A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of your eye. Cataracts are very common as you get older. In fact, more than half of all Americans age 80 or older either have cataracts or have had surgery to get rid of cataracts.
At first, you may not notice that you have a cataract. But over time, cataracts can make your vision blurry, hazy, or less colorful. You may have trouble reading or doing other everyday activities.
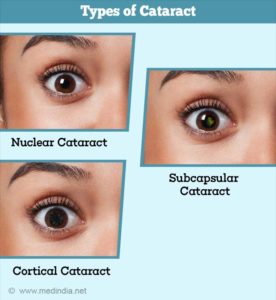
There are 3 types of Cataracts:
1-Nuclear cataracts, which form in the lens’ nucleus, are the most common type of cataracts. Because opacity develops in the center of the lens, known as the central nucleus, nuclear cataracts interfere with a person’s ability to see objects in the distance. Usually the result of advancing age, nuclear cataracts can take years to develop and often give the nucleus a yellow tint.
2=Cortical cataracts begin at the outer rim of the lens and gradually work toward the central core. Thus, this type of cataract resembles spokes of a wheel. Patients with cortical cataracts often notice problems with glare, or a “halo” effect around lights. They may also experience a disruption of both near and distance vision.
3-Subcapsular cataracts progress the most rapidly. While nuclear cataracts take years to develop, subcapsular cataracts reach an advanced stage within a matter of months. Posterior subcapsular cataracts affect the back of the lens, causing glare and blurriness. This type of cataract is usually seen in patients who suffer from diabetes, extreme nearsightedness or retinitus pigmentosa, as well as among those who take steroid medication.
Obesity is most commonly linked to the development of posterior subcapsular cataracts. According to researchers at Harvard University, individuals with a BMI of 33 had at least a 30 percent greater likelihood of developing cataracts, compared to subjects with a BMI of 23 or below.
**Congenital cataracts exist and refer to cataracts that are present from birth, as well as to those that develop in early childhood. These cataracts can be nuclear, cortical, or subcapsular. Congenital cataracts may be linked to an infection contracted by the mother during pregnancy or to a genetic condition such as Fabry disease, Alport syndrome, or galactosemia. Because clear vision is essential to the development of the child’s eyes and brain, it is important to diagnose congenital cataracts as early as possible.
Most cataracts form as a result of advancing age. Other possible causes of cataracts include environmental factors and certain medications, such as antidepressants. If your medical history or lifestyle increases your risk of developing cataracts, it is important to have your eye health monitored regularly by a qualified ophthalmologist.
Over 50 percent of Americans over the age of 80 have cataracts
RISK FACTORS:
1 Age
Age is the main reason cataracts form. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the eye disease appears in over 22 million Americans over the age of 40. Over 50 percent of Americans over the age of 80 have cataracts. In fact, if we live long enough, nearly all of us will eventually develop this condition. Because the lens of the eye cannot shed old cells naturally, protein that accumulates on the lens gradually builds up over time, progressively obscuring vision by preventing light from reaching the retina.
2 History of Cataracts in the family
3 Ultraviolet Radiation (UVA or UVB)
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation, especially UVB rays, can cause changes in pigment that lead to the formation of cataracts. This is especially common in tropical climates, where high concentrations of UV exposure occur year-round. To protect the eyes from sun damage, it is important to wear sunglasses with a high level of UVA/UVB protection.
4 Trauma to the eye
Injury or trauma to the eye increases a patient’s risk of developing cataracts. Individuals who have experienced inflammation in the eye, either post-operatively or as the result of another eye disease, are also more likely to eventually develop cataracts. For instance, iritis is an ocular condition that causes chronic inflammation inside the eye, and is commonly linked to early and rapid cataract formation.
5 Have certain health problems, like diabetes
6 Smoking and Alcohol
Lifestyle habits such as smoking or consuming alcohol are often considered causes of cataracts.
7 Medications
Certain medications are well-known causes of cataracts, and some drugs can also accelerate their development. Steroid medications – whether pills, injections, or eye drops – are most frequently associated with cataract formation. If you are taking steroid medications to manage a long-term condition, it is important to note any visual changes and to have your ocular health managed by a qualified ophthalmologist.
Most cataracts are caused by normal changes in your eyes as you get older.
When you’re young, the lens in your eye is clear. Around age 40, the proteins in t he lens of your eye start to break down and clump together. This clump makes a cloudy area on your lens — or a cataract. Over time, the cataract gets more severe and clouds more of the lens.