There is an alarming number of people in America that have issues with their thyroid, in fact it’s a huge number, around 59 million people suffer from a thyroid problem. A thyroid handles your metabolism and is a gland located in the neck area. It can have huge negative affects on your health if it is not treated properly. Many people aren’t even aware that they have any symptoms that are connected with a thyroid; but before going into the problems lets first talk about what the thyroid is.
The Anatomy & Physiology of the Thyroid Gland:
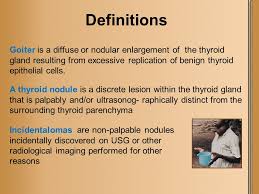
The thyroid is a small gland, measuring about 2 inches (5 centimeters) across, that lies just under the skin below the Adam’s apple in the neck. The two halves (lobes) of the gland are connected in the middle (called the isthmus), giving the thyroid gland the butterfly shapes organ, sort of looking like a bow tie. Normally, the thyroid gland cannot be seen and can barely be felt. If it becomes enlarged, doctors can feel it easily, and a prominent bulge (goiter) may appear below or to the sides of the Adam’s apple.
How the Thyroid Gland Works:
- The thyroid is part of the endocrine system, which is made up of glands that produce, store, and release hormones into the bloodstream so the hormones can reach the body’s cells. The thyroid gland uses iodine from the foods you eat to make two main hormones:
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Thyroxine (T4)
T4, the major hormone produced by the thyroid gland, has only a slight effect, if any, on speeding up the body’s metabolic rate. When this occurs instead, T4 is converted into T3, the more active hormone. The conversion of T4 to T3 occurs in the liver and other tissues. Now yes T3 is made by the thyroid but if too much in the body it is converted to T4, more inactivating or decreasing your T3 levels to prevent metabolism too high in the body causing metabolic problems. Many factors control the conversion of T4 to T3, including the body’s needs from moment to moment and the presence or absence of illnesses.
The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones, which control the speed at which the body’s chemical functions proceed (metabolic rate). This is the vital function of this gland.
Thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate in two ways:
1. By stimulating almost every tissue in the body to produce proteins
2. The stimulating other areas of the body. This depends on all how much hormone the thyroid is releasing in the blood stream. This in turn will decrease or increase the amount of oxygen that cells use. Which all depends upon how much of the 2 major hormones the thyroid secretes as the factor. If the thyroid is doing low hormone release this will decrease metabolism in the body or if the organ is in high hormone release it will increase metabolism in the body.
Thyroid hormones affect many vital body functions through either increasing or decreasing metabolism. This would all be effected on the rate of thyroid hormone releasing from the pituitary and how much T3 or T4 is being released from the thyroid, Did you know in turn this will effect the following areas of the body:
A. the heart rate B. the rate at which calories are burned C. skin maintenance D. growth E. heat production
F. fertility E. digestion G. breathing H. CNS and Peripheral Nervous System I. Body Wt. & Temp J. Cholesterol and much more!
If metabolism is increased so will all these functions listed above regarding its activity; or metabolism that is decreased so will all these functions listed above.
In a nut shell the thyroid gland is the gland that releases hormones that plays an impact on metaboloism = the way your body uses energy. The thyroid’s hormones regulate vital body functions.
Two Thyroid Hormones made and released by this organ that impact your metabolism=Triiodothyronine-also known as T3 and T4-also known as thyroxine.
It is important that T3 and T4 levels are neither too high nor too low but within normal range of therapeutic levels. Two glands in the brain—the hypothalamus and the pituitary communicate to maintain T3 and T4 balance.
The Hypothalamus:
A structure deep in your brain, acts as your body’s smart control coordinating center. Its main function is to keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis. It does its job by directly influencing your autonomic nervous system or by managing hormones. and one of the organs it affects is the THYROID.
The pituitary gland:
This organ sometimes called the “master” gland of the endocrine system because it controls the functions of many of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypothalamus by nerve fibers and blood vessels (a part of the brain that affects the pituitary gland). The pituitary gland itself consists of 2 major structures:
- Anterior lobe – this is where TSH is produced and released.
- Posterior lobe
This is how the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland work:
The Hypothalamus produces and releases Thyroid Releasing Hormone when T3 & T4 are low in the blood. The Pituitary produces and releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone TSH to tell your thyroid how much thyroid hormone it needs to make.
The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) and responds by releasing thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The TRH stimulates the pituitary telling it to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and causing the following effect in the body:
- When T3 and T4 levels are low in the blood, the pituitary gland releases more of TSH to tell the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormones.
- If T3 and T4 levels are high, the pituitary gland releases less TSH to the thyroid gland to slow production of these hormones. The inhibiting release of TRH and TSH through a negative feedback loop.
T3 and T4 travel in your bloodstream to reach almost every cell in the body. The hormones regulate the speed with which the cells/metabolism work. For example, T3 and T4 regulate your heart rate and how fast your intestines process food. So if T3 and T4 levels are low, your heart rate may be slower than normal, and you may have constipation/weight gain. If T3 and T4 levels are high, you may have a rapid heart rate and diarrhea/weight loss.
Did you know the third hormone produced by the thyroid gland is called calcitonin. Calcitonin is made by C-cells. It is involved in calcium and metabolism of the bone only.