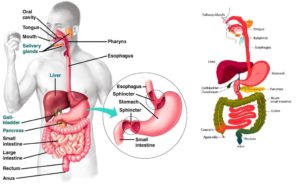
How our stomach including, gallbladder, pancreas and liver work with digestion:
During digestion of a meal, smooth muscles in the walls of the gallbladder contract to push bile into the bile ducts that lead to the duodenum. Once in the duodenum, bile helps with the digestion of fats. Gallbladder: A pear-shaped reservoir located just under the liver that receives and stores bile made in the liver. The gallbladder sends this stored bile into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of food.
The stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas and liver are four of the most important digestive organs in the human body.
These organs work together to produce and store secretions that digest our food into its most basic building blocks. Once digested, these small molecules pass into our intestines to be absorbed and to feed our body’s tissues. These are major organs that actually produce hormones for food digestion or store the hormones for digestion that help to coordinate their functions and even lead to the feeling of fullness after consuming a meal since it allows the food to get in smaller pieces to moves into the large intestines where the stool forms into a more solid form to evacuate via our rectum to the anus.
The common bile duct is formed by the union of the common hepatic and the cystic ducts. It leads to the duodenum, where a sphincter muscle guards its exit. This sphincter normally remains contracted until the bile is needed, so that bile collects in the common bile duct and backs up to the cystic duct. When this happens, the bile flows into the gallbladder and is stored there.
Yes the gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver so that there is a sufficient supply of bile on hand to digest fats at any given time. Remember this, that the pancreas stores the pancreatic juice produced by its own exocrine glands so that it is prepared to digest foods at all times but passes the bile to the gallbladder which reaches the small intestines via the common bile duct (between the gallbladder and the duodenum). The small intestine is made up of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. In living humans, the small intestine alone measures about 6 to 7 meters long. After death, this length can increase by up to half. It has a surface area of over 200 meters.
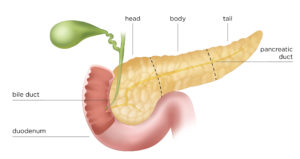
The pancreas is a large gland that makes digestive juices and hormones, including insulin. The digestive juices flow down a tube (pancreatic duct) into the duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of the small bowel and is joined to the stomach.
Another tube (duct) joins the duodenum. The bile duct comes down from the gallbladder and liver and joins the duodenum right next to the pancreatic duct. The place where the two ducts join and meet the bowel is called the ampulla of Vater.

So there is a relation between digestion in 5 major areas the stomach to the intestines, the gallbladder and theliver with the pancreas.
How does cancer relate to these areas?
Well if your diagnosed with intestinal blockage that shows cancer cells you need to know where its located. If cancer cells where questionable by the doctor in certain tests done in the stomach or small intestines. You need to find out where the location is and if your told the small intestines find out if the MD questions the cancer cells going to the common bile duct to the gall bladder that could further end up in the pancreas also. If pancreatic cancer is determined this now means in the 3 parts of the pancreas cancer is high probability being in the head of the pancreas. The pancreas has a tail, body and head the head is located to easy access of spreading the cancer in ducts and to the gallbladder which can further have its cancer cells go into the small intestines from the bile duct that is connected to release stored bile when needed for digestion in the small intestines.