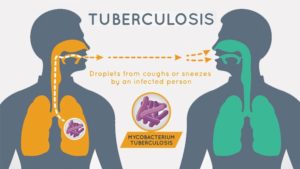
Spreads via coughing and talking near someone so in active TB the patient is put in droplet isolation. A restricted room and anyone who visits the pt in the room wears a mask.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body.
Approximately 8.6 million individuals are diagnosed with tuberculosis (TB), and 1.3 million will die of the disease globally, but it is commonly found in the developing world. TB is a highly contagious but treatable infection that predominantly affects the lungs and throat, but can also spread to the kidney, bones, and brain. So what is tuberculosis exactly? Find out what causes this highly contagious infection, who is most at risk for developing it, and how to treat the different kinds and prevent the spreading of this old world disease.
Tuberculosis, commonly abbreviated to TB, is an infection caused by slow-growing bacteria that festers in areas of the body containing an abundant amount of blood and oxygen, hence why it is commonly found in the lungs. TB found in the lungs is known as pulmonary TB and tuberculosis that spreads to other organs is called extrapulmonary TB. TB is highly contagious, but treatment is often effective and can take between six to nine months to treat, or in severe cases, can take up to two years to treat an infected patient. TB can also be either latent or active. Latent TB is when the immune system is defending the body against TB bacteria and keeping it from becoming active, with no visible symptoms. Active TB is when the TB bacteria are growing inside of the body and symptoms have become noticeable in the patient, and it is easy to spread the disease to others= CONTAGIOUS.
Pulmonary TB is contagious, however extrapulmonary TB does not spread as easily as it is usually contained within another part of the body. TB spreads when an individual has active TB breathes out air that has the TB bacteria in it and another individual breathes in the bacteria from the air. Even more bacteria can become airborne when an infected person coughs or laughs as well.
RISK FACTORS IN DEVELOPING TUBERCULOSIS:
1-Those at risk of developing TB are individuals who have HIV or another illness that weakens the immune system, individuals who have close contact with a patient with active TB such as living in the same house as an infected patient, and those caring for a patient with active TB, such as doctors and nurses.
2-Other risk factors include individuals who live or work in crowded places such as prisons, nursing homes, homeless shelters or wherever individuals may have active TB, as well as individuals who abuse drugs and alcohol.
3- Individuals with poor access to health care, where it is commonly seen in the developing world, as well as homeless individuals and migrant farm workers.
4-As well, traveling to places where untreated TB is common puts an individual at risk, such as Latin America, Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Russia. It is important to note individuals who are at a high risk for developing TB should get tested once or twice a year.
5-As well, traveling to places where untreated TB is common puts an individual at risk, such as Latin America, Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Russia. It is important to note individuals who are at a high risk for developing TB should get tested once or twice a year. So people who make it in the United States via customs with this disease or left here to another country picking up TB bringing it in America passing customs put many at risk and pick up the TB and continue spreading it till treated and healed. Just like the others who pick it up in or out of America but spread it in the U.S. There needs to be closer checking on visitors coming in or citizens that leave home and come back in America to be checked for TB. This will help decrease the amount of people in America with TB by getting diagnosed immediately with treatment.