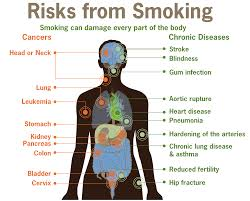
Let’s start with what smoking actually does to the body. Smoking harms nearly every organ of the body. Smoking causes many diseases and reduces the health of smokers in general. It primarily starts at the lungs. How? Well think of your lung tissue with openings all over which are air sacs called alveoli. This is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity which does the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in and out of our body, when we inhale and exhale. The thing to know about this tissue is that before you start smoking the alveoli are expandable (think of it like a rubber band) allowing the person to get a good exchange of oxygen getting in the body to go to all our tissues and carbon dioxide getting out of the body (O2=oxygen being the fuel to our tissues and without it causes cellular starvation, carbon dioxide=CO2 being an acid / toxin to the human body and exhaled by the lungs). After years of smoking the alveoli stretches out not allowing a good exchange of O2 and CO2. The sad thing for a smoker is the alveoli cannot REVERSE back after damage has already occurred unless you had a lung transplant with continuing to smoke, which no M.D. or health insurance would allow. More realistic would be QUIT the bad habit. The tissue doesn’t get completely better but it improves when you quit. So the pt with Emphysema has alveoli that can’t exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide from the blood like it use to at the bottom of the lungs, prior to even starting to smoke. Also, after smoking years and when diagnosed with COPD you have difficulty breathing (that is why smoking is a major cause of bronchitis or Emphysema=types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease=COPD and it is not REVERSIBLE). Emphysema is the worst type of COPD you can get. COPD is the third leading cause of death in the U.S., and the economic burden of COPD in the U.S. in 2007 was $42.6 billion in health care costs and lost productivity. Isn’t this reason enough to stop smoking?
Emphysema is an enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, with destruction of their walls. People with emphysema have historically been known as “Pink Puffers”, due to their pink complexion.
Chronic bronchitis is defined in clinical terms as a cough with sputum production on most days for 3 months of a year, for 2 consecutive years. People with advanced COPD that have primarily chronic bronchitis were commonly referred to as “Blue Bloaters” because of the bluish color of the skin and lips (cyanosis) along with hypoxia and fluid retention.
Know when the lungs get effected in time the heart gets effected. One Affects the other in time. The heart can’t live without the lungs and vice versa.
References
- S. Department of Health and Human Services. The Health Consequences of Smoking: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 2004 [accessed 2013 June 28].
- S. Department of Health and Human Services. How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: What It Means to You. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 2010 [accessed 2013 June 28].
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annual Smoking-Attributable Mortality, Years of Potential Life Lost, and Productivity Losses—United States, 2000–2004. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2008;57(45):1226–8 [accessed 2013 June 28].
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. QuickStats: Number of Deaths from 10 Leading Causes–National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2010. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2013:62(08);155. [accessed 2013 June 28].
- Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup DF, Gerberding JL. Actual Causes of Death in the United States. JAMA: Journal of the American Medical Association 2004;291(10):1238–45 [cited 2013 June 28].
- S. Department of Health and Human Services. Reducing the Health Consequences of Smoking: 25 Years of Progress. A Report of the Surgeon General. Rockville (MD): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 1989 [accessed 2013 June 28].
- Ockene IS, Miller NH. Cigarette Smoking, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 1997;96(9):3243–7 [accessed 2013 June 28].
- Institute of Medicine. Secondhand Smoke Exposure and Cardiovascular Effects: Making Sense of the Evidence. [PDF–707 KB] Washington: National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medicine, 2009 [accessed 2013 June 28].
- S. Department of Health and Human Services. Women and Smoking: A Report of the Surgeon General. Rockville (MD): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Office of the Surgeon General, 2001 [accessed 2013 June 28].