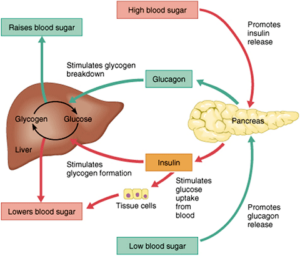
The foods we eat that has calories=sugar, starches and carbohydrates are made up of sugar molecules either single or in groups (glucose and fructose for instance). When food reaches our stomach in time digestion starts to take place where the sugar is broken down in the stomach and the intestines into individual glucose units. It turns out glucose is the most common and important one. The glucose then passes into the liver where 60 to 80 % gets stored=inactive glucose that’s converted to glycogen in this organ.
The remainder of glucose not stored in the liver goes in our bloodstream=active sugar & is ready to be utilized by the body where it is needed by many organs. It’s used as the principle source of energy (brain for energy, the muscles for both energy and some storage, liver for more glucose storage=that’s converted to glycogen, and even fat tissue using it for triglyceride production). Glucose does get sent to other organs for more storage.
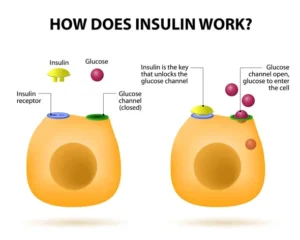
Insulin plays an important role in the glucose being distributed throughout the body. Without insulin the glucose would not pass through your blood cells to go in the the cell otherwise it would go nowhere causing the glucose to build up outside the cell which happens in a diabetic and the primary problem of diabetes=hyperglycemia. When the glucose goes in the cell hyperglycemia does not happen unless it is due to something else causing high glucose; like a drug such as dexamethasone or glucocorticoids.
When digestion occurs a process happens which is the BREAKDOWN of the sugars , released into the circulatory system which gives you extra glucose, than the pancreas senses that and releases insulin, the insulin allows sugar to pass into the blood cells & to be stored somewhere or utilized by the body (without this process hyperglycemia would occur like in a diabetic). When the glucose in the blood reaches the liver a cell sensor picks it up and allows the glucose to go into the organ where glucose is stored as glycogen=inactive glucose. Insulin plays a key role in multiple parts of your metabolism. Insulin allows protein synthesis, fat synthesis and cell growth to occur in the body. Now understanding how the body works lets understand how this has anything to do with controlling obesity. Learn about this in Part 2 tomorrow.