Cervical cancer screening used to all be so simple==PREVENTION. Women were told just go for your annual Pap but now we have new tests to screen for cervical cancer, plus updated guidelines that—for most women—mean routine screening is done every few years rather than annually. Dr. Warner Huh of the University of Alabama, Birmingham sorts out the new landscape of Pap and HPV tests.
Human papillomavirus, or HPV, is a common sexually transmitted infection. So common that most (~80%) sexually active people will be infected with HPV at some point.
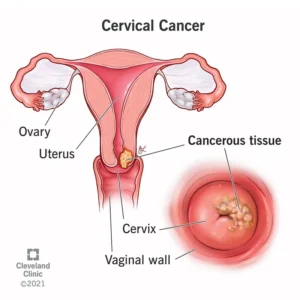
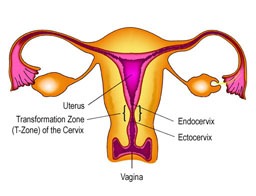
Cervical cancer begins in the cervix, the narrow organ at the bottom of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The cervix dilates during childbirth to allow for passage of a baby.
Picking up on risk factors and warning signs could save an individual from a lifetime of suffering. These include whether or not you’ve contracted HPV, if you eat a whole diet, have used birth control, have HIV, smoke cigarettes, or if it’s just in your genetics.
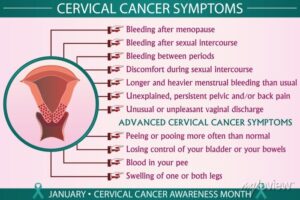
Here are some signs to watch out for:
Leg Pain – Some women exhibiting early stages of cervical cancer experience swelling and pain in the leg. When the cervix swells it can lead to an obstructed blood flow, which eventually causes the leg to swell and gives a sore, painful sensation. This may be a sign of early cervical cancer.
Vaginal discharge colored with blood – It’s normal for a woman to experience small amounts of clear discharge without color or odor. However, bloody, dark, or smelly discharge is usually a sign of infection. But sometimes, it’s a sign of cervical or endometrial cancer.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding – More than 90% of women diagnosed with endometrial cancer experience irregular bleeding. If you have already undergone menopause, any bleeding — spotting included — should be evaluated. Haven’t gone through menopause yet? See your doctor if you experience bleeding between periods, heavy bleeding or bleeding during sex.
Discomforting Urination – Keeping track of urination can help reveal the presence of cervical cancer in several ways. The most immediately obvious and prevalent symptom is discomfort while urinating. You may experience burning, stinging, or a tight sensation. This is another symptom to see a doctor about either way.
Irregular Urination – The appearance of the urine and urinary habits can also be symptoms of cervical cancer. If you notice strange changes in the frequency of your urine, loss of bladder control (incontinence) or a discoloration – especially with blood – seek the input of a medical professional.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles – There should be some level of consistency when it comes to monthly periods. If time, frequency, or any other changes disrupt the regular routine, it can also be a sign that you’re at a much higher risk for cancer and will require regular screenings.
Uncomfortable Sex – Painful intercourse, otherwise known as dyspareunia, is another discomforting side effect of cervical cancer. There are several possible reasons for this symptom to develop, as is the case with many of the symptoms on this list. This symptom is most commonly linked to conditions that require medical attention, however, so it shouldn’t be ignored.
Pain in the pelvis or abdominal area – Abdominal pain or discomfort — including gas, indigestion, pressure, bloating, and cramps — can signal ovarian cancer. And, constant pelvic pain or pressure can be a sign of endometrial cancer.
Back Pain – Back pain is common, affecting around 80 percent of the population, and it can happen for a wide variety of reasons, but if accompanied with other symptoms from the list, go for a medical check-up.