The top 3 degenerative eye diseases – cataracts, glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration – can result in vision loss or complete blindness. Fortunately today, effective treatment options are available – and newer treatments are on the horizon. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent or slow vision loss associated with degenerative eye conditions; if you experience any changes to your vision or any unusual eye symptoms, schedule an appointment with an eye-doctor as soon as possible.
Part I Cataracts
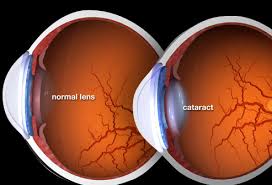
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging. Cataracts are very common in older people. By age 80, more than half of all Americans either have a cataract or have had cataract surgery.
A cataract can occur in either or both eyes. It cannot spread from one eye to the other.
Yes. Although most cataracts are related to aging, there are other types of cataract:
-Secondary cataract. Cataracts can form after surgery for other eye problems, such as glaucoma. Cataracts also can develop in people who have other health problems, such as diabetes. Cataracts are sometimes linked to steroid use.
-Traumatic cataract. Cataracts can develop after an eye injury, sometimes years later.
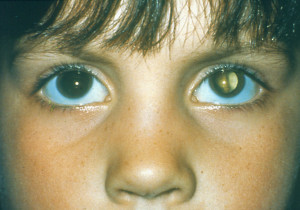
-Congenital cataract. Some babies are born with cataracts or develop them in childhood, often in both eyes. These cataracts may be so small that they do not affect vision. If they do, the lenses may need to be removed.
-Radiation cataract. Cataracts can develop after exposure to some types of radiation
The most common symptoms of a cataract are:
- Cloudy or blurry vision.
- Colors seem faded.
- Glare. Headlights, lamps, or sunlight may appear too bright. A halo may appear around lights.
- Poor night vision.
- Double vision or multiple images in one eye. (This symptom may clear as the cataract gets larger.)
- Frequent prescription changes in your eyeglasses or contact lenses.
- These symptoms also can be a sign of other eye problems. If you have any of these symptoms, check with your eye care professional.
- TREATMENT
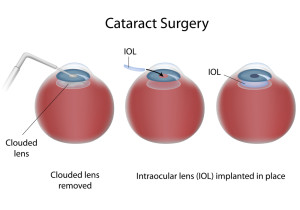
- The symptoms of early cataract may be improved with new eyeglasses, brighter lighting, anti-glare sunglasses, or magnifying lenses. If these measures do not help, surgery is the only effective treatment. Surgery involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial lens.
- A cataract needs to be removed only when vision loss interferes with your everyday activities, such as driving, reading, or watching TV. You and your eye care professional can make this decision together. Once you understand the benefits and risks of surgery, you can make an informed decision about whether cataract surgery is right for you. In most cases, delaying cataract surgery will not cause long-term damage to your eye or make the surgery more difficult. You do not have to rush into surgery.
- Sometimes a cataract should be removed even if it does not cause problems with your vision. For example, a cataract should be removed if it prevents examination or treatment of another eye problem, such as age-related macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy. If your eye care professional finds a cataract, you may not need cataract surgery for several years. In fact, you might never need cataract surgery. By having your vision tested regularly, you and your eye care professional can discuss if and when you might need treatment.
- If you choose surgery, your eye care professional may refer you to a specialist to remove the cataract.
- If you have cataracts in both eyes that require surgery, the surgery will be performed on each eye at separate times, usually four to eight weeks apart.
- Many people who need cataract surgery also have other eye conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration or glaucoma. If you have other eye conditions in addition to cataract, talk with your doctor. Learn about the risks, benefits, alternatives, and expected results of cataract surgery.
Know the risks of cataract eye surgery:
As with any surgery, cataract surgery poses risks, such as infection and bleeding. Before cataract surgery, your doctor may ask you to temporarily stop taking certain medications that increase the risk of bleeding during surgery. After surgery, you must keep your eye clean, wash your hands before touching your eye, and use the prescribed medications to help minimize the risk of infection. Serious infection can result in loss of vision.
Cataract surgery slightly increases your risk of retinal detachment. Other eye disorders, such as high myopia (nearsightedness), can further increase your risk of retinal detachment after cataract surgery. One sign of a retinal detachment is a sudden increase in flashes or floaters. Floaters are little “cobwebs” or specks that seem to float about in your field of vision. If you notice a sudden increase in floaters or flashes, see an eye care professional immediately. A retinal detachment is a medical emergency. If necessary, go to an emergency service or hospital. Your eye must be examined by an eye surgeon as soon as possible. A retinal detachment causes no pain. Early treatment for retinal detachment often can prevent permanent loss of vision. The sooner you get treatment, the more likely you will regain good vision. Even if you are treated promptly, some vision may be lost.
Talk to your eye care professional about these risks. Make sure cataract surgery is right for you.