The kidneys are important organs with many functions in the body, including producing hormones, absorbing minerals, and filtering blood and producing urine. While they are important and kidney failure can be fatal, a human only needs one healthy kidney to survive.
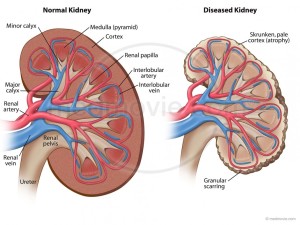
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that extract waste from blood, balance body fluids, form urine, and aid in other important functions of the body.
They reside against the back muscles in the upper abdominal cavity. They sit opposite each other on either side of the spine. The right kidney sits a little bit lower than the left to accommodate the liver.
When it comes to components of the urinary system, the kidneys are multi-functional powerhouses of activity, for if the kidneys aren’t working, meaning they don’t filter toxic wastes out of our blood stream (with other functions it does) than the waste products don’t get dumped into the urinary bladder from the renal tubes, called right and left ureters. In human anatomy, the ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle fibers that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. If the kidneys are not working they are not filtering our blood (same principle as filtering beer to make it to perfection, the kidneys do it for our blood to be able to have the cells do their function to the optimal levels with keeping toxins out of the body in preventing many blood problems with more due to acidosis (toxin build up). In the adult, the ureters are usually 25–30 cm (10–12 in) long and ~3–4 mm in diameter.
The kidneys have multiple functions. Some of the core actions of a healthy kidney or kidneys of a human body include:
- Waste excretion: There are many things your body doesn’t want inside of it. The kidneys filter out toxins, excess salts, and urea (a toxin), a nitrogen-based waste created by cell metabolism. * Urea is an organic chemical compound and is essentially the waste produced by the body after metabolizing protein. Naturally the compound urea is produced when the liver breaks down protein or amino acids, and ammonia, the kidneys then transfer the urea from the blood to the urine, when they do filtering of the blood. * Urea is a byproduct of protein metabolism, the ending result. *Extra nitrogen is expelled from the body through urea because it is extremely soluble (solid); it is a very efficient process. The average person excretes about 30 grams of urea a day, mostly through urine but a small amount is also secreted in perspiration. Synthetic versions of the chemical compound can be created in liquid or solid form and is often an ingredient found in fertilizers, animal food, and diuretics, just to name a few . Urea is what gives our urine the color yellow. *In the gastrointestinal tract, blood proteins are broken down into ammonia (could be due to high protein eating to drugs with actual conditions); and goes to the liver converting it to Urea. It is then released into the blood stream where the kidney’s take it up and eliminate it. Urea is then eliminated by the kidney’s, but not produced by it. *Urea is synthesized in the liver and transported through the blood to the kidneys for removal.
- A Healthy Kidney or Kidneys functions in the human body:
- Water level balancing: As the kidneys are key in the chemical breakdown of urine, they react to changes in the body’s water level throughout the day. As water intake decreases, the kidneys adjust accordingly and leave water in the body instead of helping excrete it which aides in electrolyte balancing in the blood with keeping the body hydrated properly.
- Blood pressure regulation: The kidneys need constant pressure to filter the blood. When it drops too low, the kidneys increase the pressure. One way is by producing a blood vessel-constricting protein (angiotensin) that also signals the body to retain sodium and water. Both the constriction and retention help restore normal blood pressure.
- Red blood cell regulation: When the kidneys don’t get enough oxygen, they send out a distress call in the form of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the bone marrow to produce more oxygen-carrying red blood cells.
- Acid regulation: As cells metabolize, they produce acids. Foods we eat can either increase the acid in our body or neutralize it. If the body is to function properly, it needs to keep a healthy balance of these chemicals. The kidneys do that, too.Because of all of the vital functions the kidneys perform and the toxins they encounter, the kidneys are susceptible to various problems.
- Acute kidney failure is a condition in which the kidneys suddenly lose their ability to function properly. This can occur for many reasons, including:
- Most people are born with two kidneys, but many people can live on just one. Kidney transplant surgeries with live donors are common medical procedures today.
- Infection
- Blood-clotting disorders
- Decreased blood flow caused by low blood pressure
- Autoimmune kidney disorders
- Urinary tract infections
- Complications from pregnancy
- DehydrationDiseases and conditions that commonly cause chronic kidney disease include:
- Chronic kidney failure – same as acute in that the kidney (s) loses its function.
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Glomerulonephritis (gloe-mer-u-lo-nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units (glomeruli)
- Interstitial nephritis, an inflammation of the kidney’s tubules and surrounding structures
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, from conditions such as enlarged prostate, kidney stones and some cancers
- Vesicoureteral (ves-ih-koe-yoo-REE-ter-ul) reflux, a condition that causes urine to back up into your kidneys
- Recurrent kidney infection, also called pyelonephritis (pie-uh-lo-nuh-FRY-tis)
- A chronic condition causes the failure to happen, what we call a secondary diagnosis. * Learn more tomorrow, on Thursday, about Acute and Chronic kidney failure.