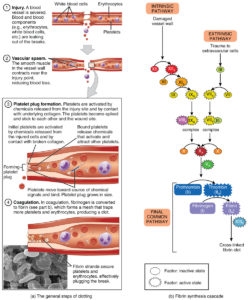
Why blood clotting is a vital important part of the bloodstream through platelets and how it works is what would we will review first to understand disseminated intra-vascular coagulopathy (DIC). It is a vital important process of the platelets that make up part of our bloodstream cells that help prevent excessive bleeding or excessive hemorrhage.
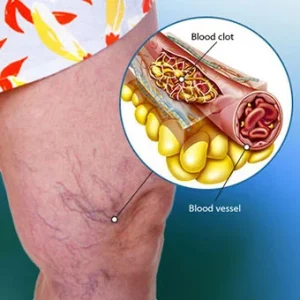
In how clotting works is platelets, which is a type of blood cell, with plasma that is in our liguid part of blood work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury (a bruise or cut in the skin) which stops the bleed. Both veins and arteries transport our blood (both solids=cells) and the liguid (the plasma) that are read by out hematocrit and hemoglobin in a CBC=complete blood count which also tell the MD our reading of red/white blood cell counts with platelets. Typically, your body will dissolve the clot after the injury has healed. However, there are times clots form on the inside of our vessels (there are variables of why this would happen that are discussed later in this topic). These situations can be dangerous and put the pt at risk for problems. This needs to be diagnosed and given appropriate treatment by your doctor or MD specialist.
Clots can occur in our veins or arteries and can occur is various areas causing
1-DVT=Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT commonly in our large veins that are commonly found in our lower extremities and less likely in our upper extremities or pelvic region or other areas where there are large veins. The problem (one the clot is wedged and stuck against the vessel) with this the clot blocks off circulation to the area below the clot to a percentage low to 100% blockage. This is where in the skin there is pain to necrosis below the clot area (for this to happen it takes numerous hours-pain to days-changes in skin color or week or more-necrosis depending on the blockage). The greater the blockage is the quicker the symptoms arise no matter where the clot is. It is estimated that each year DVT affects as many as 900,000 people in the United States by the American Heart Association and kills up to 100,000 by the Centers for Control and Prevention (CDC).
-Paget-Schroetter Syndrome (PSS) – It’s a rare kind of DVT that typically happens to a young, healthy person who plays sports that use the upper arms a lot, like swimming and baseball. The vein can get squeezed by the muscles around it. This pressure, along with repeated movements, can cause a clot in your shoulder. Symptoms like swelling, chest pain, and a blue color to your skin may come on suddenly. PSS can be serious if it’s not treated right away.
2-Atrial Fibrillation
Another area where blood clotting can occur is in the heart. We see commercials all the time about atrial fibrillation=irregular rhythm with the heart beat. In the commercial its usual an add for a med called a anticoagulant that does the opposite of what platelets do=clotting to prevent this problem from happening in the heart which indirectly prevents clotting in all vessels as well. The med thins the blood. The major problem with this diagnosis, atrial fibrillation without being on a anticoagulant, is blood can pool in the heart causing a clot to form in the heart and at some point, especially when the rhythm is rapid and more irregular that usual=RVR-rapid ventricular rate over 100 beats per minute and usually over 130 to over 150, the clot can break off.
3-Heart Attack
Know this, more often than not, a broken piece of plaque within the arteries triggers the formation of a blood clot. This blood clot is the reason for a heart attack. As the blood clot potentially restricts the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart, depending on the severity, the heart attack can cause sudden death.
There are other areas where blood can form clots but not as common in what was mentioned above. Blood clots can arise anywhere in your body. They develop when blood thickens and clumps together. When a clot forms in a deep vein in the body, it’s called deep vein thrombosis. Deep vein blood clots typically occur in the lower leg or thigh.
The biggest consequence of any blood clot no matter where it is it can break off in time for many especially with a DVT. Than there is atrial fibrillation patients not on a anti-coagulant or anti-platelet like Coumadin, Eliquis, heparin, and lovenox to Plavix, Brilinta, Ticlid and Integrilin with other medications (listed commonly used in my nursing career) it puts them at risk for a clot to break off in the heart due to pooling blood causing a clot formation and when it breaks off it could go the the lungs causing pulmonary embolus or the brain a stroke.
For understanding the meaning lets review; Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot develops in the deep veins, usually in the lower extremities. A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a part of the DVT clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, which can be life-threatening. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to DVT, PE, or both.
When a clot breaks off it floats now in the bloodstream and can in time make it back to the heart putting the pt at risk for a heart attack if it didn’t get stuck elsewhere, like going to the lungs putting the pt at risk for a pulmonary embolism or now in circulation making it to the brain putting the pt at risk for a stroke! Clots are common in making the strokes in what we call ischemic stroke and another name “silent stroke”. Silent strokes are much more common than strokes that cause classic symptoms such as face drooping, arm weakness and speech difficulty and affect nearly 800,000 Americans each year. According to the statement, one in four people over 80 have one or more silent strokes.