had nerve damage from polio. You may also have weakness in muscles that you didn’t realize had been affected by polio. Overuse or underuse of the muscles can lead to weakness.
- Fatigue. You may find that the activities you used to do without getting tired are now causing fatigue. You may often feel tired, have a heavy feeling in your muscles, or feel sleepy. At times you may have trouble thinking clearly.
- Muscle or joint pain. Muscles affected by polio tend to be weaker than normal. To make up for this weakness, other muscles have to work harder. This puts extra wear and tear on muscles, joints, and tendons, sometimes leading to aches, cramping, and pain.
Depending on which muscles are affected, this trio of muscle weakness, fatigue, and pain can make daily activities more difficult. For example, people with shoulder or arm weakness may have trouble getting dressed. People who have weakness in their legs may have trouble walking or climbing stairs.
Post-polio syndrome is rarely life-threatening, but the symptoms can significantly interfere with an individual’s ability to function independently. Respiratory muscle weakness, for instance, can result in trouble with proper breathing, affecting daytime functions and sleep. Weakness in swallowing muscles can result in aspiration of food and liquids into the lungs and lead to pneumonia.
Only a polio survivor can develop PPS.
The severity of weakness and disability after recovery from poliomyelitis tends to predict the relative risk of developing PPS. Individuals who had minimal symptoms from the original illness are more likely to experience only mild PPS symptoms. A person who was more acutely affected by the polio virus and who attained a greater recovery may experience a more severe case of PPS, with greater loss of muscle function and more severe fatigue.
The exact incidence and prevalence of PPS is unknown. The U.S. National Health Interview Survey in 1987 contained specific questions for persons given the diagnosis of poliomyelitis with or without paralysis. No survey since then has addressed the question. Results published in 1994-1995 estimated there were about 1 million polio survivors in the U.S., with 443,000 reporting to have had paralytic polio. Accurate statistics do not exist today, as a percentage of polio survivors have died and new cases have been diagnosed. Researchers estimate that the condition affects 25 to 40 percent of polio survivors.
What causes PPS?
The cause of PPS is unknown but experts have offered several theories to explain the phenomenon—ranging from the fatigue of overworked nerve cells to possible brain damage from a viral infection to a combination of mechanisms. The new weakness of PPS appears to be related to the degeneration of individual nerve terminals in the motor units. A motor unit is formed by a nerve cell (or motor neuron) in the spinal cord or brain stem and the muscle fibers it activates. The polio virus attacks specific neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord. In an effort to compensate for the loss of these motor neurons, surviving cells sprout new nerve-end terminals and connect with other muscle fibers. These new connections may result in recovery of movement and gradual gain in power in the affected limbs.
Years of high use of these recovered but overly extended motor units adds stress to the motor neurons, which over time lose the ability to maintain the increased work demands. This results in the slow deterioration of the neurons, which leads to loss of muscle strength. Restoration of nerve function may occur in some fibers a second time, but eventually nerve terminals malfunction and permanent weakness occurs. This hypothesis explains why PPS occurs after a delay and has a slow and progressive course.
Through years of studies, scientists at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and at other institutions have shown that the weakness of PPS progresses very slowly. It is marked by periods of relative stability, interspersed with periods of decline.
How is PPS diagnosed?
The diagnosis of PPS relies nearly entirely on clinical information. There are no laboratory tests specific for this condition and symptoms vary greatly among individuals. Physicians diagnose PPS after completing a comprehensive medical history and physical examination, and by excluding other disorders that could explain the symptoms.
Physicians look for the following criteria when diagnosing PPS:
- Prior paralytic poliomyelitis with evidence of motor neuron loss. This is confirmed by history of the acute paralytic illness, signs of residual weakness and atrophy of muscles on neuromuscular examination, and signs of motor neuron loss on electromyography (EMG). Rarely, people had subtle paralytic polio where there was no obvious deficit. In such cases, prior polio should be confirmed with an EMG study rather than a reported history of non-paralytic polio.
- A period of partial or complete functional recovery after acute paralytic poliomyelitis, followed by an interval (usually 15 years or more) of stable neuromuscular function.
- Slowly progressive and persistent new muscle weakness or decreased endurance, with or without generalized fatigue, muscle atrophy, or muscle and joint pain. Onset may at times follow trauma, surgery, or a period of inactivity, and can appear to be sudden. Less commonly, symptoms attributed to PPS include new problems with breathing or swallowing.
- Symptoms that persist for at least a year.
- Exclusion of other neuromuscular, medical, and skeletal abnormalities as causes of symptoms.
PPS may be difficult to diagnose in some people because other medical conditions can complicate the evaluation. Depression, for example, is associated with fatigue and can be misinterpreted as PPS. A number of conditions may cause problems in persons with polio that are not due to additional loss of motor neuron function. For example, shoulder osteoarthritis from walking with crutches, a chronic rotator cuff tear leading to pain and disuse weakness, or progressive scoliosis causing breathing insufficiency can occur years after polio but are not indicators of PPS.
Polio survivors with new symptoms resembling PPS should consider seeking treatment from a physician trained in neuromuscular disorders. It is important to clearly establish the origin and potential causes for declining strength and to assess progression of weakness not explained by other health problems. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) of the spinal cord, electrophysiological studies, and other tests are frequently used to investigate the course of decline in muscle strength and exclude other diseases that could be causing or contributing to the new progressive symptoms. A muscle biopsy or a spinal fluid analysis can be used to exclude other, possibly treatable, conditions that mimic PPS. Polio survivors may acquire other illnesses and should always have regular check-ups and preventive diagnostic tests. However, there is no diagnostic test for PPS, nor is there one that can identify which polio survivors are at greatest risk.
Is there a treatment for PPS?
There are currently no effective pharmaceutical treatments that can stop deterioration or reverse the deficits caused by the syndrome itself. However, a number of controlled studies have demonstrated that non-fatiguing exercises may improve muscle strength and reduce tiredness. Most of the clinical trials in PPS have focused on finding safe therapies that could reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have tried treating persons having PPS with high doses of the steroid prednisone and demonstrated a mild improvement in their condition, but the results were not statistically significant. Also, the side effects from the treatment outweighed benefits, leading researchers to conclude that prednisone should not be used to treat PPS.
Preliminary studies indicate that intravenous immunoglobulin may reduce pain and increase quality of life in post-polio survivors.
A small trial to treat fatigue using lamotrigine (an anticonvulsant drug) showed modest effect but this study was limited and larger, more controlled studies with the drug were not conducted to validate the findings.
Although there are no effective treatments, there are recommended management strategies. Patients should consider seeking medical advice from a physician experienced in treating neuromuscular disorders. Patients should also consider judicious use of exercise, preferably under the supervision of an experienced health professional. Physicians often advise patients on the use of mobility aids, ventilation equipment, revising activities of daily living activities to avoid rapid muscle tiring and total body exhaustion, and avoiding activities that cause pain or fatigue lasting more than 10 minutes. Most importantly, patients should avoid the temptation to attribute all signs and symptoms to prior polio, thereby missing out on important treatments for concurrent conditions. Always go to your physician for advisement before starting any exercise regimen to make sure your M.D. clears the activity first, for your safety!
There is no cure for polio, only treatment to alleviate the symptoms. Heat and physical therapy is used to stimulate the muscles and antispasmodic drugs are given to relax the muscles. While this can improve mobility, it cannot unfortunately reverse permanent polio paralysis.
How Polio can be PREVENTED:
Polio can be prevented through immunization. Polio vaccine, given multiple times, almost always protects a child for life. Post Polio if it happens in a polio pt too late and no cure or if diagnosed with Polio too late for cure. So vaccinate when young so you’ll never get it!