Many many women and their doctors don’t know that heart disease is the number one killer of women. Furthermore, the heart disease that is seen in women is often not quite the same as heart disease in men.
Let’s remember that Heart disease is an umbrella term that includes heart failure, coronary artery disease (CAD), arrhythmias, angina, and other heart-related infections, irregularities, and birth defects
These facts lead to two common (and sometimes tragic) misapprehensions held by many women and their doctors: That women don’t really get much heart disease, and when they do, it behaves pretty much like the heart disease that men get.
The truth is that not only is heart disease very common in women, but also, when women get heart disease it often acts quite differently than it does in men. Failing to understand these two fundamental truths leads to a lot of preventable deaths and disability in women with heart disease.
If you are a woman, you need to know the basics about heart disease – especially heart disease as it behaves in women.
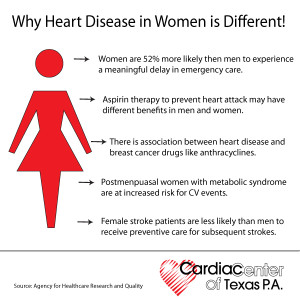
When women have angina, they are more likely than men to experience “atypical” symptoms. Instead of chest pain, they are more likely to experience a hot or burning sensation, or even tenderness to touch, which may be located in the back, shoulders, arms or jaw – and often women have no chest discomfort at all. An alert doctor will think of angina whenever a patient describes any sort of fleeting, exertion-related discomfort located anywhere above the waist, and they really shouldn’t be thrown off by such “atypical” descriptions of symptoms. However, unless doctors are thinking specifically of the possibility of CAD, they are all too likely to write such symptoms off to mere musculoskeletal pain or gastrointestinal disturbances.
Women are more likely than men to have heart attack symptoms unrelated to chest pain, such as:
-
-
- Neck, jaw, shoulder, upper back or abdominal discomfort.
- Shortness of breath.
- Right arm pain.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Sweating.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness.
- Unusual fatigue.
-
Heart attacks (or myocardial infarctions) also tend to behave differently in women.
Frequently, instead of the crushing chest pain that is considered typical for a heart attack, women may experience nausea, vomiting, indigestion, shortness of breath or extreme fatigue – but no chest pain. Unfortunately, these symptoms are also easy to attribute to something other than the heart. Furthermore, women (especially women with diabetes) are more likely than men to have “silent” heart attacks – that is, heart attacks without any acute symptoms at all, and which are diagnosed only at a later time, when subsequent cardiac symptoms occur.
The Diagnosis Of CAD in Women Can Be More Difficult; Tests done to help diagnose:
Diagnostic tests that work quite well in men can be misleading in women. The most common problem is seen with stress testing – in women, the electrocardiogram (ECG) during exercise can often show changes suggesting CAD, whether CAD is present or not, making the study difficult to interpret. Many cardiologists routinely add an echocardiogram or a thallium study when doing a stress test in a woman, which greatly improves diagnostic accuracy.
In women with typical CAD, coronary angiography is every bit as useful as in men; it identifies the exact location of any plaques (i.e., blockages) within the coronary arteries, and guides therapeutic decisions. However, in women with atypical coronary artery disorders (to be discussed in the next section), coronary angiograms often appear misleadingly normal. Thus, in women angiography is often not the gold standard for diagnosis, as it is for most men.
CAD In Women Can Take Atypical Forms.
At least four atypical coronary artery disorders can occur in women, usually in younger (i.e., pre-menopausal) women. Each of these conditions can produce symptoms of angina with apparently “normal” coronary arteries (that is, coronary arteries that often appear normal on angiogram). The problem, obviously, is that if the physician trusts the results of the angiogram, he/she is likely to miss the real diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease in Women – Those we can’t change = Nonmodifiable Factors:
Age and Family History, Gender, Ethnicity.
The risk of having heart disease increases with age and this is due to stiffening of heart muscles which makes the heart less efficient in pumping blood around the body. You can determine your heart age by using this tool, developed by the British Heart Foundation: https://www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/risk-factors/check-your-heart-age.
Another risk factor you cannot change is if you have a history of heart disease among family members. This can double your risk, so if your mother, father, sister or brother has suffered from heart disease before the age of 60 you are at a greater risk of developing heart disease.
Modifiable Risk Factors – Those we can change are:
1-Smoking is the single largest preventable cause of death in Australia, and approximately 40% of women who smoke die due to heart disease, stroke or blood vessel disease. Smokers are 2-4 times more at risk of developing heart disease compared to non-smokers. In 2011/2012, over 1.3 million women in Australia smoked, and 89% of them did this on a daily basis. While these numbers are for women aged 15 and over, the largest group were in the 25-34 age group.
Passive smoking (exposure to the cigarette smoke of others) also causes an increase in the risk of developing heart disease, which increases further in people having high blood pressure or high cholesterol. Women who smoke and also take the contraceptive pill have a 10 times higher risk of having a heart attack.
2-Alcohol. Do you know that drinking too much alcohol increases the risk of heart disease? Excessive drinking causes more weight gain (due to increased calories!), increase in blood pressure and blood lipids. Over a long period of time it can weaken the heart muscle and cause abnormal heart rhythms. Try and not drink alcohol every day, limit it to two standard drinks at a time and aim for at least two alcohol free days a week and make sure you don’t increase the amount you drink on the other days. Periodically take a break from any alcohol for a week or more and you will notice many benefits including a better nights sleep.
3.High Blood Pressure or Hypertension. Your blood pressure is a measurement of how ‘hard’ your heart is working to push blood around your body, through the blood vessels. It can be a ‘silent’ killer and if you do not know your blood pressure then it is worth having it checked by your GP. Changing your lifestyle will reduce your blood pressure. A recent study suggests that keeping your blood pressure under 140/90 can increase your life expectancy by 5 years at the age of 50 years. You can assess your high blood pressure through your MD monthly or less expensive buy a b/p machine and check your b/p everyday especially if your on antihypertensive meds to make sure your b/p isn’t under 100/60 to prevent hypotension.
4.Diabetes. Do you have diabetes and if so, is it under control?
Diabetes doubles your risk of having heart disease. People who have uncontrolled diabetes are at risk of having heart disease at an earlier age. For pre-menopausal women, having diabetes cancels the protective effects of hormone present in women and significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Taking steps to find out what your blood sugar is and keeping it well-controlled is essential.
5.Obesity- Do you know your body fat content? If you think that you are overweight then you put yourself at risk of having heart disease. Being overweight will increase your blood pressure and contribute to developing diabetes. In addition to that, women who carry weight around their middle (belly fat) as opposed to their hips are twice as likely to develop heart disease.
By taking the steps to reduce your weight, you can reduce your risk of heart disease. A great tool developed by National Heart Foundation of Australia calculates if you might be at risk: http://www.heartfoundation.org.au/healthy-eating/Pages/bmi-calculator.aspx
6- INACTIVE-Are you physically active every day? Recent research indicates that “sitting is the new smoking” and being physically inactive can double your risk of having heart disease. It is important to get some exercise every day, such as a 30 minute walk where you raise your heart rate. It also raises your serotonin levels (feel-good hormone) and can reduce depression
7- STRESS-We could almost ask – do you know anyone who is not stressed?! However, while everyday life is stressful, those people who are almost constantly stressed are at risk of adopting unhealthy behaviours in order to reduce their stress levels. Examples include increasing their alcohol intake or smoking in order to relax; or tending to eat more junk food because they are often short of time. All of these factors increase their risk of heart disease.
Women, stress and the risk of heart disease
Along with poor diet, lack of exercise and smoking, unmanaged stress may increase the risk for heart disease. Now medical experts are discovering that mental stress affects women in different, and in some cases, more devastating ways, especially if they already have coronary conditions. One study that…
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States. Every year, 1 in 4 deaths are caused by heart disease. The good news? Heart disease can often be prevented when people make healthy choices and manage their health conditions. Communities, health professionals, and families can work together to create opportunities for people to make healthier choices. Make a difference in your community: Spread the word about strategies for preventing heart disease and encourage people to live heart healthy lives
 +
+