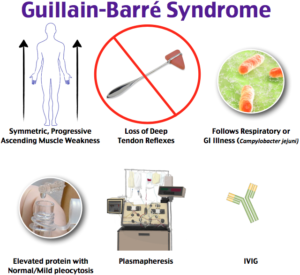
Guillain-Barre (gee-YAH-buh-RAY) syndrome is a rare disorder in which your body’s immune system attacks your nerves. Weakness and tingling in your extremities are usually the first symptoms.
These sensations can quickly spread, eventually paralyzing your whole body. In its most severe form Guillain-Barre syndrome is a medical emergency. Most people with the condition must be hospitalized to receive treatment.
The exact cause of Guillain-Barre syndrome is unknown. But it is often preceded by an infectious illness such as a respiratory infection or the stomach flu.
There’s no known cure for Guillain-Barre syndrome, but several treatments can ease symptoms and reduce the duration of the illness. Most people recover from Guillain-Barre syndrome, though some may experience lingering effects from it, such as weakness, numbness or fatigue.
Causes:
The exact cause of Guillain-Barre syndrome isn’t known. The disorder usually appears days or weeks after a respiratory or digestive tract infection. Rarely, recent surgery or immunization can trigger Guillain-Barre syndrome. Recently, there have been a few cases reported following infection with the Zika virus.
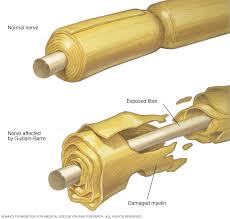
In Guillain-Barre syndrome, your immune system — which usually attacks only invading organisms — begins attacking the nerves. In AIDP, the most common form of Guillain-Barre syndrome in the U.S., the nerves’ protective covering (myelin sheath) is damaged. The damage prevents nerves from transmitting signals to your brain, causing weakness, numbness or paralysis.
Sign and Symptoms of Guillain=Barre:
As Guillain-Barre syndrome progresses, muscle weakness can evolve into paralysis.
Signs and symptoms of Guillain-Barre syndrome may include:
- Prickling, pins and needles sensations in your fingers, toes, ankles or wrists
- Weakness in your legs that spreads to your upper body
- Unsteady walking or inability to walk or climb stairs
- Difficulty with eye or facial movements, including speaking, chewing or swallowing
- Severe pain that may feel achy or cramplike and may be worse at night
- Difficulty with bladder control or bowel function
- Rapid heart rate
- Low or high blood pressure
- Difficulty breathing
Risk factors
Guillain-Barre syndrome can affect all age groups. But you’re at slightly greater risk if:
- You’re a man
- You’re a young adult
Guillain-Barre syndrome may be triggered by:
- Most commonly, infection with campylobacter, a type of bacteria often found in undercooked poultry
- Influenza virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Zika virus
- Hepatitis A, B, C and E
- HIV, the virus that causes AIDS
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Surgery
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Rarely, influenza vaccinations or childhood vaccinations