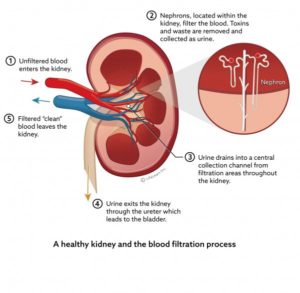
Chronic kidney disease occurs when a disease or condition impairs kidney function, causing kidney damage to worsen over several months or years.
Diseases and conditions that cause chronic kidney disease include:
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Glomerulonephritis (gloe-mer-u-low-nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units (glomeruli)
- Interstitial nephritis (in-tur-STISH-ul nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the kidney’s tubules and surrounding structures
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, from conditions such as enlarged prostate, kidney stones and some cancers
- Vesicoureteral (ves-ih-koe-yoo-REE-tur-ul) reflux, a condition that causes urine to back up into your kidneys
- Recurrent kidney infection, also called pyelonephritis (pie-uh-low-nuh-FRY-tis)
An early way to find out if you may have chronic kidney disease (CKD) is by taking a UACR (urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio) test once a year. A UACR test can detect how much small protein, called albumin, is in your urine, which is one of the earliest indicators of CKD or kidney damage. A damaged kidney can’t filter as well as it should and lets some protein pass into the urine. A healthy kidney doesn’t let any protein pass into the urine.
A UACR urine test isn’t always part of a routine health screening and is different from usual urinalysis tests that are commonly used at doctor appointments, so be sure to ask your healthcare provider specifically for a UACR urine test.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of chronic kidney disease include:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Being African-American, Native American or Asian-American
- Family history of kidney disease
- Abnormal kidney structure
- Older age
Complications
Chronic kidney disease can affect almost every part of your body. Potential complications may include:
- Fluid retention, which could lead to swelling in your arms and legs, high blood pressure, or fluid in your lungs (pulmonary edema)
- A sudden rise in potassium levels in your blood (hyperkalemia), which could impair your heart’s ability to function and may be life-threatening
- Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease
- Weak bones and an increased risk of bone fractures
- Anemia
- Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction or reduced fertility
- Damage to your central nervous system, which can cause difficulty concentrating, personality changes or seizures
- Decreased immune response, which makes you more vulnerable to infection
- Pericarditis, an inflammation of the saclike membrane that envelops your heart (pericardium)
- Pregnancy complications that carry risks for the mother and the developing fetus
- Irreversible damage to your kidneys (end-stage kidney disease), eventually requiring either dialysis or a kidney transplant for survival
Prevention
To reduce your risk of developing kidney disease:
- Follow instructions on over-the-counter medications. When using nonprescription pain relievers, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), follow the instructions on the package. Taking too many pain relievers could lead to kidney damage and generally should be avoided if you have kidney disease. Ask your doctor whether these drugs are safe for you.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If you’re at a healthy weight, work to maintain it by being physically active most days of the week. If you need to lose weight, talk with your doctor about strategies for healthy weight loss. Often this involves increasing daily physical activity and reducing calories.
- Don’t smoke. Cigarette smoking can damage your kidneys and make existing kidney damage worse. If you’re a smoker, talk to your doctor about strategies for quitting smoking. Support groups, counseling and medications can all help you to stop.
- Manage your medical conditions with your doctor’s help. If you have diseases or conditions that increase your risk of kidney disease, work with your doctor to control them. Ask your doctor about tests to look for signs of kidney damage.