Inflammatory Disease- Sarcoidosis or Sarcoid is a inflammatory disease that consists of granuloma.
Wide Spread Disease- Disease is wide spread in multiple organs.
Relapse-
- The Sarcoidosis disease tends to come and go all of a sudden.
- Disease may progressively develop as a serious illness.
- Patient may experience several relapse throughout the life.
Granulomas-
- Sarcoidosis or Sarcoid is a gradual progressive disease.
- Microscopic lumps called granulomas start to appear in the affected organs.1
- In most of the cases, these granulomas tend to clear with or without treatments.
- There are few instances where granuloma grows in size and continues to be a part of the organ.
- Granuloma eventually ends up as fibrotic lump but may cause several complications.
Causes
Doctors don’t know the exact cause of sarcoidosis. Some people appear to have a genetic predisposition to develop the disease, which may be triggered by bacteria, viruses, dust or chemicals.
This triggers an overreaction of your immune system and immune cells begin to collect in a pattern of inflammation called granulomas. As granulomas build up in an organ, the function of that organ can be affected.
Risk factors
While anyone can develop sarcoidosis, factors that may increase your risk include:
- Age and sex. Sarcoidosis often occurs between the ages of 20 and 40. Women are slightly more likely to develop the disease.
- Race. African-Americans have a higher incidence of sarcoidosis than do white Americans. Also, sarcoidosis may be more severe and may be more likely to recur and cause lung problems in African-Americans.
- Family history. If someone in your family has had sarcoidosis, you’re more likely to develop the disease.
Complications
For most people, sarcoidosis resolves on its own with no lasting consequences. But sometimes it causes long-term problems.
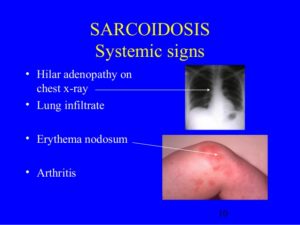
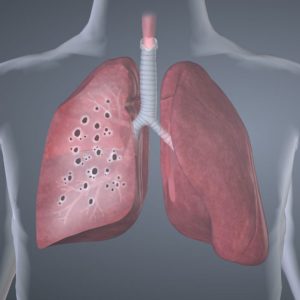
- Lungs. Untreated pulmonary sarcoidosis can lead to permanent scarring in your lungs, making it difficult to breathe.
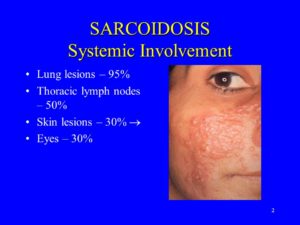
- Eyes. Inflammation can affect almost any part of your eye and can eventually cause blindness. Rarely, sarcoidosis also can cause cataracts and glaucoma.
- Kidneys. Sarcoidosis can affect how your body handles calcium, which can lead to kidney failure.
- Heart. Granulomas in your heart can cause abnormal heart rhythms and other heart problems. In rare instances, this may lead to death.
- Nervous system. A small number of people with sarcoidosis develop problems related to the central nervous system when granulomas form in the brain and spinal cord. Inflammation in the facial nerves, for example, can cause facial paralysis.