In general, kidney transplantation involves four phases:
- The evaluation and listing phase
- The pre-transplant waiting phase
- The transplant surgery
- The postoperative care and maintenance phase
________________________________________________
What is GFR & how it relates to kidney damage?
GFR – glomerular filtration rate is the best test to measure your level of kidney function and determine your stage of kidney disease. Your doctor can calculate it from the results of your blood creatinine test, your age, body size and gender. Your GFR tells your doctor your stage of kidney disease and helps the doctor plan your treatment. If your GFR number is low, your kidneys are not working as well as they should. The earlier kidney disease is detected, the better the chance of slowing or stopping its progression.
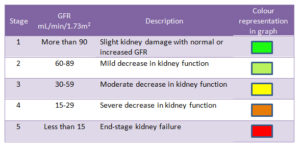
What are the Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
| Stage | Description | (GFR) |
| At increased risk | Risk factors for kidney disease (e.g., diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, older age, ethnic group) | More than 90 |
| 1 | Kidney damage with normal kidney function | 90 or above |
| 2 | Kidney damage with mild loss of kidney function | 89 to 60 |
| 3a | Mild to moderate loss of kidney function | 59 to 44 |
| 3b | Moderate to severe loss of kidney function | 44 to 30 |
| 4 | Severe loss of kidney function | 29 to 15 |
| 5 | Kidney failure | Less than 15 |
| Your GFR number tells you how much kidney function you have. As kidney disease gets worse, the GFR number goes down. | ||
What happens if my test results show I may have chronic kidney disease?
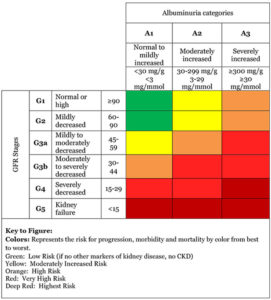
- A GFR below 60 for three months or more or a GFR above 60 with kidney damage (marked by high levels of albumin in your urine) indicates chronic kidney disease. Your doctor will want to investigate the cause of your kidney disease and continue to check your kidney function to help plan your treatment.
- Typically, a simple urine test will also be done to check for blood or albumin (a type of protein) in the urine. When you have albumin in your urine it is called albuminuria. Blood or protein in the urine can be an early sign of kidney disease.
- People with a high amount of albumin in their urine are at an increased risk of having chronic kidney disease progress to kidney failure; (See chart below looking at both where stages of chronic renal failure with albumin levels are when looked at together to put finalize what CRF stage you are in).
- Your doctor may also suggest further testing, if necessary, such as:
- Imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan to get a picture of your kidneys and urinary tract. This tells your doctor whether your kidneys are too large or too small, whether you have a problem like a kidney stone or tumor and whether there are any problems in the structure of your kidneys and urinary tract.
- A kidney biopsy, which is done in some cases to check for a specific type of kidney disease, see how much kidney damage has occurred and help plan treatment. To do a biopsy, the doctor removes small pieces of kidney tissue and looks at them under a microscope.
-
What is a normal GFR number in a lifetime?
- In adults, the normal GFR number is more than 90. GFR declines with age, even in people without kidney disease.See chart below for average estimated GFR based on age.
- Your doctor may also ask you to see a kidney specialist called a nephrologist who will consult on your case and help manage your care.
| Age (years) | Average estimated GFR |
| 20–29 | 116 |
| 30–39 | 107 |
| 40–49 | 99 |
| 50–59 | 93 |
| 60–69 | 85 |
| 70+ | 75 |
To treat CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE (CRF):
Follow a diet that is easy on your kidneys. A dietitian can help you make an eating plan with the right amounts of salt (sodium) and protein. You may also need to watch how much fluid you drink each day.
Make exercise a routine part of your life. Work with your doctor to design an exercise program that is right for you.
Do not smoke or use tobacco.
Do not drink alcohol.
When kidney function falls below a certain point, it is called Kidney failure. Kidney failure affects your whole body. It can cause serious heart, bone, and brain problems and make you feel very ill. Untreated kidney failure will be life-threatening at some point.
When you have kidney failure, you will probably have two choices: start dialysis or get a new kidney (transplant). Both of these treatments have risks and benefits. Talk with your doctor to decide which would be best for you.
Always talk to your doctor before you take any new medicine, including over-the-counter remedies, prescription drugs, vitamins,or herbs. These can hurt the kidneys further.
In COMPLETE RENAL FAILURE you have 2 choices for Rx.:
1**-Dialysis is a process that filters your blood when your kidneys no longer can. It is not a cure, but it can help you feel better and live longer. There is hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
2-**Kidney transplant may be the best choice if you are otherwise healthy. With a new kidney, you will feel much better and will be able to live a more normal life. But you may have to wait for a kidney that is a good match for your blood and tissue type. And you will have to take medicine for the rest of your life to keep your body from rejecting the new kidney.
John for your knowledge – Westchester Medical Center enjoys a long and illustrious history in kidney transplantation, having performed well over 2100 kidney transplants since the program opened in 1989.
Making treatment decisions when you are very ill is hard! It is normal to be worried and afraid. Discuss your concerns with your loved ones and your doctor. It may help to visit a dialysis center or transplant center and talk to others who have made these choices.